Table of Contents
OJEE syllabus 2025 is framed by the Odisha Joint Entrance Exam. OJEE syllabus comprises subjects and well-explained topics on individual subjects such as MBA, Mechanical Engineering, Electrical Engineering and much more. OJEE 2025 syllabus contains 12 modules.
Before starting with the preparation, candidates must go through the syllabus completely to score high in the examination. Along with the Syllabus, candidates must also have a fair idea about the OJEE exam pattern 2025, like the total number of questions, types of questions, important topics in the syllabus and much more.
OJEE syllabus 2025 has been released by the exam conducting body. OJEE 2025 exam success depends on the preparation of the candidate through understanding the exam pattern and syllabus.
OJEE Syllabus 2025 PDF Download
OJEE syllabus 2025 has been released by the Odisha Joint Entrance Exam soon on the official portal at ojee.nic.in. For reference, candidates can go through the OJEE syllabus 2025 in the table below.
| Syllabus | PDF Download Link |
| OJEE 2025 Syllabus | Download Here |
OJEE 2025 Syllabus for B.Pharm, BAMS, and BHMS
OJEE syllabus for B. Pharmacy and other courses are important to understand to ace in the exam. The syllabus for these courses is standard. The questions will be based on various topics from Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics / Biology (Botany and Zoology).
Aspirants should also carefully study the OJEE exam pattern 2025 before appearing for the exam. The candidates will be given three hours to solve 180 Multiple Choice Questions and
OJEE 2025 B.Pharm Syllabus - Physics (45 Questions)
All candidates who wish to pursue either of the three courses mentioned above, i.e., B.Pharm, BHMS, or BAMS, need to attempt the Physics section of the question paper mandatorily. The questions will be based on the following topics prescribed in the syllabus. Candidates can refer the OJEE syllabus 2025.
- Measurements and Motion: Fundamental and derived physical quantities, Concept of Mass, Length and Time, Measurement of different quantities in SI Units. Errors in measurement, Combination of errors, Dimension of physical quantities, Dimension analysis of physical quantities- Conversion of physical quantities from one system of units to another. Concepts of vectors and scalars, Components of vectors, Unit vectors, Addition, Subtraction, and Multiplication (vector and scalar) of vectors. Lami’s Theorem. Equations of linear motion for uniformly accelerated bodies (by calculus method). Newton’s laws of motion, Conservation of energy and momentum, Collision in one dimension, Work Power, Energy, Sliding, and Rolling friction. Circular Motion- radial and tangential acceleration, Centripetal force, Banking of tracks, Kepler’s laws of Planetary Motion (Statements only). Newton’s law of Gravitation. Earth satellites- Orbital and Escape velocities. Moment of Inertia-definition and expression of Moment of Inertia for rod, ring, and circular disc (about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the body). Angular momentum and Conservation of angular momentum, Projectile motion.
- Heat and Thermodynamics: Concept of Temperature, Scales of Temperature (Celsius, Fahrenheit, Kelvin), Definition of the mechanical equivalent of heat (J), Thermal energy, Heat Capacity, Specific heat of solids and liquids, Latent heat, Heat transfer-Thermal conductivity of solids, Steady-state, Kirchhoff’s laws of heat radiation, Stefan’s law of heat radiation, Newton’s Law of cooling.Kinetic Theory of gases- Pressure of an ideal gas, Kinetic interpretation of temperature, Degrees of freedom, Law of equipartition of energy.
First Law of Thermodynamics, Specific heats of a gaseous system, Relation between Cp and Cv, Work done during Isothermal and Adiabatic processes, Carnot’s conceptual heat engine and its efficiency, Second law of thermodynamics, Absolute Scale of Temperature. - Liquids: Surface Tension and Surface Energy, Excess pressure across a spherical liquid surface, Expression for a capillary rise. Streamlined and turbulent flow, Bernoulli’s equation and its application, Viscosity- coefficient of viscosity, Stokes law.
- Characteristics of Materials: Elastic and Plastic behaviours of solids, Elastic limit, Young’s modulus, Shear and Bulk modulus, Poisson's ratio.
- Electricity and Magnetism: Electric field intensity and Potential at a point in an electric field, Relation between them, Capacitance- dielectric constant, and its effect on capacitance. Series and parallel grouping of capacitances, Energy stored in a charged capacitor, Ohm’s law, Variation of resistance of metallic conductors with temperature, Kirchhoff’s laws, and its application to a balanced Wheatstone bridge. Combination of Cells and resistors- series and parallel. Heating effect of electric current and Joule’s law, Electric power, and electric energy. Magnetic Permeability and Susceptibility of materials, Properties of dia, para, and ferromagnetic materials. Biot–Savart’s law- Magnetic Field due to a circular coil at its centre. Moving coil galvanometer (deadbeat only). Force on a moving charge in a uniform magnetic field. Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction and Lenz’s law, EMF induced in a rotating coil in a magnetic field. Alternating current-self and Mutual induction, the Phase relation between Voltage and Current in pure resistive, capacitive and inductive circuits. Principle of a transformer, elementary idea on electromagnetic waves.
- Waves and Motion: Simple harmonic motion, wave propagation, characteristics of wave motion, longitudinal and transverse waves, superposition of waves:- Stationary waves, Beats. Open and closed organ pipes, the velocity of sound in air- effect of pressure, temperature, and humidity on it. Doppler Effect, laws of transverse vibration of string (Statement only).
- Optics: Reflection and refraction at curved surfaces. Spherical mirror and thin lens formula and refraction through a prism. Total internal reflection, Dispersion, Huygens principle (statement only), Young’s double-slit experiment.
- Electronic Devices: Thermionic emission, Statement of Richardson’s equation and Child’s Law, Vacuum triode- construction and characteristics, Relationship between valve constants, Descriptive idea of energy bands:- conductors, insulators, and semiconductors, Intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors, p-type and n-type semiconductors. PN junction, PNP and NPN transistor, PN Junction as a rectifier
- Relativity and Nuclear Physics: Postulates of the special theory of relativity, variation of mass with velocity (Statement only), mass-energy equivalence relation (Statement only).Atomic nucleus, nuclear forces, nuclear mass, binding energy, mass defect, artificial radioactivity, radioisotopes, and their uses. Nuclear fission, the energy released during nuclear fission, chain reaction, controlled chain reaction, nuclear fusion, energy generation in the Sun, and radiation hazards.
OJEE 2025 B.Pharm Syllabus - Chemistry (45 Questions)
It is one of the compulsory subjects for all those who wish to pursue BAMS, B.Pharm or BHMS. The complete OJEE syllabus 2025 for Chemistry is tabulated below.
- Solid State: Characteristics, Classification, Solubility, Melting points, a Crystal structure of simple ionic compounds. Radius ratio and coordination number: density calculation, lattice points, and voids.
- Liquid State: Characteristics, Boiling and Freezing points, Viscosity, Surface tension, Osmosis, Raoult’s law, Lowering of vapour pressure, Depression of freezing points, Elevation of boiling points, Anomalous molecular masses; Association and dissociation.
- Solutions: Types of solutions, concentration, and different ways of expressing concentration (percentage, ppm, strength, normality, molarity, molality, and formality) and Interrelations.
- Gaseous State: Gas laws, Kinetic model of gases, ideal gas equation, Van der Waals’ equation, compressibility factor, Average, root mean square and most probable velocities.
- Atoms and Molecules: Symbols, Valency, Atomic mass, Molecular mass, Avogadro’s law, Mole concept, Determination of the equivalent mass of zinc and copper, Atomic mass by Dulong Petit’s method, and Molecular mass by Victor Mayor’s method. Stoichiometry and calculations based on stoichiometry.
- Structure of Atoms and Molecules: Fundamentals particles and their properties, Rutherford and Bohr models of the atom, Hydrogen spectrum, Energy levels, Shells and Sub-shells, s,p and d orbitals, Quantum numbers, Pauli’s exclusion principle, Aufbau-principle, Hund’s rule, Electronic configuration of atoms, Extra stability of half-filled and filled subshells. 2 3 Chemical bonds: Ionic, Covalent, Coordinate and Hydrogen bond, Hybridisation- sp, sp, sp, dsp2,dsp3, d2sp3 shapes of molecules, VSEPR theory, Molecular Orbital Theory of simple diatomic molecules.
- Periodic Classification: Periodic table and periodic laws, s, p, d, and f block elements, Periodicity in properties such as atomic and ionic radii, ionization enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy, electronegativity, and oxidation states.
- Energetics: Internal energy, Enthalpy, Heats of reactions, Bond energy, Hess’s law, Idea of enthalpy, entropy and free energy, spontaneity, and conditions of equilibrium.
- Equilibria: Reversible reaction, Law of mass action, Equilibrium constant Kp, Kc, Kx and their relation. It's an application to ammonia synthesis and dissociation of HI, Decomposition, and thermal dissociation. Theory of acids and bases, Dissociation of weak acids and bases, Ostwald’s dilution law, an Ionic product of water, Common ion effect, Solubility product and their applications, pH, Hydrolysis of salts, Buffer solutions.
- Kinetics: Rate of reaction, Factors affecting the rate, Rate constant, Order and Molecularity of a reaction, Simple zero and First-order reaction, Half-life period, Arrhenius equation and Activation Energy, Collision theory (qualitative idea only).
- Types of Chemical Reactions: Neutralization and oxidation– Reduction reaction, Equivalent mass, Oxidation number, Balancing chemical reactions, by Ion electron method, Reactions involving KMnO4, K2Cr2O7, Na2S2O3, oxalate, etc.
- Non-metals: Group study, Preparation, Properties, and uses of elements or compounds of hydrogen (ortho and para hydrogen, isotopes of hydrogen, D2O and H2O2). Allotropes of carbon, Nitrogen family (NH3 and HNO3). Oxygen and sulfur family (O2, H2S, SO2, H2SO4, and its manufacturer contact process), Halogens, Hydrogen halides and Interhalogen compounds, Zero group elements (properties & uses).
- Electrochemistry: Electrolysis, Electrical Conductivity (Specific, Equivalent and molar), Faraday’s laws, Kohlrausch's law, Galvanic cell, Cell reaction, Nernst equation, Standard electrode potential, Electrochemical series e.m.f. of simple cells. Fuel cells.
- Nuclear Chemistry: Radioactivity, Rate of disintegration, Group displacement law, Half-life and average life period, Stability of nuclear (N/P ratio) Carbon dating, Nuclear Fission, and Fusion. Induced radioactivity by protons, neutrons, and alpha particles.
- Metals and Metallurgy: The occurrence of metal, Minerals, and ores, flux, slag calcination, roasting, smelting (by reduction of oxides), and refining. General trends incharacteristics, and principles of extraction of Na, Mg, Ca, Al, Cu, and Fe and their oxides, hydroxides, chlorides, nitrates, and sulfates.
- Introductory: Functional Groups and organic radicals, Nomenclature by IUPAC system (substitutive method), Isomerism (Structural and stereoisomerism – optical and geometrical) EZ & RS nomenclature, Electron mobility – Inductive effect, Resonance, Electromeric effect, and Hyperconjugation; their applications. Types of organic reactions – addition, substitution, elimination reactions. The idea of electrophiles and nucleophiles; Reaction intermediates – the idea of carbocations, carbanion & free radicals; their stabilities.
- Aliphatic Compounds: Methods of preparation and properties of alkanes, alkenes, alkynes (acidity of terminal alkynes), haloalkanes, alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, acid derivatives (acid chlorides, esters, and amides), nitroalkanes, and amines.
- Aromatic Compounds: Aromaticity (Huckel’s rule), Aromatic hydrocarbon (Preparation and reactions – Substitution, addition, ozonolysis) Phenols (Preparation and reactions): Aldehydes (Preparations and reactions); Acids (Preparation and reactions). Amines (Preparation and reactions); Diazonium salts (synthetic application).
- Biochemistry: Biological importance of organic compounds such as carbohydrates, amino acids, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids (only by a metabolic process).
- Chemistry in the Service of Mankind: The general idea of fertilizers, pesticides, and polymers (nylon, terylene, neoprene, buna-S, PVC, Teflon bakelite). Medicine-analgesic, antipyretic, antibiotic, and antiseptic (structure and preparation not required).
- Environmental Chemistry: Source, effect, and control measures of air and water pollution.
OJEE 2025 B.Pharm Syllabus - Mathematics (45 Questions)
The candidates can either attempt the Mathematics or Biology paper. Those candidates who will attempt the mathematics section must master all the topics tabulated below if they seek admission to BHMS, BAMS, and B.Pharm through OJEE 2025. Candidates can go through OJEE 2025 syllabus.
- Logic: Statement, Negation, Implication, Converse, Contrapositive, Conjunction, Disjunction, Truth Table. Different methods of proof, Principle of Mathematical induction.
- Algebra of Sets: Set operation, Union, Intersection, Difference, Symmetric difference, Complement, Venn diagram, the Cartesian product of sets, Relation, and functions, Equivalence relation, Kinds of functions and their domain and range, Composite function, Inverse of a function.
- Number System: Real numbers (algebraic and order properties, rational and irrational numbers), Absolute value, Triangle inequality, AM≥ GM, Inequalities(simple cases), Complex numbers, Algebra of complex numbers, Conjugate and the square root of a complex number, Cube roots of unity, De Moivre’s theorem with a simple application. Permutations and Combinations - simple applications, Binomial theorem for a positive integral index, Identities involving binomial coefficients.
- Determinants and Matrices: Determinants of the third order, Minors and cofactors, Properties of determinants, Matrices up to third order, Types of matrices, algebra of matrix, adjoint, and universe of a matrix, Application of determinants and matrices to solution of linear equations (in three unknowns).
- Trignometry: Compound angles, Multiple and Submultiple angles, Solution of trigonometric equations, Properties of triangles, Inverse circular function, Sum and product of sine and cosine functions.
- Coordinate Geometry of Two Dimentions: Straight lines, Pairs of straight lines, Circles, Equations of tangents and normals to a circle, Equations of a parabola, Ellipse and hyperbola in simple forms, their tangents and normals. A condition of tangency. Rectangular and Conjugate hyperbolas.
- Coordinate Geometry of Three Dimentions: Distance and Division formulae, Direction cosines and direction ratios, Projection, Angle between two planes, and the angle between a line and a plane. A distance of a point from a line and a plane. Equation of a sphere – generalcequation, Equation of sphere when endpoints of a diameter are given.
- Quadratic Polynomials: Roots of a quadratic polynomial, Factorisation of quadratic polynomials, Maximum and minimum values of quadratic polynomials for all real values of a variable, sign of quadratic polynomial for all real values of a variable, Solution of quadratic inequations. Sequence and Series: Definition, Infinite geometric series, Arithmetic-geometric series, Exponential and Logarithmic series
- Differential Calculus: Concept of limit, Continuity of functions, Derivative of standard Algebraic and Transcendental functions, Derivative of composite functions, functions in parametric form, Implicit differentiation, Successive differentiation (simple cases), Leibnitz theorem, Partial differentiation, Application of Euler’s theorem, Derivative as a rate measure, Increasing and decreasing functions, Maxima and Minima, Indeterminate forms, Geometrical application of derivatives such as finding tangents and normals to plane curves.
- Integral Calculus: Standard methods of integration (substitution, by parts, by partial fraction, etc), Integration of rational, irrational functions and trigonometric functions. Definite integrals and properties of definite integrals, Areas under plane curves.
- Differential Equations: Definition, order, degree of a differential equation, General and particular solution of a differential equation, the formation of a differential equation, solution of differential equations by the method of separation of variables, homogeneous differential equations of the first order and first degree, Linear differential equations of form by/dx +p(x)y = q(x), Solutions of differential equations of form d2y/dx2 =f(x)
- Probability and Statistics: Average (mean, median and mode). Dispersion (standard deviation and variance), Definition of probability, Mutually exclusive events, Independent events, Compound events, Conditional probability, Addition theorem.
- Number System: Decimal, binary, octal, and hexadecimal numbers and their conversion.
OJEE 2025 B.Pharm Syllabus - Biology (45 Questions)
Candidates can go through the syllabus 2025. The Biology section of OJEE question paper will contain questions from the topics mentioned below.
- Diversity of Plant Life: Five-kingdom system of classification with its merits and demerits. Structure, reproduction, and economic importance of Bacteria and Viruses. Life history of representative members of different plant groups: Spirogyra, Saccharomyces, Funaria, Dryopteris, Cycas.
- Morphology of Angiosperms: Normal and Modified roots, stems, and leaves, Inflorescence, Flower and its parts, Pollination, Fertilization, Fruits.
- Taxonomy of Flowering Plants: Principles and units of classification (species, genus, family) Binomial nomenclature, Studies of important families: Malvaceae, Fabaceae, Asteraceae, Brassicaceae, Liliaceae.
- Cell: Structure and functional Theory, Totipotency, Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cell, Structure of typical plant cell: Cell Wall, Cell Membrane, Cell Organelles (Plastids, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, Golgi bodies, Lysosomes, Peroxisomes). Important compounds of the cell: Structure and functions of water, amino acids, proteins, carbohydrates, and fats.Properties and chemical nature of enzymes. Mode of enzyme action.
- Continuity of Life: Cell division: Mitosis, Meiosis, and their significance, Mendel’s laws of inheritance: Monohybrid and Dihybrid cross, Incomplete dominance, Multipleallelism.
- Genetics Materials: Structure of nucleic acids. Evidence to establish ‘DNA as genetic material’ (Griffith and Avery’s experiment). concept of gene, Transcription, and translation in Prokaryotes. Regulation of gene expression – induction and repression. Recombinant DNA and Tissue culture technique: Recombinant DNA techniques and its significance. Genebank, Production of Transgenic plants with examples, Tissue culture technique.
- Compexities of Plant Life: Meristematic and tissues, Internal structures of dicot and monocot stems, roots and Isobilateral and Dorsiventral leaves, Normal secondary growth in dicot stem. Processes in plants: Diffusion, Osmosis, Plasmolysis, Imbibition, Absorption, and transport of water and minerals, Transpiration and its significance, Life energy, and ATP, Respiration, and Fermentation, Photosynthesis, Biological nitrogen fixation. Growth and development: Growth regulators – Physiological effects of Auxins, Gibberellin, Cytokinin, Ethylene, and Abscisic acid. Elementary idea of photoperiodism and vernalization. Plant movements (with special reference to geotropism and phototropism)
- Ecology: Man and environment, Ecological adaptations (Hydrophytes and Xerophytes), plant succession (Hydrosere, Xeresere), Structure and function of Ecosystem.
- Economic Botony: Economic importance of plants like Rice, Gram (green gram) Jute, Groundnut, Mango, Tulsi.
- Common Plant Diseases: Symptoms and control measures of the following plant diseases: Powdery mildew of peas, a Bacterial blight of rice, Mosaic disease of Papaya.
- Animal World: Definition, Scope, and branches of Zoology. Characteristics of living organisms (the elementary idea of metabolism, transfer of energy at a molecular level, open and closed system, homeostasis, growth & reproduction, adaptation, survival, and death). Classification (Artificial, Natural, Phylogenetic) Two-Kingdoms & Five-Kingdoms – their merits and demerits. Species concept, binomial nomenclature, scientific names of some common animals: Fishes – Rohi, Bakura, Mirikali, Kau. Amphibians – Frog, Toad. Reptiles – House Lizard, Garden Lizard, Crocodile, Turtle, Cobra, Krait. Birds – Fowl, Peacock, Pigeon, Crow. Mammals – Tiger, Elephant, Cat, Dog, Rabbit, and Man.
- Divesity of Animal Life: Introductory Concept: (1) concept of the body plan, symmetry, coelom, germ layers, homeothermic and poikilothermic animals. (2) Salient features of Non-chordate phyla with examples, General characters of chordates up to class levels with examples.
- Animal Morphology: Morphology of Paramecium, Sycon, Hydra Planaria, Ascaris, Earthworm, Cockroach, Pila, Starfish, Amphioxus, Bony fish, Cartilaginous fish, Frog, Calotes, Pigeon & Rabbit.
- Animal Hisology: Types – Epithelial, Connective (details about blood and lymph), Muscular & Nervous – Organs and Organ Systems.
- Animal Locomotion: Joints and Muscles in the movement of man, mechanism of muscle contraction, Disorders – Arthritis and Osteoporosis
- Animal Physiology: Animal Nutrition – Intracellular and Intercellular digestion, Digestive system of cockroach, Digestive system and process in human (ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation, and egestion) role of hormones indigestion, malnutrition and under-nutrition.
- Animal Respiration: Types of respiration (cutaneous, tracheal, bronchial and pulmonary), Structure and function of a respiratory system in man: Respiratory organs, mechanism of pulmonary respiration, pulmonary exchange of gas, transport of gases. Common respiratory disorders – prevention and cure.
- Animal Circlation: Open Circulation closed circulatory system in man, Structure of Heart, Cardiac Cycle, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Portal System, Coronary Circulation, Blood Pressure, Respiratory pigments, Blood groups (A B O & Rh), Blood Coagulation, Blood-related disorder – Hypertension, Atherosclerosis & Arteriosclerosis, Pacemaker.
- Animal Excretion: Types of Excretion (Ammonotelism, ureotelism, and uricotelism), Excretion in a cockroach, Excretion in human – Structure, and function of the kidney, Role of liver in excretion: Ornithine Cycle. Disorders related to excretion – kidney failure, dialysis, kidney transplantation, Role of ADH.
- Control and Co-ordination: The nervous system of cockroach, Nervous system of human – central, peripheral & autonomic, the transmission of nerve impulse, reflex action, sense organs (Eye and Ear).
- Human Endocrine System: Endocrine glands (Name, Location, Hormones and their functions), hormones as messengers and regulators, feedback controls, and hormonal disorders.
- Genetics: Mendelism, linkage, and crossing over, recombination, sex chromosomes, sex determination, sex-linked inheritance, chromosomal aberrations (structural).
- Animal Reproduction and Human Development: Types of reproduction – Asexual reproduction (Binary fission, multiple fission, budding), Sexual reproduction in human – male and female reproductive system, menstrual cycle.
- Human Development: Gametogenesis (spermatogenesis, oogenesis), fertilization, development up to 3 germ layers, the fate of germ layers, extraembryonic membranes, and structure and function of the placenta.
- Cellular Growth: Hormonal control of growth, Types of regeneration and mechanism (in Planaria), ageing (Senescence).
- Biology in Human Welfare: Common problems of adolescence (drugs, alcohol, and tobacco), social and moral implications, mental and addictive disorders, and risk of indiscriminate use of drugs and antibiotics.
- Biotechnology: Animal tissue culture, bio-war, biopiracy, cloning, and transgenic animals. Elementary idea - organ transplantations, immunity and immune disorders, vaccines and vaccination (recent advances).
- Modern Techniques in Diseases Diagnosis: Basic methods of estimation of haemoglobin, sugar, and urea in blood, ELISA, and WIDAL tests. Basic principles of ECG, EEG, CT SCAN, MRI, Ultra Sound and Endoscopy, DNA Finger Printing.Human Diseases: Types, Causes, diagnosis, prevention and treatments – AIDS, STD, Cancer, and Diabetes.
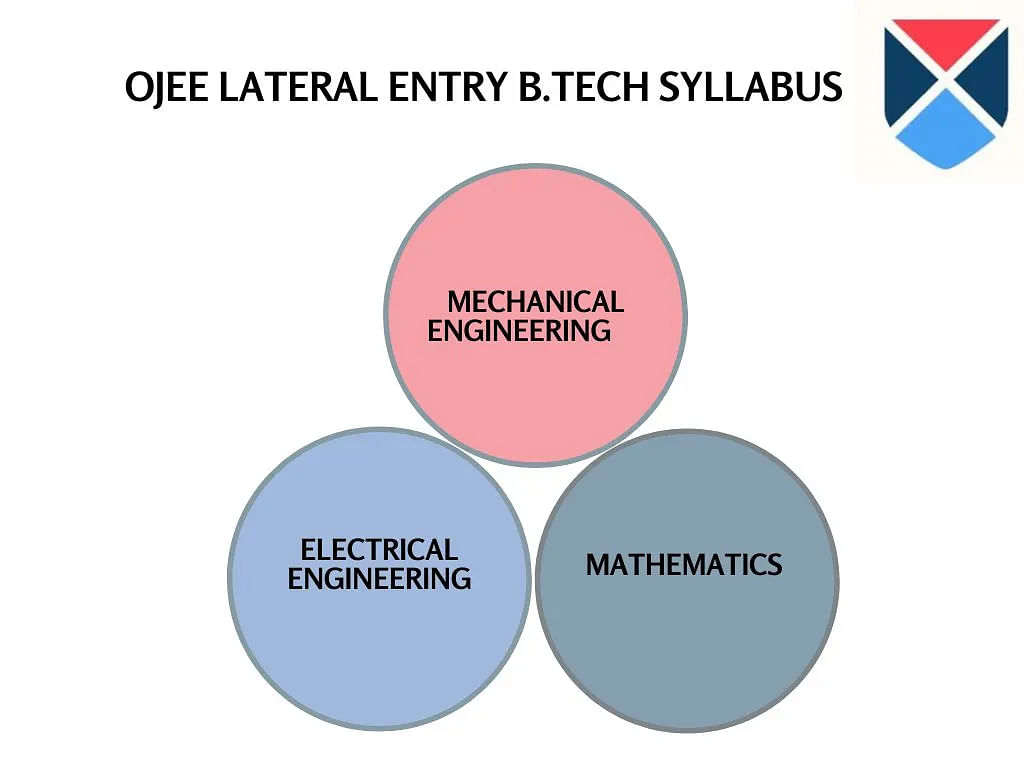
OJEE LE Syllabus 2025
The special examination contains three different sections which are a total of 120 objective-type questions. Candidates have to appear for OJEE Lateral Entry Diploma in two different shifts.
| Particulars | Details |
| First Shift | Engineering Mechanics and Electrical Engineering |
| Second Shift | Mathematics |
OJEE LE 2025 B.Tech Electrical Engineering Syllabus
Candidates can find the OJEE LE B.Tech Electrical Engineering detailed syllabus of various sections of the LE Diploma mentioned in the table below.
| Fundamentals | Wiring and Power building |
| A-C Theory | Measuring Instruments |
| Generation of Electrical Power | Storage Devices |
| Conversion Of Electrical Energy | - |
OJEE LE 2025 B.Tech Syllabus for Mathematics
The most important topics in OJEE B.Tech syllabus for the Mathematics of Lateral Entry course have been tabulated below. Candidates get a clear idea on B.Tech mathematics syllabus.
| Algebra | Calculus |
| Matrices and Determinants | Ordinary Differential Equation |
| Trigonometry | Co-ordinate Geometry Of Three Dimensions |
| Analytical Geometry | Statistics and Probability |
OJEE LE 2025 B.Tech Mechanical Syllabus
OJEE LE B.Tech mechanical syllabus given in topic-wise. The syllabus for mechanics of OJEE LE B.Tech Mechanical syllabus is tabulated below as per previous year syllabus for candidates references.
| Force Moments | Simple Lifting Machine |
| Centre of Gravity and Moment of Inertia | Simple stress and Strain |
| Friction | Dynamics |
OJEE Lateral Entry MCA Syllabus 2025
The OJEE LE MCA syllabus is given in topic-wise in the table below. The given topics are important in MCA syllabus as per pervious year syllabus.
| Logic | Sequence and Series |
|---|---|
| Algebra of Sets | Vectors |
| Number System | Differential Calculus |
| Determinants and Matrices | Integral calculus |
| Trigonometry | Differential Equations |
| Coordinate geometry of two dimensions | Probability and Statistics |
| Coordinate geometry of three dimensions | Number System |
| Quadratic Polynomials | - |
OJEE MCA Syllabus 2025
OJEE is also a gateway to the MCA course in various colleges in the state. Given below are the topics included in the Computer Application section as per the previous year syllabus.
- Introduction to Computer - C language
- Computer Arithmetic
The OJEE syllabus for MCA Mathematics is tabulated below.
| Logic | Sequence and Series |
| Algebra Of Sets | Vectors |
| Number System | Differential Calculus |
| Determinants and Matrices | Integral Calculus |
| Trigonometry | Differential Equations |
| C-ordinate Geometry of Two dimensions | Probability and Statistics |
| Coordinate Geometry of Three Dimensions | Number System |
| Quadratic Polynomial | - |
OJEE MBA Syllabus 2025
OJEE 2025 question paper for MBA will contain mainly 4 sections such as quantitative techniques, verbal reasoning and comprehension, analytical reasoning, general knowledge. The topics covered under each of the sections of OJEE MBA syllabus have been tabulated below.
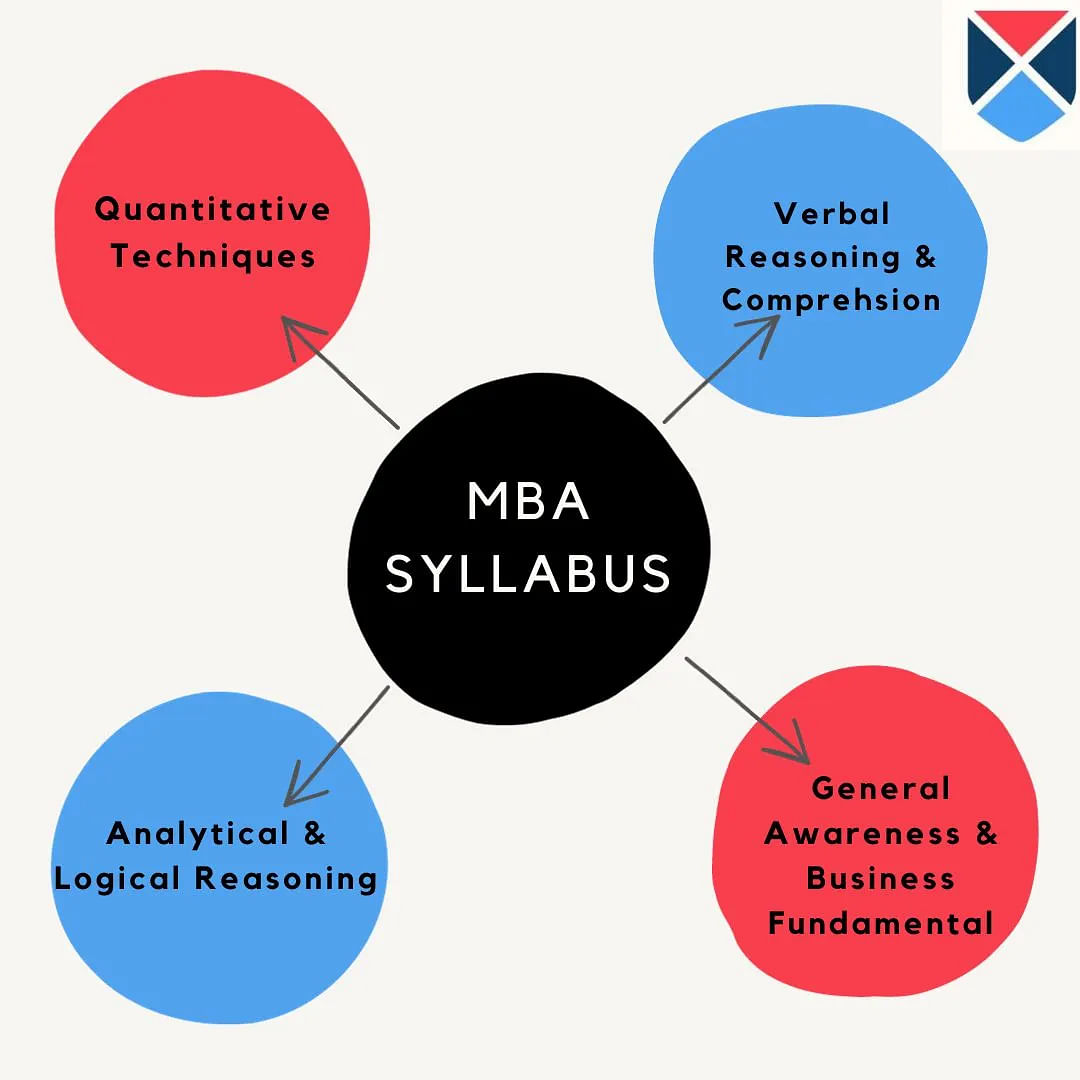
Section 1: OJEE Quantitative Techniques Syllabus
The topics under the quantitative techniques are as follows. The topics are percribed as per the previous year syllabus.
| Quantitative Techniques Syllabus | |
| Arithmetic | Geometry |
| Percentage | Average |
| Number systems | Profit and Loss |
| Ratio and Proportion | Time, speed and distance |
| Mensuration | Quadratic equation |
| Trigonometry | Probability |
Section 2: OJEE Analytical and Logical Reasoning
The second section of OJEE MBA syllabus is of Analytical and Logical Reasoning, the topics prescribed as per the previous year syllabus under this section are as follows.
| Analytical and Logical Reasoning Syllabus | |
| Data Interpretation | Codes |
| Time and Sequence | Blood Relations |
| Series | Statements and conclusions |
Section 3: OJEE Verbal Reasoning Syllabus and Comprehension
OJEE MBA syllabus for Verbal Reasoning and Comprehension is given in the table below as per the previous year syllabus.
| Verbal Reasoning and Comprehension Syllabus | |
| Sequence of words | Passages |
| Fill in the blanks | Analogy |
| Sentence Completion | Word puzzles |
| Antonyms | Synonyms |
| Grammar | Vocabulary |
| Syllogisms | Idioms |
| Para Jumbles | Action, cause and effect |
Section 4: General Awareness and Business Fundamentals
This section of OJEE MBA syllabus will test the candidate's general awareness and business fundamentals. The topics of this section of th OJEE MBA syllabus has been tabulated below as per the previous year syllabus.
| General Awareness and Business Fundamentals Syllabus | |
| Codes in Data Communication, Data Structuring | Terminals, Networking |
| Operating Systems | Computer Arithmetics |
| Software developments and inventions | Basic fundamentals of PC, Hardware |
| General Awareness regarding National Stock Exchanges, Budget | Economics, policies |
| Current Affairs and Events | Medicine, Science & Technology related research, developments |
| Corporate awards | International events |
| Political events | Financial and budget related topics |
| Sports events | Cinema Awards, National Awards |
OJEE PGAT Syllabus 2025
Details for PGAT OJEE are given below based on the previous year analysis. OJEE PGAT 2025 is an offline exam that is conducted for a two-hour duration. The question paper will have a total of 90 questions. The exam is conducted for M.Tech/ M.Arch program. It is conducted during Shift III of OJEE.
Note: Candidates have to answer questions based on the following topics:
Analytical and Logical Reasoning- questions are based on the usage of systematic series based on mathematical procedures to conclude. Questions are based on judgments, based on statements.
Engineering Mathematics- there are questions based on various mathematical methods that are used in the engineering industry.
OJEE Important Topics 2025
The important topics for OJEE, which candidates need to study and revise, are tabulated below. Candidates are advised to read these topics thoroughly before going for the exam.
- Quantitative Techniques: Arithmetic, percentage, number systems, ratio proportion, and mensuration.
- General Awareness and Business Fundamentals: Current affairs, sports events, awards, computer arithmetic.
- Verbal Reasoning and Comprehension: Grammer, comprehension, synonyms, antonyms, error spotting.
OJEE Subject-wise Weightage 2025
Every subject in OJEE has a defined number of questions from a particular subject. Understanding this will help the candidates in understanding the exam pattern which will be helpful for them in their exams. The subject wise weightage for OJEE 2025 is tabulated below.
| Subject | Weightage |
| Physics (Compulsory) | 45 |
| Chemistry (Compulsory) | 45 |
| Either Mathematics or Biology | 45 |
OJEE Subject-wise Weightage for B.Tech and B.Tech Lateral Entry
As per the pervious year syllabus the subject wise weightage for B.Tech and B.Tech Lateral Entry for OJEE 2025 is tabulated below.
| Subject | Weightage |
| Basic Electrical Engineering | 40 |
| Engineering Mathematics | 40 |
| Engineering Mechanics | 40 |
OJEE Marking Scheme 2025
The Odisha Joint Entrance Exam has prescribed the OJEE exam marking scheme 2025. The marking scheme has been tabulated below.
|
OJEE Session 2025 |
Number of Questions |
Duration |
Marks Per Questions |
|
OJEE Session 1 |
120 |
2 |
4 |
|
OJEE Session 2 |
60-90 |
1 |
4 |
|
OJEE Session 3 (Slot 1) |
60 |
1 |
4 |
|
OJEE Sesssion 3 (Slot 2) |
60-120 |
2 |
4 |
FAQs on OJEE Syllabus
Q: How should I start preparing for OJEE 2025 exam?
Candidates require at least a minimum of six months for complete preparation. To begin with, understand the OJEE syllabus and exam pattern. Completely prepare the syllabus and start practising mock test papers and previous year's papers to understand the weak and strong areas in the subjects.
Q: Which topics are important in quantitative techniques?
In quantitative techniques, the most important topics to be referred to are Arithmetic, Percentage, Number systems, Ratio and Proportion, and Mensuration.
Q: What is the subject wise weightage in OJEE exam?
The physics and chemistry papers are mandatory, and each carries 45 marks, while mathematics and biology are optional subjects. One should choose any one among those two, and each carries 45 marks.
Q: Is OJEE syllabus difficult?
In terms of difficulty level the OJEE syllaubs is easy to moderate.
Q: What are the main topics of OJEE Chemistry?
Some Chemistry important topics for OJEE Preparation are Solid State, Liquid State, Solutions, Gaseous State, Structure of Atoms and Molecules etc.