The SI unit of force is newton where 1 newton is equal to 1kg x 1 m/s2. Its formula is F=ma where ‘m’ is the mass of the object and ‘a’ is the acceleration./
Table of Contents
The SI unit of force is newton (N), where 1 newton is equal to 1kg x 1 m/s2. Force is described as an external cause that, when applied, modifies or tends to modify the condition of the body. The formula of force (f) acting on an object with mass (m) and acceleration (a) is F=ma.
Derivation of SI Unit of Force
Newton, which is the SI Unit of Force is the universally accepted system of measurement. It is denoted by the letter N written in uppercase.
As per Newton’s second law of motion, force is defined as the product of mass and acceleration and is equal to the rate of change in momentum (P). We already know that momentum (P) is the product of mass (m) and velocity (v). Let us check out the derivation of SI unit of force in detail below:
Force = Rate of change of momentum
= P/ t (where P stands for momentum and t for time)
We know that P= mv
So, Force = mv/ t
= mass*velocity / time
Newton = (kg*m)/sec⁻²
N= kg/ms2
Where,
Unit of Force = Newton (N)
Unit of mass = Kilogram (kg)
Unit of time = Second (s)
Unit of velocity = Metre / Second (m/s)
What is the Force?
Force is an external push or pull applied to a body that results in a change in its state, speed, direction, or position. It is a vector quantity which has both magnitude and direction. Newton is the derived SI unit of force denoted by capital N. From Newton’s Second law of Motion, Force can be mathematically represented as
Force (F) = mass (m) x acceleration (a)
What are the Effects of Force?
Force is defined as the physical quantity that has the capacity to change the shape and speed of the body. Listed below are a few effects of force:
- Force can make a stationary object move or stop a moving object
- It can make a change in the state of the body of the position
- Can change the speed of a moving object
- Can change the direction of any moving object
- Change the shape or size of an object
- Can accelerate a moving body
- Can decelerate or bring the moving body to stop
Force Formula Derivation
Force is a product of mass and acceleration. It is a vector quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
F=ma
Where
F= Force
m= Mass
a= Acceleration
Acceleration (a) is defined as the rate of change of velocity of an object in a particular specified time. It can be expressed as,
a= v/t
Where
v= Velocity
t= Time
So that Force can be rewritten as
F=mv/t
Substituting for units we get
N= kg. m/s.s
=kgm/s2
Here unit of force= N= kg/ms2
unit of mass = kg
unit of velocity = m/s
unit of time = s
We already know that P=mv, where p is the momentum,
Therefore,
F= p/t = dp/dt
The formula for force can be used to find out the force, mass, acceleration, momentum, velocity in any given problem.
Unit of Force
Force is represented as,
Force = (Mass)x(Acceleration)
Unit of Force is Newton (N)
Unit of Mass is Kilograms (kg)
Unit of Acceleration is Meter/second2 (m/s2)
Types of Forces
Contact forces and non-contact forces are the two categories of forces. More details about the types of forces are given below:
- Contact Forces: The forces that are directly in touch with the object where the force is to be applied or is in touch through a medium are known as contact forces. Some of the contact forces are muscular forces, mechanical force or frictional force.
- Non-contact Forces: The forces that act without any medium or any direct contact with the object are called non-contact forces. Some of the non-contact forces are magnetic forces, electrostatic forces, gravitational forces, etc.
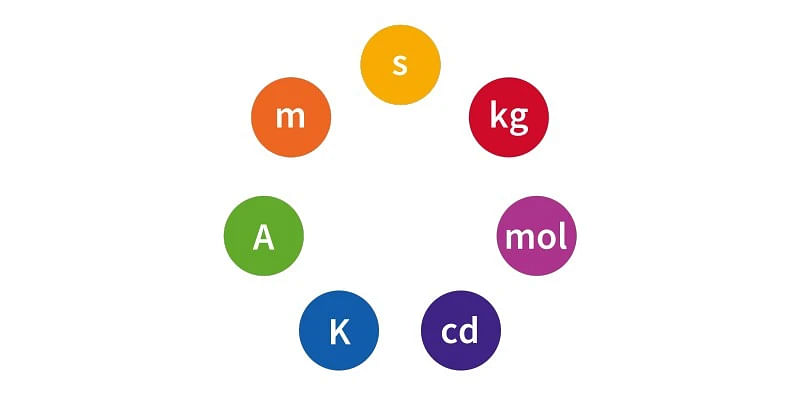
SI Unit
The International System of units is an internationally accepted metric system that is important as they are based on precise standards and the base used in SI units is 10 which makes it easier for conversion. There are 7 base units and 22 derived units of force. The table below shows the base SI units of force for reference:
| Sl. No. | Quantity | SI Unit | SI Unit Symbol |
| 1 | Length | Metre | m |
| 2 | Mass | Kilogram | kg |
| 3 | Time | Second | s |
| 4 | Electric Current | Ampere | A |
| 5 | Thermodynamic Temperature | Kelvin | k |
| 6 | Amount of Substance | Mole | mol |
| 7 | Luminous Intensity | Candela | cd |
Other Units of Force
The unit of force is classified into two systems namely gravitational system and absolute system. When the force is dependent on the gravitational forces, the unit of force is expressed in the gravitational system. When the force is independent of the gravitational forces, the unit of force is expressed in an absolute system.
There are other units of force apart from Newton. Newton is the SI unit of force, whereas in the foot-pound-second (FPS) system, where mass is measured in pounds, the unit of force called Poundal, pdl and pound-force is used to express the force dependent on gravitational forces. Other units of force are Dyne, Gram-force, Poundal, Poundal-force, and Kilogram-force.
Dyne (Dyn)
Dyne is a derived unit of force specified in the centimeter-gram-second (CGS) system. 1 dyne is the force applied to move a body of mass 1 g moving with an acceleration of 1 cm/s2. This unit of force is normally used when working with small objects. The conversion value from dyne to SI unit of force is:
So, 1 g⋅cm/s2 = 1 dyn
1 dyn = 10-5 N
Therefore, the conversion value from dyn to SI unit of force is 1 N= 100,000 dynes
Poundal (pdl)
When a body of mass 1 pound is subjected to an acceleration of 1 foot/second2, the force applied to the body is 1 poundal which is a unit of the FPS (foot-pound-second) system. Poundal is rarely used for scientific measurements.
Unit of Force = pound⋅foot/second2
1 lb⋅ft/s2 = 1 pdl
The conversion value from pdl to SI unit of force is, 1 pdl = 0.1382 N
Gram Force (gf)
Gram force is another unit of force in the centimetre-gram-second (CGS) system. 1 gram force is defined as the force acting on a body of mass 1 g due to gravitational acceleration. The other term for gram force is pond denoted by p.
1 p = 1 gf
The conversion value from gf to SI unit of force is 1 gf = 0.00980665 N
Pound Force (lbf)
Pound Force is another unit of force in the FPS system. 1 pound-force is defined as the force acting on a body of mass 1 avoirdupois pound due to Earth’s gravity. This is a non-technical term of force and denotes the weight of a body.
1 lbf = 4.448222 N
Kip or Kipf
1 kip is defined as 1000 pounds force and is mainly used by civil engineers in situations where pound-force is too small a measurement for heavy loads.
1 kip = 1000 lbf
Ton Force
1 ton-force is the force acting on a body of mass 1 ton due to Earth’s gravity.
1 tf = 9806.65 N
Ounce Force (ozf)
1 ounce force is the unit of force acting on a body of mass 1 ounce due to the gravitational acceleration of the Earth.
1 ozf = 1/16 lbf
The conversion value from ozf to SI unit of force is 1 ozf = 0.278014 N.
Sthene
1 sthene is defined as the force applied to a body of mass 1 ton to give it an acceleration of 1 m/s2. Sthene is a unit of the MTS (metre-tonne-second) system.
1 sthene = 1 ton⋅m/s2
The conversion value from sthene to SI unit of force is 1 sthene = 1000 N
Kilogram Force (kgf)
1 kilogram-force is the unit of force acting on a body of mass 1 kg due to Earth’s gravitational field.
1 kgf = 9.80665 N
The conversion value from kgf to SI unit of force is 1 kgf = 1000 gf
















POST YOUR COMMENT