The NCERT solutions for class 10 Science chapter 12 Electricity has questions related to electric cells, electric bulbs, electric circuits, switches, conductors and insulators. Students can download this chapter in the PDF format.
The NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity is expected to carry 7-8 marks as per the examination trend based on the previous year. NCERT solutions for class 10 are important for the examination as they will help the students to understand the concepts clearly. Moreover, these solutions are designed by exam experts based on the latest CBSE class 10 syllabus 2023-24.
The NCERT solutions for class 10 Science chapter 12 includes all the important definitions, concepts, and methodologies that will benefit the students. Students are advised to carefully review these electricity class 10 NCERT solutions to score good marks in the board examination. Find below for more details on topics, pdf and features.
Table of Contents
- Download PDF for NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity: Important Questions
- Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Mind Map
- Why to Refer to NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity?
Download PDF for NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity
Students can refer to the link mentioned below to download the electricity class 10 NCERT solutions. It includes all the new concepts which will be helpful for the candidates for their final examination.
| NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity | Download |
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity: Important Questions
The electricity class 10 solutions consists of various important questions with which students must familiarize themselves. The detailed question and answers are mentioned below, along with the page number for students' reference.
Page Number: 200
Question 1
What does an electric circuit mean ?
Answer:
A continuous and closed path along which an electric current flows is called an electric circuit.
Question 2
Define the unit of current.
Answer:
Unit of current is ampere. If one coulomb of charge flows through any section of a conductor in one second then the current through it is said to be one ampere.
I = Q/t or 1 A = I C s-1
Question 3
Calculate the number of electrons constituting one coulomb of charge.
Answer:
Charge on one electron, e = 1.6 x 10-19 C
Total charge, Q = 1 C
Number of electrons, n =
Q/e = 1C/1.6x.10−19= 6.25 x 1018
Page Number: 202
Question 1
Name a device that helps to maintain a potential difference across a conductor.
Answer:
A. Battery.
Question 2
What is meant by saying that the potential difference between two points is IV?
Answer:
The potential difference between two points is said to be 1 volt if 1 joule of work is done in moving 1 coulomb of electric charge from one point to the other.
Question 3
How much energy is given to each coulomb of charge passing through a 6 V battery ?
Answer:
Energy given by battery = charge x potential difference
or W = QV = 1C X 6V = 6J.
Page Number: 209
Question 1
On what factors does the resistance of a conductor depend ?
OR
List the factors on which the resistance of a conductor in the shape of a wire depends. [CBSE2018]
Answer:
The resistance of a conductor depends (i) on its length (ii) on its area of cross-section and (iii) on the nature of its material.
Question 2
Will current flow more easily through a thick wire or a thin wire of the same material, when connected to the same source ? Why ?
Answer:
The current will flow more easily through a thick wire than a thin wire of the same material. Larger the area of cross-section of a conductor, more is the ease with which the electrons can move through the conductor. Therefore, smaller is the resistance of the conductor.
Question 3
Let the resistance of an electrical component remains constant while the potential difference across the two ends of the component decreases to half of its former value. What change will occur in the current through it ?
Answer:
When potential difference is halved, the current through the component also decreases to half of its initial value. This is according to ohm’s law i.e., V ∝ I.
Question 4
Why are coils of electric toasters and electric irons are made of an-alloy rather than a pure metal ?
OR
Why are alloys commonly used in electric heating devices? Given reason. [CBSE 2018]
Answer:
The coils of electric toasters, electric irons and other heating devices are made of an alloy rather than a pure metal because (i) the resistivity of an alloy is much higher than that of a pure metal, and (ii) an alloy does not undergo oxidation (or burn) easily even at high temperature, when it is red hot.
Page Number: 213
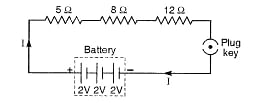
Question 1
Draw a schematic diagram of a circuit consisting of a battery of three cells of 2 V each, a 5Ω resistor, an 8 Ω resistor, and a 12 Ω resistor, and a plug key, all connected in series.
Answer:
The required circuit diagram is shown below:
Question 2
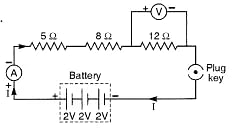
Redraw the circuit of Questions 1, putting in an ammeter to measure the current through the resistors and a voltmeter to measure the potential difference across the 12 Ω resistor. What would be the readings in the ammeter and the voltmeter ?
Solution:
The required circuit diagram is shown on the right.
Total voltage, V = 3 x 2 = 6V
Total resistance, R = 5Ω + 8Ω + 12Ω = 25Ω
Page Number: 216
Question 1
Judge the equivalent resistance when the following are connected in parallel :
(i) 1 Ω and 106 Ω,
(if) 1 Ω and 103 Ω and 106 Ω.
Answer:
When the resistances are connected in parallel, the equivalent resistance is smaller than the smallest individual resistance.
(i) Equivalent resistance < 1 Ω.
(ii) Equivalent resistance < 1 Ω.
Question 4
How can three resistors of resistances 2Ω, 3 Ω, and 6Ω be connected to give a total resistance of (i) 4 Ω, (ii) 1 Ω ?
Solution:
(i) We can get a total resistance of 4Ω by connecting the 2Ω resistance in series with the parallel combination of 3Ω and 6Ω.
![]()
(ii) We can obtain a total resistance of 1Ω by connecting resistors of 2 Ω, 3 Ω and 6 Ω in parallel.
![]()
Page Number: 220
Question 1
What determines the rate at which energy is delivered by a current ?
Answer:
Resistance of the circuit determines the rate at which energy is delivered by a current.
Question 2
An electric motor takes 5 A from a 220 V line. Determine the power of the motor and the energy consumed in 2 h.
Answer:
Here, I = 5 A, V = 220 V, t = 2h = 7,200 s
Power, P = V I = 220 x 5 = 1100 W
Energy consumed = P x t = 100 W x 7200 s = 7,20,000 J = 7.2 x 105 J
Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Mind Map
The chapter 12 of class 10 Science includes topic like Electricty which is the scoring chapter. Students must thoroughly understand this topic for their fina examination as well as for the competitive exams. Refer to the details mentioned below for students reference.
Electricity
Study of Electric Charges at Rest and in Motion
Charge
Something associated with the matter due to which it produces and experiences electric and magnetic effects. Resides on the outer surface of the conductor.
Q = ne S.I. unit coulomb (C)
Electric Current (I)
The time rate of flow of charge (Q) through any cross-section
I = Q/t S.I. unit ampere (A)
Types of Current
Direct Current
Current whose magnitude and direction does not vary with time.
Alternating Current
Current whose magnitude and direction periodically changes with time.
Electric Potential
Work done per unit charge
V = W/Q
S.I. unit volt
Ohm’s law: If the physical conditions remain same, current I ∝ V => V = IR
R-electric resistance Substances which obey ohm’s law called ohmic and that do not obey called non-ohmic substances.
Dependence of Resistance
On length (l) and area of cross-section (A)
R ∝ l
∝ 1/A
R = ρl/A
ρ = resistivity
Resistivity depends on the material of the conductor only.
On Temperature
Rt = R0( 1 + αt)
α = temperature coefficient of resistance
Resistance (R): Obstruction offered to flow of electrons.
SI unit ohm
Resistance, R ∝ ℓ2/m
l = length and
m = mass of conducting wire
After stretching, if length increases by n times then resistance will increase by n2 times i.e., R2 = n2 R1. Similarly
if radius be reduced to 1/n
times then area of cross-section decreases 1/n2
times so the resistance becomes n4 times i.e.. R2 = n4 R1
After stretching, if length of a conductor increases by x%, then resistance will increase by 2x% (valid only if x< 10%).
- Using n conductors of equal resistance, the number of possible combinations is 2n-1 .
- If the resistances of n conductors are totally different, then the number of possible combinations will be 2n .
Grouping of Resistances
Series Grouping of Resistances
Equivalent resistance, resistance, Rs = R1 + R2 + … + Rn
In this case same current flows through each resistance but potential difference in the ratio of resistance.
In this case same potential across each resistance but current distributes in the reverse ratio of their resistances
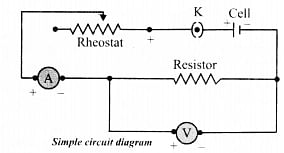
Electric Circuit
The arrangement of various electrical components along which electric current flow.
Heating Effect of Electric Current
As current flows through a conductor, the free electrons lose energy which is converted into heat.
Joule’s heating law
H ∝ I2
H ∝ R
H ∝ t
H = I2Rt = VIt
Practical Applications
- Electric heater, electric iron and water heater, etc. work on the principle of heating effect of current
- Electric bulb glows when electric current flows through the filament of the bulb
Electric Power
Rate at which electric energy is dissipated or consumed in a circuit,
P = VI ,
or P = I2R = V2/R
Watt is a smaller unit of power, its other bigger units are kilowatt (KW),
Megawatt (MW) and Horsepower (HP)
1 KW = 103W 1 MW = 106W
1 hp =746 W
The commercial unit of electrical energy is 1 Kwh.
1 Kwh = 3.6 × 106J
Elements of Circuit
Cell
Direct current source of electromotive force. Combination of two or more cells is called battery.
![]()
Rheostat
Wire of special type of alloy like manganin, Eureka, nichrome, etc. is wound on a hollow cylinder of china clay. It controls the current in the electric circuit.
![]()
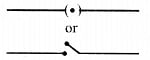
Switch
It is used to close or open the electric circuit, controls the movement of electrons in a circuit.
Voltmeter
Measures the potential difference between two points in the circuit. Its resistance is high and it is used in parallel with the resistance wire.
![]()
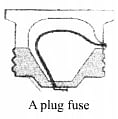
Fuse
It is a safety device having very thin wire which is made up of either tin or alloy of tin and lead.
This wire has low melting point so it melts and breaks the circuit easily if the current in the circuit exceeds.
Ammeter
Measures the value of current flowing in the circuit.
The resistance of ammeter is small and it is used in series with the circuit.
![]()
LED
It is a device which glows even if a weak electric current is allowed to flow through it
Now that you are provided all the necessary information regarding Electricity class 10 NCERT solutions and we hope this detailed article on NCERT solutions for class 10 Science chapter 12 Electricity is helpful. If you have any doubt regarding this article or NCERT solutions for class 10 Science chapter 12 Electricity, leave your comments in the comment section below and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
Topics Covered in NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12
Some of the important topics covered in the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity are given below.
- Ohm’s law
- Resistivity and Resistance
- Factors that affect the Resistance of a Conductor
- Parallel and Series Combination of Resistors and their applications
- Heating Effect of Electric Current and its Applications
- Electric Power
- The interrelation between P, V, I and R
Why to Refer to NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity?
NCERT solutions will help the candidates to score higher marks in their final examination. The experts with new concepts and ideas prepare these solutions.
- The electricity class 10 NCERT is designed in simple language to help the candidates understand the concept easily.
- The NCERT solutions have many extra questions based on the latest CBSE curriculum for the candidates.
- After referring to the NCERT solutions, candidates must also use the latest syllabus and previous year's questions to better prepare.



POST YOUR COMMENT