Women education in India has been the talk of the world for almost a decade now. The female literacy rate in 2021 has substantially increased by 10.5% compared to 2001. Women's education can inturn increase the GDP of the country.
Table of Contents
Women's Education in India: Women's Education in India is the talk of the world as women being educated significantly increases the GDP of the country as they also become income contributors in families. According to a recent survey, the female literacy rate in India is 70.3%, while the male literacy rate is predicted to be 84.7%.
According to the NSO, India's average literacy rate is 77.7%, which is expected to increase substantially with time and the availability of learning resources all over the country.
Women Education: Top 8 Welfare Schemes
India has done significantly well in providing education to its citizens. The nation's rate is 73.2%, of which 59% of women are literate. The government has established many welfare schemes to motivate women's education in India. The following are a few welfare schemes.
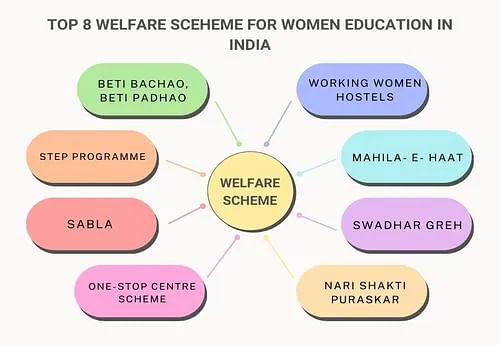
1. Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao
The Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao social campaign was launched on 22nd January 2015 and is famous for women's empowerment. The scheme aims to exterminate female foeticide and provide them with an appropriate education.
2. Working Women Hostels
The Working Women Hostels scheme was established to provide a working environment that includes accommodation facilities where women may get more employment opportunities.
3. Support the Training and Employment Programme (STEP)
These schemes provide adequate education and uplift women to be self-employed or bidding entrepreneurs in various sectors. This scheme is open to women above the age of 16.
4. Mahila- E- Haat
The Mahila scheme was launched in 2016 by the Ministry of Women and Child Development. It provides a platform to let women entrepreneurs or women with small-scale businesses display or sell their products and services.
5. SABLA
Rajiv Gandhi Scheme for Employment of Adolescent Girls (RGSEAG), known as SABLA, was initiated on 1st April 2011 by the Government of India. It aims at providing food and nutritious ingredients.
6. Swadhar Greh
The Swadhar Greh scheme was established in 2002 by the Union Ministry of Women and Child Development. The scheme provides shelter, food, care, and clothing to unaided women. Thus, women abandoned by their families and women who survived any disaster are aided with basic needs.
7. One-Stop Centre Scheme
The One-stop Centre scheme was established with the 'Nirbhaya' fund on 1st April 2015 by the Ministry of Women and Child Development. The scheme provides counselling services, legal requirements, police aid, shelter and food to violence victims both in public and private.
8. Nari Shakti Puraskar
The Nari Shakti Puraskar initiative is taken by the Ministry of Women and Child Development to acknowledge women by awarding them for their excellent contributions to society and empowering women.
Also Read: Top 10 Women's Colleges In Kolkata 2024
Importance of Women's Education
Education for all is one of the major tasks being carried out by the Indian government but still, we have the lowest female literacy rate in Asia. India is working but the pace is slow as we haven’t achieved what we should have been so far. Women’s Education is critical to the country’s entire development.
A well-educated woman is capable of managing her personal and professional life. The reasons why women’s education is important are :
- Basic Rights
Education is a basic right for everyone, and when we say everyone, we should not forget that women are also a part of this lot. Society has a large population of women, and we cannot have such a large population as illiterate; it will be our huge loss.
All girls and women, whether they are rich, poor, young, old, married, unmarried, widowed, or with any social status, have their basic right to education. Education is not a privilege but a fundamental right.
- It Brings Equality to Society
When we talk about discrimination and inequality as a problem, we often misunderstand that it begins at the root level. When a boy goes to school and his sister stays back at home, he eventually starts believing that he is superior to a girl. But it’s actually teaching both men and women to promote the concepts of equality and democracy.
- It Makes them Empower, Independent, and Helps Build Self-confidence.
Education is very important for everyone. It helps develop skills that make an individual capable of offering services to others and earning a livelihood. If a woman is educated and capable of earning and bearing her own expenses, she does not need to depend on others or family for her own requirements.
This gives women the confidence to make their own decisions and realize their own worth and uniqueness.
Also Read: Top MA Womens Colleges in Tamil Nadu 2024
Women Education in India
After Independence, women were liberated from the custom of in-house traditions. Higher education came into practice as the Constitution framed the Right to Education. Article 45 of the Indian constitution talks about compulsory education for children. The new India surpassed the myth and stereotype of what is preferable and non-preferable to women.
Today, what we know about women's education is entirely different from the early stages. Women have already modified gender roles and eradicated some strong wrong beliefs from people's minds. But now, women have started working towards achieving goals and being independent to make any situation favour their interests. Their holistic approach to the working environment makes them dazzle even in the lame light.
The female literacy rate from 1991-2021 increased by 10.5%, whereas the male literacy rate rose by 11.72%. Below is the percentage of female literacy rate in different census years.
| Census Year | Female (Per Cent) | Total Population (Per Cent) |
| 2021 | 75.1 | 94 |
| 2011 | 64.6 | 74 |
| 2001 | 53.7 | 65 |
| 1991 | 39.8 | 52.2 |
| 1981 | 29.8 | 43.6 |
| 1971 | 22 | 34.5 |
| 1961 | 15.4 | 28.3 |
| 1951 | 8.9 | 18.3 |
Read More: Top Women's Colleges in India 2024: Engineering, Law, MBA
History of Women's Education
During the Vedic Period, women enjoyed equality in all spheres of life. India was a glorified nation, and even other fellow citizens used to hail down because of its greatness. People were incredibly vigilant towards Atharvaveda, Upanayana, etc., as reading and learning them are considered sacred. They were advised to study distinctive texts and practice them to decipher all twigs of knowledge.
However, after coming through a meticulous stage, the aura of women's education declined severely. The stigma of being confined to their respective houses snatched the significance of women's education in India.
During the period of Buddhism, women started strengthening the glories of life. Many prestigious Universities were established, and women enrolled in allied courses to study. Moreover, women are well-versed in philosophical studies and are usually advised on the establishment of any reforms.
Also Read: Top 10 Women's Colleges in Chennai 2024
Factors Affecting Female Literacy Rate
Women's education has long been a topic of insightful discussions worldwide. People often talk about how education is the primary tool for governing and achieving anything one wants. It is one such tool no thief can steal.
Many institutes, universities, colleges, and schools are established to educate the youth of our nation. Parents' trust has made their children believe in themselves and free their minds of pessimistic thoughts. Yet, globally, more than two-thirds of women are illiterate, out of 796 million illiterate people.
The dilemma lies in an individual's education based on what education is to the family rather than the entire nation. The overall literacy rate in India is 74%, whereas the female literacy rate is 64.6%, which is drastically increasing every year through various government benefits offered.
Different factors were found to be responsible for the decrease in the female literacy rate.
- Social discrimination
- Gender inequality
- Occupation of girl child in domestic chores
- Economic exploitation
Other reasons that are commonly mentioned for girls' drop-out rates at the primary and middle school level are,
- Costs too much
- Less interest in studies
- Early-age marriage
- Required for work in the family business or farm
- Required for household work
Apart from the above reasons, the non-availability of educational centres in close proximity, unsafe means of travel, and lack of proper toilets are additional reasons for girls' drop-outs.
Also Read: Top 10 Women's Engineering Colleges in Hyderabad
Benefits of Women's Education
If the nation's women were educated, the generation would be educated, leading to the country's development. Moreover, educating women leads to many reforms, a better understanding of concepts.
Below are a few benefits of women's education.
- If women educate themselves, the nation will have a steady population, and family planning will be a priority.
- Women's education would make them self-sufficient, and the age of marriage would probably extend, and women would be more independent of their needs and decisions.
- Women will be able to refrain from dramatic situations and look after themselves and their families.
- Women can examine themselves in various fields.
- Women's education gives power to equality.
- Many social discrepancies will be exclaimed, and a powerful system might be established.
- Women's education helps women to voice their opinions.
Read More: Top 10 Women Colleges in Delhi University
Non-Profit Organizations Promoting Women Education
Various organizations promote and work for promoting women education in India. These organizations fight against emphasizing the importance of women's education in India and gender equality.
Some of the non-profit organizations that promote women's education are,
- Educate Girls Bond: It creates new opportunities for girls' education and promotes gender equality by providing education for young girls throughout India.
- Global Grassroots: The organization promotes leadership in women and girls in their communities by employing mindfulness throughout designing a social solution.
- Pratham: It is designed to improve education for children in Mumbai.
- Campaign for Female Education (CAMFED): It is an international non-profit organization supporting marginalized girls to succeed through education.
- Girls Who Code: An international organization aiming to provide opportunities for women to learn and develop specialized skills in computer science
8 Influential Women in the Education Field
Women are considered the nation's building block; empowering women is similar to empowering a nation. Indian Women have remarked their country's name and made us proud in every aspect. Below are the influential women in India.
| Names | Influential position |
| Avani Chaturvedi | First Indian woman fighter pilot to fly MiG-21 Bison |
| Manika Batra | Top-ranked Female table tennis player from India |
| Gita Gopinath | First Indian female appointed as chief economist at the International Monetary Fund (IMF). |
| Hima Das | First Indian Women Athlete who won gold at the IAAF World Under 20 Athletics Championships. |
| Chungneijang Mary Kom Hmangte | World Amateur Boxing Champion and has won medals in all seven world championships. |
| Padmasree Warrior | Former Cisco CTO made it to America's top Women in Tech published in Forbes. |
| Komal Mangtani | Business Intelligence Team at Uber. |
A nation's well-being is defined if the women are strong and capable of withstanding any storm. We preach to women by the names of goddesses. We bow down in front of them to achieve success. They are the individuals who rule the world, and we need to treat them with the utmost dignity in all spheres of life to build the most influential and prominent country. New strategies and initiatives like sociocultural practices promote women's education by introducing social empowerment tools with access to education, health care, and access to equal opportunities legally.























POST YOUR COMMENT