
Table of Contents
MET syllabus 2025 is set by the university to test the ability of the students in different aspects. The syllabus is similar to that of the class 12 and of similar difficulty. MET 2025 also tests the personality, attitude, and knowledge of the student.
The candidates can start preparing for the exam by going through the syllabus and practicing regularly. To prepare for the MET 2025 syllabus, one must know the MET exam pattern 2025.
MET 2025 Syllabus
Candidates who are eligible for MET 2025 and who are preparing for MET 2025 into various programs like MBBS, BDS, B.Tech, B.Pharma, and PharmD should be aware of the exam pattern and syllabus from which the questions will be taken from. The eligible candidates have to go through the syllabus to improve themselves and to pass this exam. The syllabus for MET 2025 is given below:
Note: Papers in Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Mathematics, and General English have questions based on 10+2 syllabus followed by major 10+2 Boards/Universities.
MET 2025 Physics Syllabus
- Units and Measurement: Need for measurement: Units of measurement; systems of units; SI units, fundamental and derived units. Length, mass and time measurements; accuracy and precision of measuring instruments; errors in measurement; significant figures. Dimensions of physical quantities, dimensional analysis, and applications.
- Kinematics: Frame of reference, Motion in a straight line: Position-time graph, speed, and velocity. Elementary concepts of differentiation and integration for describing motion, uniform and non-uniform motion, average speed and instantaneous velocity, uniformly accelerated motion, velocity-time, and position-time graphs. Relations for uniformly accelerated motion (graphical treatment).
- Scalar and vector quantities; Position and displacement vectors, general vectors and their notations; equality of vectors, multiplication of vectors by a real number; addition and subtraction of vectors, relative velocity, Unit vector; Resolution of a vector in a plane, rectangular components, Scalar and Vector product of vectors. Motion in a plane, cases of uniform velocity and uniform acceleration-projectile motion, uniform circular motion.
- Laws of Motion: Intuitive concept of force, Inertia, Newton's first law of motion; momentum and Newton's second law of motion; impulse; Newton's third law of motion. Law of conservation of linear momentum and its applications.
- Equilibrium of concurrent forces, Static and kinetic friction, laws of friction, rolling friction, lubrication. Dynamics of uniform circular motion: Centripetal force, examples of circular motion (vehicle on a level circular road, vehicle on a banked road).
- Work and Energy: Work is done by a constant force and a variable force; kinetic energy, work-energy theorem, power. The notion of potential energy, the potential energy of a spring, conservative forces: conservation of mechanical energy (kinetic and potential energies); non-conservative forces: motion in a vertical circle; elastic and inelastic collisions in one and two dimensions.
- The motion of System of Particles and Rigid Body: Centre of a mass of a two-particle system, momentum conservation and center of mass motion. Centre of a mass of a rigid body; the center of mass of a uniform rod. Moment of a force, torque, angular momentum, law of conservation of angular momentum and its applications.
- Equilibrium of rigid bodies, rigid body rotation, and equations of rotational motion, comparison of linear and rotational motions. Moment of inertia, the radius of gyration, values of moments of inertia for simple geoMETrical objects (no derivation). Statement of parallel and perpendicular axes theorems and their applications.
- Gravitation: Kepler's laws of planetary motion, the universal law of gravitation. Acceleration due to gravity and its variation with altitude and depth. Gravitational potential energy and gravitational potential, escape velocity, orbital velocity of a satellite, Geo-stationary satellites.
- Properties of Bulk Matter: Elastic behavior, Stress-strain relationship, Hooke's law, Young's modulus, bulk modulus, shear modulus of rigidity, Poisson's ratio; elastic energy. Pressure due to a fluid column; Pascal's law and its applications (hydraulic lift and hydraulic brakes), the effect of gravity on fluid pressure. Viscosity, Stokes' law, terminal velocity, streamline and turbulent flow, critical velocity, Bernoulli's theorem, and its applications.
- Surface energy and surface tension, angle of contact, excess of pressure across a curved surface, application of surface tension ideas to drops, bubbles and capillary rise.
- Heat, temperature, thermal expansion; thermal expansion of solids, liquids, and gases, anomalous expansion of water; specific heat capacity; Cp, Cv - caloriMETry; change of state - latent heat capacity. Heat transfer-conduction, convection and radiation, thermal conductivity, qualitative ideas of Blackbody radiation, Wien’s displacement law, Stefan's law, and the Greenhouse effect.
- Thermodynamics: Thermal equilibrium and definition of temperature (zeroth law of thermodynamics), heat, work, and internal energy. The first law of thermodynamics, isothermal and adiabatic processes. The second law of thermodynamics: reversible and irreversible processes, Heat engine and refrigerator.
- The behavior of Perfect Gases and Kinetic Theory of Gases: Equation of state of a perfect gas, work done in compressing a gas. Kinetic theory of gases - assumptions, the concept of pressure. Kinetic interpretation of temperature; RMS speed of gas molecules; degrees of freedom, the law of equipartition of energy (statement only) and application to specific heat capacities of gases; the concept of the mean free path, Avogadro's number.
- Oscillations and Waves:
- Periodic motion - period, frequency, displacement as a function of time, periodic functions. Simple harmonic motion (S.H.M) and its equation; phase; oscillations of a loaded spring-restoring force and force constant; energy in S.H.M. Kinetic and potential energies; simple pendulum derivation of expression for its period. Free, forced and damped oscillations (qualitative ideas only), resonance.
- Wave motion: Transverse and longitudinal waves, speed of wave motion, displacement relation for a progressive wave, principle of superposition of waves, reflection of waves, standing waves in strings and organ pipes, fundamental mode and harmonics, Beats, Doppler effect
- Electrostatics: Electric Charges; Conservation of charge, Coulomb's law-force between two point charges, forces between multiple charges; superposition principle and continuous charge distribution. Electric field, electric field due to a point charge, electric field lines, electric dipole, electric field due to a dipole, torque on a dipole in a uniform electric field.
- Electric flux, statement of Gauss's theorem and its applications to find field due to an infinitely long straight wire, uniformly charged infinite plane sheet and uniformly charged thin spherical shell (field inside and outside).
- Electric potential, potential difference, electric potential due to a point charge, a dipole and system of charges; equipotential surfaces, electrical potential energy of a system of two point charges and electric dipole in an electrostatic field. Conductors and insulators, free charges and bound charges inside a conductor.
- Dielectrics and electric polarization, capacitors and capacitance, the combination of capacitors in series and parallel, the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor with and without dielectric medium between the plates, energy stored in a capacitor.
- Current Electricity: Electric current, flow of electric charges in a METallic conductor, drift velocity, mobility and their relation with electric current; Ohm's law, electrical resistance, V-I characteristics (linear and non-linear), electrical energy and power, electrical resistivity and conductivity, Carbon resistors, colour code for carbon resistors; series and parallel combinations of resistors; temperature dependence of resistance.
- The internal resistance of a cell, potential difference, and emf of a cell, a combination of cells in series and parallel, Kirchhoff's laws and simple applications, Wheatstone bridge, METer bridge. PotentioMETer - principle and its applications to measure potential difference and for comparing EMF of two cells; measurement of internal resistance of a cell.
- Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism: Concept of the magnetic field, Oersted's experiment. Biot - Savart law and its application to current carrying circular loop. Ampere's law and its applications to an infinitely long straight wire.
- Straight and toroidal solenoids (only qualitative treatment), a force on a moving charge in uniform magnetic and electric fields, Cyclotron. Force on a current-carrying conductor in a uniform magnetic field, the force between two parallel current-carrying conductors-definition of an ampere, torque experienced by a current loop in a uniform magnetic field; moving coil galvanoMETer-its current sensitivity and conversion to amMETer and voltMETer.
- Current loop as a magnetic dipole and its magnetic dipole moment, magnetic dipole moment of a revolving electron, magnetic field intensity due to a magnetic dipole (bar magnet) along its axis and perpendicular to its axis, torque on a magnetic dipole (bar magnet) in a uniform magnetic field; bar magnet as an equivalent solenoid, magnetic field lines; earth's magnetic field and magnetic elements. Para-, dia- and ferromagnetic substances, with examples. Electromagnets and factors affecting their strengths, permanent magnets.
- Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents: Electromagnetic induction; Faraday's laws, induced EMF and current; Lenz's Law, Eddy currents. Self and mutual induction. Alternating currents, peak and RMS value of alternating current/voltage; reactance and impedance; LC oscillations (qualitative treatment only), LCR series circuit, resonance; power in AC circuits, power factor, wattless current. AC generator and transformer.
- Electromagnetic Waves: Basic idea of displacement current, Electromagnetic waves, their characteristics, their Transverse nature (qualitative ideas only). Electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, X-rays, gamma rays) including elementary facts about their uses.
- Optics:
- Ray Optics: Reflection of light, spherical mirrors, mirror formula, refraction of light, total internal reflection and its applications, optical fibres, refraction at spherical surfaces, lenses, thin lens formula, lens maker’s formula, magnification, power of a lens, combination of thin lenses in contact, refraction and dispersion of light through a prism. Scattering of the light - blue color of the sky and reddish appearance of the sun at sunrise and sunset. Optical instruments: Microscopes and astronomical telescopes (reflecting and refracting) and their magnifying powers.
- Wave optics: Wavefront and Huygen's principle, reflection and refraction of plane wave at a plane surface using wavefronts. Proof of laws of reflection and refraction using Huygen's principle. Interference, Young's double-slit experiment and expression for fringe width, coherent sources and sustained interference of light, diffraction due to a single slit, width of central maximum, resolving power of microscope and astronomical telescope, Polarisation, plane polarised light, Brewster's law, uses of plane polarised light and Polaroids.
- Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter: Dual nature of radiation, Photoelectric effect, Hertz and Lenard's observations; Einstein's photoelectric equation-particle nature of light. Matter waves-wave nature of particles, de-Broglie relation, Davisson-Germer experiment (experimental details should be omitted; only conclusion should be explained).
- Atoms and Nuclei: Alpha-particle scattering experiment; Rutherford's model of atom; Bohr model, energy levels, hydrogen spectrum. Composition and size of nucleus, Radioactivity, alpha, beta and gamma particles/rays, and their properties; radioactive decay law. Mass-energy relation, mass defect; binding energy per nucleon and its variation with mass number; nuclear fission, nuclear fusion.
- Electronic Devices: Energy bands in conductors, semiconductors and insulators (qualitative ideas only) Semiconductor diode – I-V characteristics in forward and reverse bias, diode as a rectifier; Special purpose p-n junction diodes: LED, photodiode, solar cell, and Zener diode and their characteristics, more zen diode as a voltage regulator.
- Junction transistor, transistor action, characteristics of a transistor and transistor as an amplifier (common emitter configuration), the basic idea of analog and digital signals, Logic gates (OR, AND, NOT, NAND and NOR).
- Communication Systems: Elements of a communication system (block diagram only); bandwidth of signals (speech, TV and digital data); bandwidth of transmission medium. Propagation of electromagnetic waves in the atmosphere, sky, and space wave propagation, satellite communication. Need for modulation, amplitude modulation.
- Experimental Skills: Familiarity with the basic approach and observations of the experiments and activities:
-
- Experiments based on the use of vernier calipers and microMETer screw gauge
- Determination of g using a simple pendulum
- Young’s modulus by Searle’s METhod
- Specific heat of a liquid using a caloriMETer
- The focal length of a concave mirror and a convex lens using UV-METhod
- Speed of sound using resonance column
- Verification of Ohm’s law using voltMETer and amMETer,
- The specific resistance of the material of a wire using METer Bridge and post office box.
MET 2025 Chemistry Syllabus
Section-A: Physical Chemistry
- Basic concepts in Chemistry: Matter and its nature, Dalton’s atomic theory, the concept of the atom, molecule, element, and compound. Laws of chemical combination, Atomic and molecular masses, mole concept and Avogadro number, molar mass, vapor density-definition. Relationship between molecular mass and vapor density.
- Concept of STP conditions, gram molar volume, percentage composition, empirical and molecular formulae, chemical equations and numerical problems in all these concepts, stoichioMETry.
- States of matter: Classification of matter – Solid, liquid and gaseous states
- Gaseous state: Gas laws – Boyle’s law, Charles’s law, Graham’s law of diffusion, Avogadro’s law, Dalton’s law of partial pressures, Gay Lussac’s Law of combining volumes, concept of absolute temperature scale, Ideal gas equation, kinetic theory of gases - postulates, concept of average, root mean square and most probable velocities, Numerical problems. I
- deal and real gases, Ideal gas equation, the value of R (SI units). Deviation of real gases from the ideal behavior. PV-P curves. Causes for the deviation of real gases from ideal behavior. Derivation of Van der Waal’s equation and interpretation of PV-P curves.
- Liquid state: Properties of liquids – vapor pressure, viscosity and surface tension, the effect of temp. on them.
- Solid-state: classifications of solids: molecular, ionic, covalent and METallic solids, amorphous and crystalline solids, Unit cell and lattices, packing in solids (fcc, bcc and hcp lattices) voids, calculations involving unit cell paraMETers, imperfection in solids, electrical and magnetic properties.
- Band theory of METals, conductors, semiconductors, and insulators and n & p-type semiconductors.
- Atomic structure: Introduction - Constituents of atoms, their charge, and mass. Atomic number and atomic mass. Wave nature of light, Electromagnetic spectrum-emission spectrum of hydrogen-Lyman series, Balmer series, Paschen series, Brackett series and Pfund series. Rydberg’s equation. Numerical problems involving the calculation of wavelength and wavenumbers of lines in the hydrogen spectrum.
- Atomic model- Bohr’s theory, (derivation of the equation for energy and radius not required). Explanation of origin of lines in the hydrogen spectrum. Limitations of Bohr’s theory. Dual nature of electron - the distinction between a particle and a wave. de Broglie’s Theory. Matter-wave equation (derivation). Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle (Qualitative). Quantum numbers - n, l, m and s, and their significance and interrelationships.
- Concept of orbital - shapes of s, p and d orbitals. Pauli’s exclusion principle and the Aufbau principle. Energy level diagram and (n+1) rule. Electronic configuration of elements with atomic numbers from 1 to 54, extra stability of half-filled and filled orbitals. Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity.
- Chemical bonding and molecular structure: Kossel – Lewis approach to chemical bond formation, the concept of ionic and covalent bonds. Ionic bonding: formation of ionic bonds, factors affecting the formation of ionic bonds, calculation of lattice enthalpy.
- Covalent bonding: valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory and shapes of simple molecules, molecular orbital theory (MOT) - linear combination of atomic orbitals (Qualitative approach), energy level diagram, rules for filling molecular orbitals, bonding and anti-bonding molecular orbitals, bond order, electronic configuration of H 2 , Li 2and O 2 Non-existence of He 2 and paramagnetism of O 2 .
- METallic bonding: Electron gas theory (Electron Sea model), the definition of METallic bond.
- Hydrogen bonding – inter and intra molecular, properties.
- Solutions: METhods of expressing the concentration of solutions – ppm, molarity, molality, normality, mole fraction, percentage (by volume and wt.), Principles of voluMETric analysis- standard solution, titrations and indicators-acid-base (phenolphthalein and METhyl orange) and redox (Diphenylamine) numerical problems.
- Vapour pressure of solutions and Raoult’s law, Ideal and non-ideal solutions, colligative properties of dilute solutions – the relative lowering of vapor pressure, depression of freezing point, elevation of boiling point, osmotic pressure, calculation of mol. wt. of a solute using colligative properties, can't Hoff factor and its significance.
- Equilibrium: Meaning of equilibrium, the concept of dynamic equilibrium.
- Equilibrium involving physical processes: solid-liquid, liquid – gas and solid-gas equilibria, Henry’s law, general characteristics of equilibrium involving physical processes.
- Equilibrium involving chemical processes: Law of chemical equilibrium, equilibrium constants (K p and Kc ) and their significance, the significance of ∆G and ∆G" in chemical equilibria, factors affecting equilibrium, concentration, pressure, temp., the effect of catalyst, Le Chatelier’s principle.
- Ionic equilibrium: Electrolytes and non-electrolytes, ionization of electrolytes, Electrolysis -Faraday’s Laws of electrolysis, numerical problems. Arrhenius theory of electrolytic dissociation, Merit, and limitations. Specific conductivity and molar conductivity - definitions and units. Strong and weak electrolytes with examples.
- Factors affecting the conductivity. Acid-Base theories (Arrhenius, Bronsted-Lowry, and Lewis) and their limitations, acid-base equilibria, ionization constants, Strengths of Acids and Bases - dissociation constants of weak acids and weak bases. Ostwald’s dilution law for weak electrolytes (eq. derivation) - expression for hydrogen ion concentration of weak acid and hydroxyl ion concentration of weak base - numerical problems. Ionic product of water, pH concept, and pH scale. pK, a and pK b values - numerical problems.
- Buffers, types of buffers, mechanism of buffer action, Henderson’s equation for pH of a buffer (derivation), preparation of buffers of required pH -numerical problems. Common ion effect,
- Solubility, the expression for K sp of sparingly soluble salts of types AB, AB 2. Relationship between solubility and solubility product of salts of types AB, AB 2. Applications of common ion effect and solubility product in qualitative analysis, numerical problems.
- Redox reactions and Electrochemistry: Electronic concept of oxidation and reduction, redox reactions, oxidation number, rules for assigning oxidation number, balancing of redox reactions, Electrode potential - Definition, factors affecting single electrode potential, Standard electrode potential, Nernst’s equation for calculating single electrode potential, construction of electrochemical cells, Daniel cell, free energy change during cell reactions (∆G).
- Reference electrodes - Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE) - construction, use of SHE for determination of SRP of other single electrodes and pH of solutions, Limitations of SHE. Electrochemical series and its applications, galvanic and electrolytic cells, half-cell and cell reactions, emf of a galvanic cell and its measurement, Nernst eq. and its applications, working principles of the dry cell, lead-acid cell and H 2 -O 2 fuel cell.
- Chemical Kinetics: Introduction, the commercial importance of rate studies, Order of a reaction, factors deciding the order of reaction-relative concentrations of the reactants and mechanism of the reaction. First-order reaction – eq. for rate constant derivation, units. Half-life period, the relation between the half-life period and order of a reaction, numerical problems.
- Determination of the order of a reaction by the graphical and the Ostwald’s isolation METhod. Zero-order, fractional-order and pseudo-first-order reactions with illustrations. Effect of temperature on the rate of a reaction,
- temperature coefficient of a reaction. Arrhenius's interpretation of the energy of activation and temperature dependence of the rate of reaction. Arrhenius Equation. Influence of catalyst on energy profile. Numerical problems on the energy of activation.
- Surface chemistry: Adsorption: Physisorption and chemisorption and their characteristics, factors affecting the adsorption of gases on solids, Freundlich and Langmuir adsorption isotherms, adsorption from solutions
- Catalysis: Homogeneous and heterogeneous, activity and selectivity of solid catalysts, enzyme catalysis, and its mechanism.
- Colloids: Introduction, colloidal system, and particle sizes. Types of colloidal systems, Lyophilic, and lyophobic sols, examples, and differences. Preparation of sols by Bredig’s arc METhod and peptization. Purification of sols - dialysis and electrodialysis. Properties of sols - Tyndall effect, Brownian movement electrophoresis, the origin of charge, coagulation, Hardy and Schulze rule, Protective action of sols. Applications of colloids. Emulsions and their characteristics.
- Chemical thermodynamics: Concepts of System and types of systems, surroundings, work, heat, energy, extensive and intensive properties, state functions. Spontaneous and non-spontaneous processes, criteria for spontaneity – tendency to attain a state of minimum energy and maximum randomness.
- The first law of thermodynamics -internal energy and enthalpy, heat capacity and specific heat, measurement of ΔU and ΔH, Hess's law of constant heat summation, enthalpy of bond dissociation, combustion, formation, atomization, sublimation, phase transition, ionization, solution, and dilution. Entropy - a measure of randomness, change in entropy, unit of entropy. Entropy and spontaneity.
- The second law of thermodynamics, Gibbs’ free energy as a driving force of a reaction, Gibbs’ equation, prediction of the feasibility of a process in terms of ∆G, standard free energy change and its relation to K p. Numerical problems.
Section - B: Inorganic Chemistry
- Periodic properties: Periodic table – periods and groups. Modern periodic law and present form of the periodic table, s,p,d and f block elements, atomic radii (Van der Waal and covalent) and ionic radii, comparison of the size of cation and anion with the parent atom, size of isoelectronic ions. Ionization energy, electron affinity, electronegativity- definition with illustrations, Fagan's rules. Variations of atomic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity, electronegativity down the group and along the period and their interpretation.
- Principles and processes of METal extractions: Modes of occurrence of elements in nature, minerals, ores, steps involved in the extraction of METals – concentration, reduction (chemical and electrolytic) and refining concerning the extraction of Al, Cu, Zn, and Fe. Thermodynamic and electrochemical principles involved in the extraction of METals.
- Hydrogen: isotopes, preparation, properties, and uses of hydrogen. Physical and chemical properties of water and heavy water, structure, preparation, reactions, and uses of hydrogen peroxide, classification of hydrides – ionic, covalent and interstitial, hydrogen as a fuel.
- S-block elements: general introduction, electronic configuration, and general trends in physical and chemical properties of elements, anomalous properties of the first element of each group, diagonal relationships. Preparation and properties of NaOH, NaCl, Na 2 CO 3 and NaHCO 3. Industrial use of lime, limestone, plaster of Paris and cement, the biological significance of Na, K, Mg and Ca.
- P-block elements: General electronic configuration and general trends in physical and chemical properties of elements across the periods and groups, unique behavior of the first element in each group.
- Group 13: Preparation, properties, and uses of boron and aluminum, structure, properties, and uses of borax, boric acid, diborane, boron trifluoride, aluminum chloride, and alums.
- Group 14: Tendency for catenation, structure, properties, and uses of allotropes and oxides of carbon, silicon tetrachloride, silicates, zeolites, and silicones.
- Group 15: properties and uses of nitrogen and phosphorus, allotropic forms of phosphorus, preparation, properties, structure, and uses of ammonia, nitric acid, phosphine and phosphorus halides (PCL 3, PCL 5 ), structures of oxides and oxoacids of nitrogen and phosphorus.
- Group 16: Preparation, properties, structures and uses of ozone, allotropic forms of sulfur, preparation, properties, structure, and uses of sulphuric acid, structures of oxoacids of sulfur.
- Group 17: Preparation, properties, and uses of hydrochloric acid, trends in the acidic nature of hydrogen halides, structures of interhalogen compounds and oxides and oxoacids of halogens.
- Group 18: Occurrence and uses of noble gases. Structures of fluorides and oxides of xenon.
- d and f block elements: Transition elements, electronic configuration, occurrence and characteristics, general trends in properties of 3d series - electronic configurations, size, variable oxidation states, color, magnetic properties, catalytic behavior, complex formation, interstitial compounds, and alloy formation. Preparation, properties, and uses of K 2 Cr 2 O 7and KMnO 4.
- Lanthanoids: Electronic configuration, oxidation states, and lanthanoid contraction.
- Actinoids: Electronic configuration, oxidation states, and comparison with lanthanoids.
- Co-ordination compounds: Werner’s theory – ligands, coordination number, denticity, chelation, IUPAC nomenclature of mononuclear coordination compounds, isomerism, bonding – valence bond approach. Importance of coordination compounds in qualitative analysis, extraction of METals and biological systems.
- Environmental chemistry: Environmental pollution – atmospheric, water and soil; Atmospheric pollution – tropospheric and stratospheric; Tropospheric pollutants - gaseous pollutants: oxides of carbon, nitrogen and sulfur, hydrocarbons, their sources, harmful effects, and prevention.
- Greenhouse effect and global warming, acid rain; Particulate pollutants – smoke, dust, smog, fumes, mist, their sources, harmful effects and prevention Stratospheric pollution – formation and breakdown of ozone, depletion of ozone layer, its mechanism and effects; Water pollution – major pollutants such as pathogens, organic wastes and chemical pollutants, their harmful effects and prevention; Soil pollution - major pollutants such as pesticides (insecticides, herbicides and fungicides) their harmful effects and prevention; Strategies to control environmental pollution.
Section – C: Organic Chemistry
- Purification and characterization of organic compounds: Purification: crystallization, sublimation, distillation, differential extraction and chromatography – principles and their applications; Qualitative analysis – detection of nitrogen, sulphur, phosphorus and halogens; Quantitative analysis – basic principles involved in the estimation of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, halogens, sulphur and phosphorus; Calculations of empirical formulae and molecular formulae, numerical problems in org. quantitative analysis.
- Basic principles of organic chemistry: Tetravalency of carbon, shapes of simple molecules – hybridization (s and p), classification of organic compounds based on functional groups, compounds containing halogens, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur. Homologs series, isomerism – structural and stereoisomerism.
- Nomenclature: covalent bond fission – homolytic and heterolytic, free radicals, carbocations, and carbanions. Stability of carbocations and free radicals, electrophiles, and nucleophiles.
- Electronic displacement in a covalent bond: Inductive effect, electromeric effect, resonance, and hyperconjugation
- Types of organic reactions: Substitution, addition, elimination, and rearrangement.
- Hydrocarbons: classification, isomerism, IUPAC nomenclature, general METhods of preparation, properties, and reactions
- Alkanes: conformers, Sawhorse and Newman projections of ethane, mechanism of halogenation of alkanes, combustion and pyrolysis.
- Alkenes: GeoMETrical isomerism, mechanism of electrophilic addition, the addition of hydrogen, halogens, water, hydrogen
- halides – Markownikoff’s and peroxide effect, ozonolysis and polymerization.
- Alkynes: Acidic character, the addition of hydrogen, halogens, water and hydrogen halides.
- Aromatic hydrocarbons: Nomenclature, benzene – structure and aromaticity, mechanism of electrophilic substitution, halogenation, nitration, Friedel – Craft’s alkylation and acylation, directive influence of the functional group in mono-substituted benzene.
- Organic compounds containing halogens: General METhods of preparation, properties, and reactions. Nature of C-X bond, mechanisms of substitution reactions, uses, environmental effects of chloroform, iodoform, freons, and DDT.
- Organic compounds containing oxygen: General METhods of preparation, properties, and reactions.
- Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers:
- Alcohols: Identification of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols, mechanism of dehydration
- Phenols: Acidic nature, electrophilic substitution reactions, halogenation, nitration and sulphonation, Reimer – Tiemann reaction.
- Ethers: Structures
- Aldehyde and Ketones: Nature of carbonyl group, nucleophilic addition to >C=O group, relative reactivities of aldehydes and ketones, important reactions such as nucleophilic addition (addition of HCN, NH 3 and its derivatives), Grignard reagents, oxidation, reduction (Wolf Kishner and Clemmensen), acidity of α–hydrogen, aldol condensation, Cannizzaro reaction, Haloform reaction, chemical tests to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones.
- Carboxylic acids: Acidic strength and factors affecting it.
- Organic compounds containing Nitrogen: General METhods of preparation, properties, reactions, and uses.
- Amines: Nomenclature, classification, structure, basic character, and identification of primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
- Diazonium salts: importance in synthetic organic chemistry
- Polymers: General introduction and classification of polymers, general METhods of polymerization – addition and condensation, copolymerization, natural and synthetic rubber, and vulcanization, some important polymers with emphasis on their monomers and uses – polyethylene, nylon 6,6; polyester and bakelite.
- Biomolecuels: general introduction and importance of biomolecules
- Carbohydrates: Classification – aldoses and ketoses, monosaccharides (glucose and fructose) and constituent monosaccharides of oligosaccharides (sucrose, lactose and maltose), polysaccharides (starch, cellulose, glycogen) importance.
- Proteins: Elementary idea of amino acids, peptide bond, polypeptide, proteins – primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary, denaturation of proteins, enzymes, hormones.
- Vitamins: Classification and functioning
- Nucleic acids – chemical constitution of DNA and RNA, biological functions of nucleic acids.
- Chemistry in everyday life:
- Chemicals in medicine – Analgesics, tranquilizers, antiseptics, disinfectants, antimicrobials, antifertility drugs, antibiotics, antacids, antihistamines – their meaning and common examples
- Chemicals in food – Preservatives, artificial sweetening agents, common examples
- Cleansing agents – Soaps and detergents, cleansing action
- Principles related to practical chemistry:
- Detection of extra elements (N, S, halogens) in organic compounds, detection of the functional groups – hydroxyl (alcoholic and phenolic), carbonyl (aldehyde and ketone), carboxyl and amino groups in organic compounds
- The chemistry involved in the titriMETric exercises: Acid-Base titrations, use of indicators, Redox titrations and their
- indicators: Chemical principles involved in the qualitative salt analysis: Cations – Pb 2+ , Cu 2+ , Al 3+ , Fe 3+ , Zn 2+ , Ni 2+ , Ca 2+ , Ba 2+ ,
- Mg 2+, NH 4+; Anions – CO 3 2− , S 2− , SO 4 2− , NO 3 − , NO 2 − , Cl − , Br − and I − .
MET 2025 Mathematics Syllabus
SETS, RELATIONS, AND FUNCTIONS
- Sets: Sets and their representations. Empty set. Finite and Infinite sets. Equal sets. Subsets. Subsets of the set of real numbers especially intervals (with notations). Power set. Universal set. Venn diagrams. Union and intersection of sets. The difference between sets. The complement of a set, Properties of Complement Sets.
- Relations and Functions: Ordered pairs, Cartesian product of sets. Several elements in the Cartesian product of two finite sets. Cartesian product of the reals with itself (up to R × R × R). Definition of relation, pictorial diagrams, domain, co-domain, and range of a relation. Function as a special kind of relation from one set to another.
- Pictorial representation of a function, domain, co-domain, and range of a function. The real-valued function of the real variable, domain, and range of these functions, constant, identity, polynomial, rational, modulus, signum and greatest integer functions with their graphs. Sum, difference, product, and quotients of functions.
- Relations and Functions: Types of relations: Reflexive, symMETric, transitive and equivalence relations. One to one and onto functions, composite functions, the inverse of a function. Binary operations. Partial fractions, Logarithms, and its related properties.
- TrigonoMETric functions: Positive and negative angles. Measuring angles in radians and degrees and conversion from one measure to another. Definition of trigonoMETric functions with the help of the unit circle. The truth of the identity
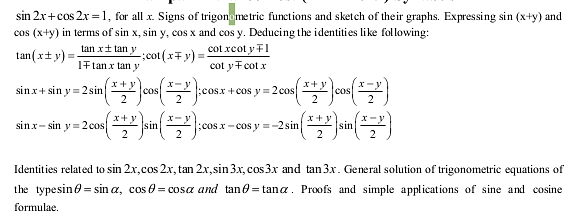
- Inverse trigonoMETric functions: Definition, range, domain, principal value branches. Graphs of inverse trigonoMETric functions. Elementary properties of inverse trigonoMETric functions.
ALGEBRA
- Principle of mathematical induction: Process of the proof by induction, motivating the application of the METhod by looking at natural numbers as the least inductive subset of real numbers. The principle of mathematical induction and simple applications.
- Complex numbers and quadratic equations: Introduction, Complex numbers, Algebra of complex numbers, Brief description of algebraic properties of complex numbers, The modulus and the conjugate of the complex number, Argand plane and polar representation, Fundamental theorem of algebra. The solution of quadratic equations in the complex number system, Square root of a complex number.
- Linear inequalities: Linear inequalities, Algebraic solutions of linear inequalities in one variable and their representation on the number line. Graphical solution of linear inequalities in two variables. The solution of a system of linear inequalities in two variables – graphically.
- Permutations and combinations: Fundamental principle of counting. Factorial n. Permutations and combinations derivation of formulae and their connections, simple applications.
- Binomial theorem: History, statement and proof of the binomial theorem for positive integral indices. Pascal’s triangle, general and middle term in binomial expansion, simple applications.
- Sequence and series: Sequence and Series. ArithMETic Progression (A.P.), ArithMETic Mean (A.M.), GeoMETric Progression (G.P.), general term of a G.P., the sum of n terms of a G.P. ArithMETic and geoMETric series, infinite G.P. and its sum, geoMETric mean (G.M.). The relation between A.M. and G.M. Sum to n terms of the special series:
![]()
Matrices:
- Concept, notation, order, equality, types of matrices, zero matrices, transpose of a matrix, symMETric and skew-symMETric matrices. Addition, multiplication and scalar multiplication of matrices, simple properties of addition, multiplication and scalar multiplication.
- Non-commutativity of multiplication of matrices and existence of non-zero matrices whose product is the zero matrices (restrict to square matrices of order 2). Concept of elementary row and column operations. Invertible matrices and proof of the uniqueness of inverse, if it exists; (Here all matrices will have real entries).
- Determinants:
- The determinant of a square matrix (up to 3 × 3 matrices), properties of determinants, minors, cofactors and applications of determinants in finding the area of a triangle. Adjoint and inverse of a square matrix. Consistency, inconsistency, and several solutions of a system of linear equations by examples, solving system of linear equations in two or three variables (having a unique solution) using the inverse of a matrix.
COORDINATE GEOMETRY, VECTORS, AND THREE-DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY
- Straight lines:
- Brief recall of 2-D from earlier classes, shifting of origin. The slope of a line and angle between two lines. Various forms of equations of a line: parallel to axes, point-slope form, slope-intercept form, two-point form, intercepts form and normal form. General equation of a line. Equation of family of lines passing through the point of intersection of two lines. The distance of a point from a line.
- Conic sections:
- Sections of a cone: circles, ellipse, parabola, hyperbola, a point, a straight line and pair of intersecting lines as a degenerated case of a conic section. Standard equations and simple properties of parabola, ellipse, and hyperbola. Standard equation of a circle.
- Vectors:
- Vectors and scalars, magnitude and direction of a vector. Direction cosines/ratios of vectors. Types of vectors (equal, unit, zero, parallel and collinear vectors), position vector of a point, negative of a vector, components of a vector, the addition of vectors, multiplication of a vector by a scalar, position vector of a point dividing a line segment in a given ratio. Scalar (dot) product of vectors, projection of a vector on a line. Vector (cross) product of vectors, scalar triple product.
- Three-dimensional geoMETry:
- Coordinate axes and coordinate planes in three dimensions. Coordinates of a point. Distance between two points and section formula. Direction cosines/ratios of a line joining two points. Cartesian and vector equation of a line, coplanar and skew lines, the shortest distance between two lines. Cartesian and vector equation of a plane. The angle between (i) two lines, (ii) two planes, (iii) a line and a plane. The distance of a point from a plane.
CALCULUS
- Limits and derivatives: Derivatives introduced as a rate of change both as that of distance function and geoMETrically. The intuitive idea of limit
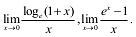 Limits of trigonoMETric functions. Definition of derivative, relate it to the slope of the tangent of the curve, a derivative of the sum, difference, product and quotient of functions. The derivative of a polynomial of trigonoMETric functions.
Limits of trigonoMETric functions. Definition of derivative, relate it to the slope of the tangent of the curve, a derivative of the sum, difference, product and quotient of functions. The derivative of a polynomial of trigonoMETric functions. - Continuity and differentiability: Continuity and differentiability, a derivative of composite functions, chain rule, derivatives of inverse trigonoMETric functions, derivative of implicit function. Concepts of exponential, logarithmic functions. Derivatives of log e z and e. Logarithmic differentiation. The derivative of functions expressed in paraMETric forms. Second-order derivatives. Rolle’s and Lagrange’s Mean Value Theorems (without proof) and their geoMETric interpretations.
- Applications of derivatives: Applications of derivatives: Rate of change, increasing/decreasing functions, tangents, and normals, approximation, maxima and minima (first derivative test motivated geoMETrically and second derivative test given as a provable tool). Simple problems (that illustrate basic principles and understanding of the subject as well as real-life situations).
- Integrals: Integration as the inverse process of differentiation. Integration of a variety of functions by substitution, by partial fractions and by parts, only simple integrals of the type
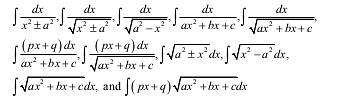
- to be evaluated.
- Definite integrals as a limit of a sum. Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (without proof). Basic properties of definite integrals and evaluation of definite integrals.
- Applications of the integrals: Applications in finding the area under simple curves, especially lines, arcs of circles/parabolas/ellipses (in standard form only), area between the two above said curves (the region should be identifiable).
- Differential equations: Definition, order, and degree, general and particular solutions of a differential equation. Formation of differential equations whose general solution is given. The solution of differential equations by the METhod of separation of variables, homogeneous differential equations of the first order and first degree. Solutions of the linear differential equation of the type –
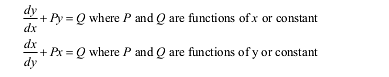
MATHEMATICAL REASONING
Mathematically acceptable statements. Connecting words/phrases - consolidating the understanding of “if and only if (necessary and sufficient) condition”, “implies”, “and/or”, “implied by”, “and”, “our”, “there exists” and their use through variety of examples related to real life and Mathematics. Validating the statements involving the connecting words - the difference between contradiction, converse, and contrapositive.
STATISTICS AND PROBABILITY
- Statistics: Measure of dispersion; mean deviation, variance and standard deviation of ungrouped/grouped data. Analysis of frequency distributions with equal means but different variances.
- Probability: Random experiments: outcomes, sample spaces (set representation). Events: Occurrence of events, ‘not’, ‘and’ & ‘or’ events, exhaustive events, mutually exclusive events. Axiomatic (set-theoretic) probability, connections with the theories of earlier classes. Probability of an event, probability of ‘not’, ‘and’, & ‘or’ events. Multiplications theorem on probability. Conditional probability, independent events, total probability, Baye’s theorem. Random variable and its probability distribution, mean and variance of haphazard variable. Repeated independent
- (Bernoulli) trials and Binomial distribution.
LINEAR PROGRAMMING
Introduction, related terminology such as constraints, objective function, optimization, different types of linear programming (L.P.) problems, the mathematical formulation of L.P. problems, graphical METhod of solution for problems in two variables, feasible and infeasible regions, feasible and infeasible solutions, optimal feasible solutions (up to three non-trivial constraints).
MET 2025 Biology Syllabus
- Biosystematics
- Cell Biology
- Chromosomes
- Cell Reproduction
- Introduction to Biology
- Biomolecules
- Origin of life and organic evolution
- Molecular Biology
- Genetics
- Biodiversity
- Man in health and diseases
- Continuity of life.
MET 2025 Botany Syllabus
- Diversity of life on earth
- Viruses
- Bacteria
- Cyanobacteria
- Kingdom Protista
- Kingdom Mycota
- Kingdom METaphyta
- Pteridophyta
- Gymnosperms
- Angiosperms
- Taxonomy and Economic Botany
- Plant histology & anatomy
- Water relations of plants
- Bioenergetics
- Growth and growth regulators in plants
MET 2025 General English Syllabus
The test of English Language for the entrance examination covers ‘General English’ of the 10 + 2 standard. It is not designed to evaluate students’ knowledge of English literature, but to test their ability to grasp the fundamental concepts in English grammar and usage.
Proficiency in the English language is tested through objective-type multiple-choice questions on grammar, vocabulary, sentence correction, synonyms, antonyms, homophones, homonyms, one-word substitutions, idioms and phrases, phrasal verbs, and usage.
Students are not required to learn the glossary of complicated grammatical jargon but should have the basic knowledge of word usage, matching of subject and verbs, correct usage of tenses, and grammatically correct sentences acceptable in standard written communication.
The syllabus will include the following areas:
- Tense – Use of proper tense and sequence of tense
- Modals (have to/had to, must, should, need, ought to and their negative forms)
- Subject-verb concord
- Pronouns
- Sentence structure
- Usages in English: Commands and requests, Statements, Questions
- Clauses: Noun clauses, Adverb clauses of condition and time, Relative clauses
- Determiners/ Use of proper articles
- Prepositions
- Vocabulary: Synonyms, Antonyms, Spellings, One-word substitutions


















