CBSE 12th Exams Scheduled From Feb 15: Check CBSE 12th Physics Chapter 5 Important Questions
Students can refer to the CBSE 12th Physics Chapter 5 Important Questions and solutions here to prepare for their upcoming CBSE Board Exam 2023.
CBSE 12th Physics Chapter 5 Important Questions: The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE), India, will conduct the class 12 Board exams between Feb 15 to Apr 5, 2023.
The Physics exam is scheduled for Mar 6. Students completing their CBSE 12th Physics revision must thoroughly study the fifth chapter, i.e., CBSE 12th Physics Magnetism and Matter.
Continue reading further to check the CBSE 12th Physics Chapter 5 Important Questions and their solutions.
Also Read: Check CBSE 12th Physics Chapter 4 Important Questions
CBSE 12th Physics Chapter 5 Important Questions & Solutions
Find the CBSE 12th Physics Chapter 5 Important Questions and solutions for the fifth Chapter (Magnetism and Matter) below.
- Question 1: The permeability of a magnetic material is 0.9983. Name the type of magnetic materials it represents.
Answer: It represents diamagnetic materials. - Question 2: The susceptibility of a magnetic material is 1.9 × 10-5. Name the type of magnetic materials it represents.
Answer: It represents a Paramagnetic substance. - Question 3: The susceptibility of a magnetic material is – 4.2 × 10-6. Name the type of magnetic materials it represents.
Answer: It represents diamagnetic substances. - Question 4: Where on the surface of Earth is the angle of dip 90°?
Answer: At the magnetic poles, the angle of dip is 90° on the surface of Earth. - Question 5: Where on the surface of Earth is the angle of dip zero?
Answer: At the magnetic equator, the angle of dip is 0°. - Question 6: Where on the surface of Earth is the vertical component of Earth’s magnetic field zero?
Answer: At the Magnetic equator the vertical component of Earth’s magnetic field is zero. - Question 7: The horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field at a place is B and angle of dip is 60°. What is the value of vertical component of earth’s magnetic field at the equator?
Answer: BH = B cos δ
BV = BH tan δ = B tan 60° = B × √3 = √3B
∴ At the equator, BV = 0 (zero). - Question 8: Current flows through a circular loop. Depict the north and south pole of their equivalent magnetic dipole.
Answer: The direction of the magnetic field lines is given by right-hand thumb rule.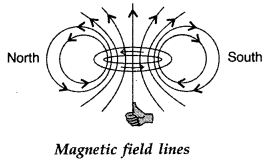
- Question 9: A straight wire extending from east to west falls with a speed v at right angles to the horizontal component of the Earth’s magnetic field. Which end of the wire would be at the higher electrical potential and why?
Answer: West end of the wire must be at the higher electric potential. According to Fleming’s Right-Hand rule, “the direction of induced emf is from West to East”. - Question 10: What are permanent magnets? Give one example.
Answer: Substances which at room temperature retain their ferromagnetic property for a long period of time are called permanent magnets.
Example: Steel, Alinco. - Question 11: Which of the following substances are diamagnetic? Bi, Al, Na, Cu, Ca and Ni.
Answer: Bi and Cu - Question 12: Is the steady electric current the only source of the magnetic field? Justify your answer.
Answer: No. A steady current is not the only source of the magnetic field. Magnets are also a source of magnetic fields. Unsteady current will also be the source of varying magnetic fields. - Question 13: At a place, the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field is B and the angle of dip is 60°. What is the value of a horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field at the equator?
Answer: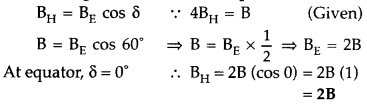
- Question 14: The figure shows the variation of intensity of magnetisation versus the applied magnetic field intensity, H, for two magnetic materials A and B :
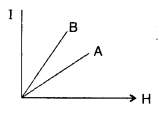
(a) Identify the materials A and B.
(b) Why does material B, has a larger susceptibility than A, for a given field at constant temperature?
Answer: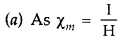
The slope of the line gives magnetic susce¬ptibilities.
For magnetic material B, it is giving a higher +ve value.
So the material is ‘ferromagnetic’.
For magnetic material A, it is giving a lesser +ve value than ‘B’.
So the material is ‘paramagnetic’.(b) Larger susceptibility is due to characteristic ‘domain structure’. More mag¬netic moments get aligned in the direction of the magnetising field in comparison to that for paramagnetic materials for the same value of a magnetising field.
- Question 15: Draw magnetic field lines when a
(i) diamagnetic,
(ii) paramagnetic substance is placed in an external magnetic field.
Which magnetic property distinguishes this behaviour of the field lines due to the two substances?
Answer:
(i) When diamagnetic material is placed in an external magnetic field.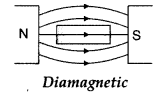
(ii) When a paramagnetic material is placed in an external magnetic field.
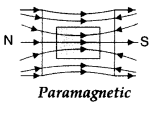
Magnetic susceptibility distinguishes this behaviour of the field lines due to the two substances. - Question 16: The susceptibility of a magnetic material is – 2.6 × 10-5. Identify the type of magnetic material and state its two properties.
Answer: Magnetic material is diamagnetic because the susceptibility of a magnetic material is negative.
Properties are :- In a non-uniform magnetic field, it tends to move slowly from stronger to weaker parts of the field.
- A freely suspended diamagnetic rod aligns itself perpendicular to the field.
- They expel magnetic field lines.
- Such substances are repelled by a magnet. [any two]




