The unique difference between assistant professor vs associate professor is that assistant professors are entry-level professors, and associate professors are promoted to assistant professors with Ph.D. degrees as a mandatory qualification.
Table of Contents
The difference between assistant professor vs associate professor is an assistant professor is a junior or entry-level faculty member. In contrast, an associate professor is a middle-level senior professor with at least 8 to 9 years of experience with a doctorate or Ph.D.
Degree instructing students. An associate professor and an assistant professor have many of the same responsibilities and employment structure. An associate professor often has tenure and more extraordinary work experience.
- Qualifications of an Assistant Professor vs Associate Professor
- Employment Responsibilities of an Assistant Professor vs Associate Professor
- Tenure of an Assistant Professor vs Associate Professor
- Salary and Perks of an Assistant Professor vs Associate Professor
Who is an Assistant Professor?
An assistant professor is a junior or entry-level faculty member at a college or University. They generally hold an MPhil or PhD and have extensive research and teaching backgrounds in their areas of specialization.
- They assist with lesson planning and monitor students' homework and tests to gauge their development.
- They can be appointed for a "non-tenure or temporary" post, lasting only between one and three years.
Who is an Associate Professor?
Promoted assistant professors are referred to as associate professors. These are middle-level professors with at least 7+ years of experience instructing students and a doctorate or Ph.D.
- Nonetheless, candidates must conduct rigorous research to expand their knowledge in the pertinent field and publish their findings in academic journals and papers to be granted the title of associate professor.
- Although an associate professor and an assistant professor have many of the same responsibilities and employment structure, an associate professor often has tenure and more significant work experience.
Also Read: Scope of Teacher Education in India
Differences Between Associate Professor vs Assistant Professor
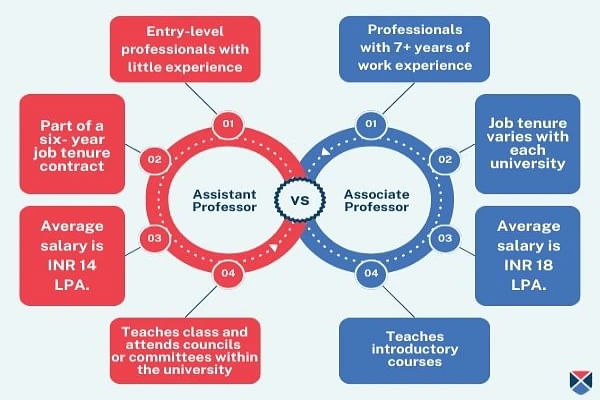
The difference between assistant professor vs associate professor on parameters like seniority, education qualification, job responsibility, salary, and perks are tabulated below and then explained for better understanding.
| Parameters | Associate Professor | Assistant Professor |
| Seniority | 5+ years Seniors | Entry-level professionals |
| Eligibility criteria | Bachelor's, Master's, Doctoral & 7+ work experience | Bachelor's, Master's, Doctoral degree |
| Job Tenure | Varies for different universities | Six-year contract |
| Responsibility | Attends councils or committees within the university | Teach introductory courses |
| Average Salary | 18 LPA | 14 LPA |
All the common differences between assistant professor vs associate professor are discussed in detail below:
1. Qualifications of an Assistant Professor vs Associate Professor
Assistant Professor: To hold the position of assistant professor, a candidate must fulfill specific academic prerequisites, such as a bachelor's, master's, doctoral, and work experience.
Associate Professor: Candidates wishing to be hired directly as associate professors must hold a PhD. In a college, one can also become an associate professor by beginning as an assistant or lecturer and rising through the ranks.
2. Employment Responsibilities of an Assistant Professor vs Associate Professor
Teaching courses, doing research in their fields of specialization, and handling various administrative duties are all duties that associate and assistant professors share.
However, although assistant professors frequently concentrate on the subjects that a full professor assigns, associate professors are expected to design their topic of study. In this sense, associate professors enjoy excellent employment stability and academic freedom.
3. Tenure of an Assistant Professor vs Associate Professor
Assistant professors can apply for tenure following the fifth year of their normally six-year contract. Applicants should know that the tenure application process can take up to a year. If an assistant professor passes a comprehensive review of his work, he can become an associate professor.
Conversely, associate professors either hold tenure already or are in the process of obtaining it. If, after being promoted to associate professor, their body of work has substantially increased, they may also apply for promotion to full professor after a few years. The procedure takes several years to finish because a committee must review everything about the candidate's publications, research, and teaching.
4. Salary and Perks of an Assistant Professor vs Associate Professor
Associate professors probably make more money than assistant professors because they have more experience. Associate professors frequently get tenure and are paid more, though this can vary by University. Because they oversee more tasks than assistant professors, associate professors may also earn more outstanding money.
Assistant professors could not get any benefits from their jobs, or they might get minimal. When comparing benefit packages, associate professors frequently provide more than assistant professors.
Also Read: Top 10 Online Teaching Platforms in India for Teachers
Tips to Choose the Right Role
Education is one of the sectors of the economy growing at the quickest rate in the country. This 400 million-person population presents a sizable market and a fantastic potential for lecturers, professors, and teachers due to its high enrollment rate.
- Being a professor, whether in an associate or assistant job, is the only way to continue reading, writing, and conducting research while engaging in the intellectual journey. Regardless of the other considerations individuals make, the enthusiasm for academics should always come first when deciding whether or not to become a professor.
- One should think about the area of expertise and the level of enjoyment with research while deciding if being a professor is the best path for you. Research opportunities may grow if you advance to associate professor from assistant professor.
- The availability of positions can occasionally influence a person's decision to become an associate professor or assistant professor.
- Earnings differences between assistant and associate professors are common.
Also Read: Different Types Of Educational Technology for Highly-Engaged Classroom
Tips for Being a Successful Professor
A few tips for being a successful professor, considering general parameters like a distinctive teaching approach, asking for feedback, and establishing a network of professionals, are explained below.
- Distinct Teaching Methodology: If an individual has a distinct and identifiable teaching style that aids students in understanding the subject matter. In that case, one may have a higher chance of making a lasting impression on them as a professor.
- Students Feedback: To be a successful professor, consider getting student input to identify where one can make changes. To find out what students thought of the experience and teaching style.
- Establish a Network of Professionals: While obtaining and keeping a professorship may be challenging, building a professional network can help open doors. Consider attending professional networking gatherings and cultivating connections with academics and other educators.























POST YOUR COMMENT