The scope of organizational behaviour has increased many-folds as it helps in improving job performance, increasing job satisfaction, and encouraging leadership at work place.
Table of Contents
The scope of organizational behavious means the study of human behaviour at three different levels. The three primary levels are, Individual behaviour, group behaviour, and organizational level behaviour. These three levels are used to investigate the personality, leadership, motivation, communication and culture of people.
The scope of organisational behaviour is increasing in today's world, where assessing and improving employees' performance holds utmost importance. Organisational behaviour encompasses a wide and diverse variety of subjects, spanning all levels of an organization. It is a multidisciplinary field that studies human behaviour in organisational settings. It focuses on how the individual, group, or structure impacts behaviour within an organization.
Understanding the definition, scope and objectives of organisational behaviour can help improve organisational effectiveness and the well-being of employees, thus achieving the goals of the company in a better way. It also helps create an effective, adaptive, and positive work environment.
What is Organisational Behaviour?
Organisational behaviour is a systematic study of how individuals and groups act within an organization. Understanding organisational behaviour can help the company improve its functionality and effectiveness, thus promoting a better work environment.
It also helps to understand how individuals and groups interact within an organization and how their interactions affect the organization's performance in reaching its goals. Understanding the right and the scope of organisational behaviour within a company can help in better management of the functions and improve the work life of the employees.
Studying organisational behaviour can help assess how employees process these changes and inculcate them into their work patterns. in addition, organisational behaviour helps fulfil objectives like improving employee behaviour, enhancing leadership skills, increasing the motivation of employees, assisting in organisational change, creating a desirable workplace culture, etc.
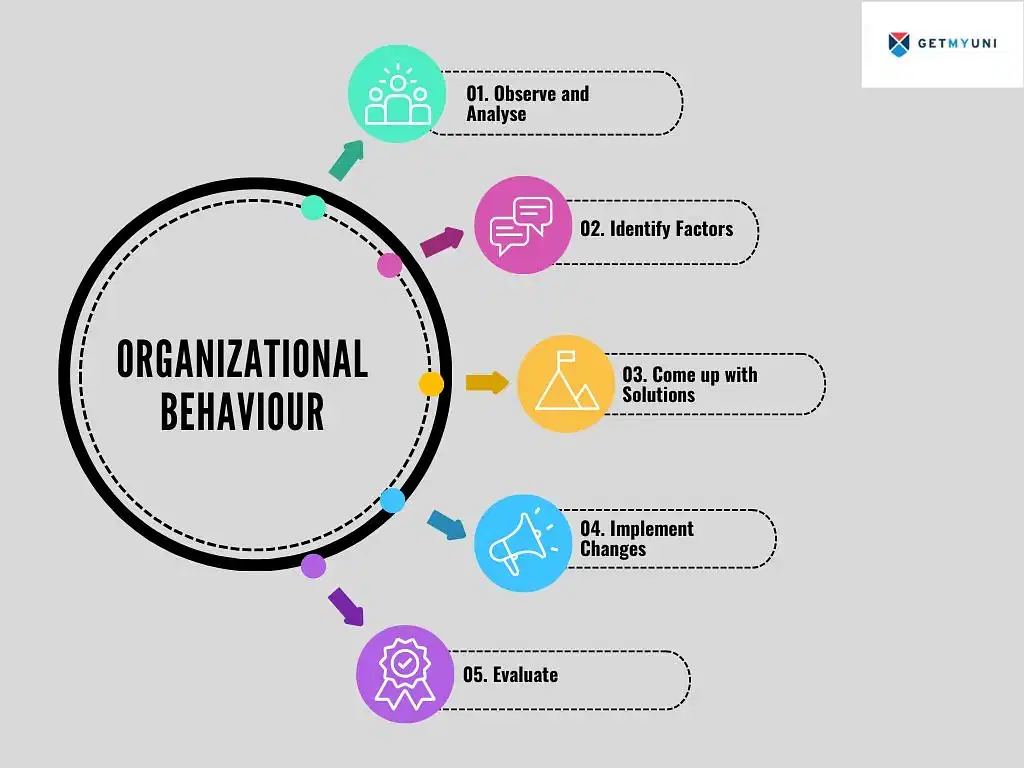

What is the Scope of Organisational Behaviour?
The scope of organisational behaviour is vast and dynamic. Thus, understanding this concept is important for the better functioning of an organization.
- Individual Behaviour
- Group Behaviour
- External Environment
- organisational Structure
- organisational Culture
- Decision Making
- Change Management
- Leadership and Power
Let’s study some of these in detail below.
1. Individual Behaviour
This area helps understand how an individual's characteristics, like personality, attitude, perception, motivation and incentives, interests, learning and development, attitudes and job satisfaction, etc., can impact a workplace.
Motivation theories, emotional intelligence, and job satisfaction are some concepts that fall under this category. Various one-to-one interaction sessions are conducted to understand the individual behaviour. Also, emphasis is being laid on importance of adult education.
2. Group Behaviour
This focuses on how people behave in groups and teams and how this impacts the work culture of an organization. It deals with topics like group dynamics, communication, leadership styles, and decision-making processes.
It helps people in fostering collaboration and managing conflicts. This is also known as group conformity. Further, it involves the study of the following aspects of a group:
- The patterns of communication
- Decision-making among group members
- Distribution of leadership roles
- Cohesiveness
- Techniques used during conflict resolution
3. External Environment
External environments are also a huge part of organisational Behaviour, impacting how an organization as a whole interacts when stimulated by external factors. Some of the important external factors that influence individual interactions include the following:
- Economic conditions
- Social trends and demographic changes
- Market conditions and competition
- Technological developments
- Policy changes
4. Organisational Structure
organisational structure is a driving force behind any organisational behaviour. Some factors of organisational structure that impact employee behaviours are:
- Distribution of leadership and hierarchy
- Type of organisational structure
- Workflow and coordination
- Change management and adaptability
- Clarity of roles and responsibilities
Here are some important links related to Human Resource Courses:
- Diploma Courses After MBA HR
- Certification Courses After MBA HR
- Diploma in Human Resource Management
Objectives of Organisational Behaviour
You must review some of the objectives related to the scope of organisational behaviour mentioned in the pointers below for reference.
- To improve employee productivity by understanding factors like employee motivation, satisfaction, and performance.
- Fostering better communication by creating communication channels, minimizing misunderstandings, and promoting collaboration within the team
- Enhancing organisational culture by creating an environment where employees feel valued, motivated, and aligned with organisational goals.
- Managing changes effectively by minimizing resistance and ensuring smooth transactions
- Developing leadership qualities among the employees, helping them manage their work more effectively.
- Facilitating decision-making skills by understanding cognitive and behavioural factors to make informed decisions.
- Promoting innovation and adaptability through continuous learning and creativity.
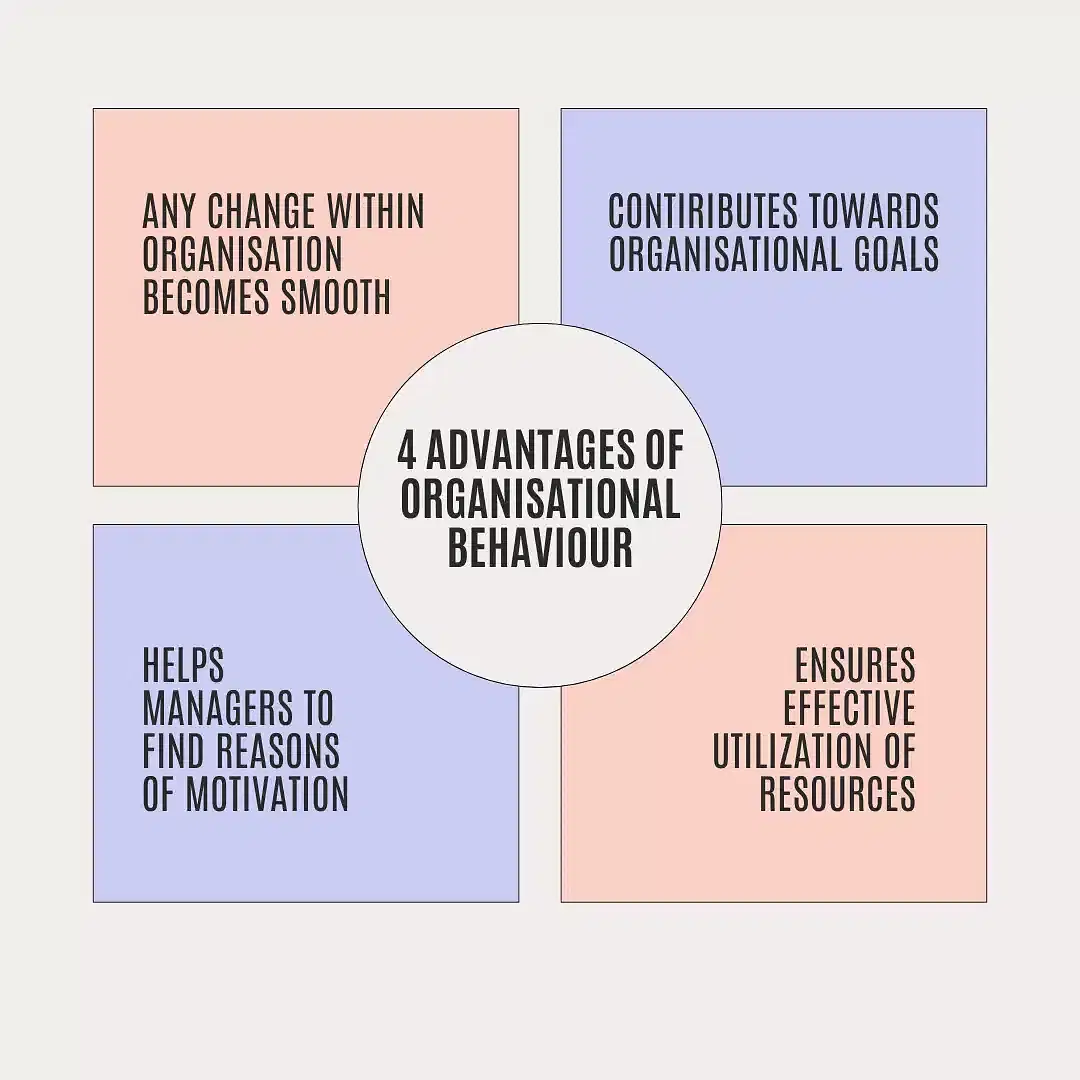
Advatnages of Organisational Behaviour
Organisations can profit from organisational behaviour in several ways, such as:
- Improved employee performance: By establishing clear goals, giving constructive criticism, and putting performance management strategies into practice, employees can perform better.
- Enhanced productivity: Organisational Behaviour can result in increased productivity levels within the company by streamlining procedures, inspiring workers, and cultivating a pleasant workplace culture.
- Higher employee morale and job satisfaction: Organisational Behaviour helps to raise employee morale and job satisfaction through good leadership, communication, and acknowledging accomplishments.
- Decreased turnover rates: As Organisational Behaviour tactics help employees feel appreciated, involved, and supported in their jobs, organisations that use them frequently see a decrease in turnover rates.
Read More: Post Graduate Diploma in Labour Law & Administrative Law
What Are the Theories of Organisational Behaviour?
Organisational behaviour (OB) is the study of human behaviour in an organisational setting. It tries to understand why and how individuals behave in the workplace, as well as how these activities affect organisational outcomes.
The organisational behaviour (OB) theories provide a framework for understanding these complicated interactions and suggestions on how to effectively manage and inspire people.
1. The Classical Management Theory: The classical management philosophy evolved in the early twentieth century and aimed to maximise efficiency and output. Frederick Winslow Taylor, Henry Fayol, and Max Weber were among the leading figures in this school of thought.
Taylor's scientific management style focused on breaking down processes into simple parts and assessing worker performance to maximise efficiency. Fayol's administrative management theory centred on organisational structure and managerial functions. Weber's bureaucratic model emphasised hierarchy, norms, and the division of labour.
2. Human Relations Theory: Elton Mayo and his colleagues developed the Human Relations Theory, which emphasises the role of social relations in the workplace. Consider an office where connections and employee satisfaction are critical. This idea emphasises the importance of positive workplace interactions and their effects on individual and group performance.
3. Scientific Management Theory: This idea, advocated by Frederick Taylor, focuses on efficiency. A factory in which duties are divided into small, exact phases. Scientific management seeks to simplify operations and increase efficiency by optimising each stage of the workflow.
4. organisational Culture Theory: Think of an organisation's culture as its distinct personality. This theory investigates how values, beliefs, and standards impact behaviour inside an organization. It's like knowing the shared norms that influence how people interact and collaborate.
5. Equity Theory: Equity Theory concentrates upon the concept of fairness. Consider a company in which employees compare their input (effort, time) and output (rewards, recognition) to those of their colleagues. This idea focuses on the significance of perceived fairness in employee happiness and performance.
Factors Affecting Organisational Behavior
Recognising the elements that influence individual and group behaviour inside a firm is an essential component of effective management and performance enhancement. In this talk, we'll go deeper into the key components that influence organisational behaviour.
1. Leadership and Management Styles: The way leaders and managers guide and engage with people has a significant impact on their behaviour. Effective leadership fosters a pleasant workplace culture, whereas ineffective leadership can lead to unhappiness and conflict.
2. Workplace Culture: organisational culture influences behaviour. A supportive and inclusive culture motivates people to collaborate and perform effectively, but a poisonous culture can cause stress and disengagement.
3. External Environment: Economic conditions, social changes, and the marketplace in which a company works can all influence behaviour. Organizations must adjust to these external pressures.
4. Legal and Ethical Considerations: Laws and ethical norms influence organisational conduct. Following legal and ethical principles is critical to sustaining a positive image of the company.
5. Communication: Honest and forthright interaction is essential. Effective communication fosters understanding and cooperation, but a lack of communication can lead to misunderstandings and conflict.
Also Check: Executive Diploma in Human Resource Management




















POST YOUR COMMENT