Mass Of Electron
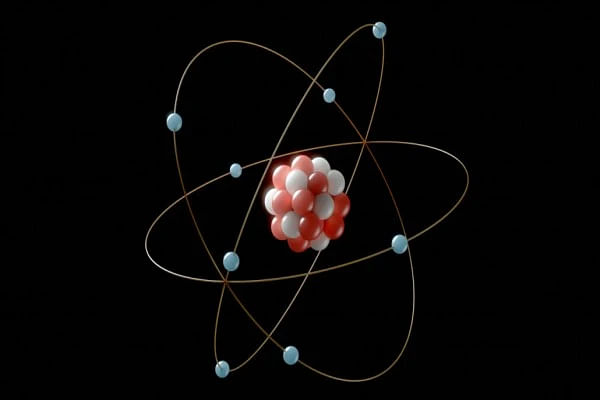
The mass of electron is the mass of a stationary electron described by the equation me = 9.10938356 × 10-31 kilograms where me is the rest mass of electron.

Mar 4, 2024