TS Intermediate Syllabus 2026: Download Latest and Revised TS Inter Syllabus PDF with Subject-wise
Table of Contents
The TS board releases the TS Intermediate syllabus 2026 for Science, Commerce, and Arts on its official website. The TS Inter 2nd year syllabus 2026 is divided mainly into three streams, i.e., Languages, Science, and Humanities.
The TS Intermediate 2026 syllabus includes the important topics and marks distribution of all the subjects. Not all subjects in the Intermediate syllabus are mandatory, and a few subjects are elective. Students of the TS Intermediate Exam 2026 can choose the streams according to their area of interest.
Also Read: TS Intermediate Time Table 2026
TS Intermediate Syllabus 2026 Stream-wise
TS Inter syllabus is divided mainly into three streams - Languages, Science, and Humanities. Not all subjects are compulsory as given in the TS Intermediate syllabus 2026. Candidates can go through the stream-wise TS Inter syllabus for 1st and 2nd year from the given table, check all core subjects, and prepare for exams.
| Stream | Major Subjects |
| Language | English |
| Telugu | |
| Hindi | |
| Sanskrit | |
| Arabic | |
| Tamil | |
| Oria | |
| French | |
| Urdu | |
| Kannada | |
| Marathi | |
| Science | Mathematics |
| Physics | |
| Chemistry | |
| Botany | |
| Zoology | |
| Humanities | Commerce |
| Economics | |
| Civics | |
| History | |
| Psychology | |
| Geography | |
| Geology | |
| Logic | |
| Public Administration | |
| Sociology | |
| Music |
TS Intermediate Syllabus 2026 For 1st Year
TS Inter syllabus for 1st year consists of three streams, i.e., Language, Science, and Humanities. English subject is mandatory for all the candidates. Candidates can go through different streams, study the TS Intermediate syllabus 2026 thoroughly, and prepare accordingly.
TS Intermediate Syllabus for 1st-Year Language
TS Intermediate 1st year language consists of Telugu, Hindi, Arab, French, etc. Candidates need to look over the intermediate 1st-year syllabus below and prepare accordingly for the exam.
TS Intermediate Syllabus for 1st-Year French Language
The French language has different units under them which include Prose and Poetry. Candidates can check the unit-wise TS Inter 2nd year deleted syllabus 2026 for the French language from the following table:
| Unit | Unit Name |
| I. Prose | École de français, Paris: Au secrétariat, Autour de l’école, La vie quotidienne, Une randonnée |
| II. Poetry | La Semaine, À Paris, Les quatre saisons |
| III. Lexique | Se présenter, Présenter quelqu’un, Les Nationalités, Les Professions, Les questions/ réponses, Au téléphone : dire au revoir, S’orienter, Rédiger un emploi du temps, Communiquer en classes, Fixer un rendez-vous au téléphone, Fixer l’heure, l’endroit, pour une réunion, Parler des prix, Dire l’heure, Faire les projets pour la soirée, Demander/Indiquer le chemin, Demander la direction, Donner les indications, Le Corps |
| IV. Culture/Civilisation | La France, Papiers d’identité, L’école, Les études, Les différentes matières, Les jours, la semaine, Paris, Versailles, Le billet de bateau-mouche, La tour Eiffel, La SNCF, Le Calendrier, Le mois, l’année, Les Parfums, Les Fromages, Les Vins, Les Saisons, Les Fêtes, La Météo, La Bretagne, La Bourgogne, La Provence, Cote d’Azur |
| V. Grammaire | L’alphabet, Les Chiffres 0 à 50, L’article défini, indéfini, Les présentateurs : C’est/ Ce sont, Quelques verbes, Pronom tonique, Les Prépositions, Les Pluriels, L’article contracte, Le présentateur « il y a », Quelques verbes, Les chiffres de 50 à l’ infini, La négation, Le pronom ‘on’, Les présentateurs « voici, voilà », Le pronom tonique, Le Futur proche, L’interrogation, Les infinitifs |
TS Intermediate Syllabus for 1st Year Science
The TS Intermediate 1st year science syllabus consists of Chemistry, Zoology, Botany, Physics, and Mathematics. Candidates can go through the following section to learn about the TS Intermediate 2026 syllabus for Science in detail.
TS Intermediate Syllabus for 1st Year Chemistry
The Chemistry syllabus includes chapters like Atomic Structure, Classification of Elements and Periodicity of Properties, Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure, State of Matter: Gases and Liquids, Thermodynamics, etc. Find below the TS Intermediate 1st year Chemistry syllabus for the 2026 academic year:
| Unit | Topics |
| 1. Atomic Structure | Developments leading to Bohr’s model of the atom and Bohr’s model of a hydrogen atom, Dual Behaviour of matter (Broglie’s equation), Heisenberg’s Uncertainty principle |
| Quantum numbers, energies of orbitals - filling of orbitals in an atom: Aufbau Principle, Pauli’s exclusion principle and Hund’s rule of maximum, multiplicity - electronic configuration of atoms-stability of filled and half filled subshells | |
| 2. Classification of Elements and Periodicity of Properties | Modern periodic law and the present form of the periodic table, Nomenclature of elements with atomic numbers greater than 100, Electronic configuration of elements, and the periodic table |
| Electronic configuration and types of elements s,p,d, and f blocks, Periodic trends in properties of elements -atomic radii, ionic radii, inert gas radii, Ionization, enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy, electronegativity, valency | |
| 3. Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure | Kossel – Lewis approach to chemical bonding, Ionic or electrovalent bond parameters, VSEPR theory: predicting the geometry of simple molecules |
| Valence Bond Theory, Hybridisation, Coordinate bond definition with examples, Molecular orbital theory – bonding in some homonuclear diatomic molecules, Hydrogen bonding | |
| 4. State of Matter: Gases and Liquids | Intermolecular forces, Thermal energy, Intermolecular forces Vs thermal interactions Gaseous State, Gas Laws, the Ideal gas equationGraham's Law of diffusion, Dalton’s law of partial pressures |
| Kinetic molecular theory of gases, Kinetic gas equation of an ideal gas (No derivation) – deduction of gas laws from the kinetic gas equation | |
| The behavior of real gases: deviation from ideal gas behavior – compressibility factor Vs pressure diagrams of real gases | |
| 5. Stoichiometry | Importance of Chemistry - Some basics |
| Atomic and molecular massesMole concept and molar mass concept of equivalent weight | |
| Percentage composition of compounds and calculations of empirical and molecular formulas of compounds | |
| Stoichiometry and stoichiometric calculations | |
| Redox reactions, Oxidation, Number Concept | |
| Types of redox reactions, Balancing of redox reactions, Oxidation, Number method of reaction (ion-electron) method | |
| 6. Thermodynamics | Thermodynamic terms, Work Enthalpy – Extensive and intensive properties |
| Enthalpies for different types of reactions | |
| Spontaneity | |
| Gibbs energy change and equilibrium | |
| Absolute Entropy and the third law of thermodynamics | |
| 7. Chemical Equilibrium and Acid Bases | Equilibrium in the physical process, Equilibrium in chemical process dynamic equilibrium, Law of chemical equilibrium - law of mass action and equilibrium constant |
| Homogeneous equilibria constant in the gaseous system, the relation between Kp & Kc, Heterogeneous equilibria | |
| Applications of the equilibrium constant, Factors affecting Equilibria- Le-Chatelier’s principle application to the industrial synthesis of ammonia and sulfur trioxideIonic equilibrium in solutions | |
| Acids and bases and salts – Arrhenius, Bronsted – Lowry and Lewis concepts of acids and basesBuffer solutions of buffer solution - preparation of acidic buffer, Solubility equilibria of sparingly soluble salt solubility product constant, common ion effect on solubility of ionic salts | |
| 8. Hydrogen and its Compounds | Position of hydrogen in the periodic tableDihydrogen-occurrence and isotopes |
| Hydrides: ionic, covalent, and non-stoichiometric hydridesPhysical and chemical properties of water, heavy water, Hydrogen as a fuel | |
| 9. s - Block Elements - Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals | Group I Elements: Alkali metals, electronic configurations; atomic and ionic radii, ionization enthalpy, hydration enthalpy, physical properties, chemical properties, uses, General characteristics of the compounds of the Alkali metals: oxides, halides, salts of oxyacids |
| General characteristics of compounds of the alkaline earth metalsAnomalous behavior of beryllium; its diagonal relationship with aluminum | |
| Anomalous properties of Lithium: Alkaline earth metals, electronic configuration; ionization enthalpy; hydration enthalpy; physical properties; chemical properties; uses | |
| 10. p- Block Elements: Group-13 Boron Family | General introduction – electronic configuration, atomic radii, ionization, enthalpy, electronegativity; physical and chemical properties |
| Important trends and anomalous properties of boron | |
| 11. p- Block Elements: Group-14 Carbon Family | General introduction - electronic configuration, atomic and covalent radii, ionization enthalpy, electronegativity; physical and chemical properties |
| Important trends and anomalous properties of carbon, Allotropes of carbon, Uses of carbon | |
| 12. Environmental Chemistry | NIL |
| 13. Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques Hydrocarbons | General introduction |
| Tetravalency of Carbon: shapes of organic compoundsStructural representations of organic compounds, Classification of organic compounds, Nomenclature of organic compounds | |
| IsomerismFundamental concepts in organic reaction mechanisms | |
| HYDROCARBONS- Classification of hydrocarbons | |
| Alkanes – nomenclature, isomerism (structural and conformations of Ethane only)Preparation and properties of Alkanes | |
| Alkenes: nomenclature, the structure of Ethene, isomerism (structural and geometrical), Methods of preparation of Alkenes, Physical and chemical properties of Alkenes | |
| Alkynes – nomenclature and isomerism, Structure of Acetylene, Methods of preparation of Acetylene, Physical properties, Chemical reactions of Acetylene | |
| Aromatic Hydrocarbons: nomenclature and isomeric structure of Benzene, Resonance, and Aromaticity, Preparation of benzene, Physical and chemical properties of Benzene, Directive influence of functional groups in monosubstituted Benzene, Carcinogenicity, and Toxicity |
TS Intermediate Syllabus for 1st Year Mathematics
The topics are mentioned in the table below for candidates to practice accordingly. Find below the TS Intermediate Mathematics syllabus for the academic year 2024:
| Unit | Unit Name |
| I. Functions | Ordered Pairs, Types of Functions, Real valued functions (Domain, Range, and Inverse) |
| III. Matrices | 3.1: Types of Matrices, 3.2: Scalar multiple of a Matrix and Multiplication of Matrices, 3.3: Transpose of a Matrix, 3.4.1 to 3.4.7: Determinants, 3.5: Adjoint and inverse of a matrix, 3.7:solutions of simultaneous linear equations, Cramer's Rule Matrix inversion method |
| IV. Addition of Vectors | Complete Chapter |
| V. Product of Vectors | Introduction, 5.1: Scalar or Dot product of two, Vectors -Geometrical, 5.2: Properties of the dot product, 5.3: Expression for scalar (Dot) Product, Angle between Vectors, 5.4: Geometrical Vector methods |
| 5.5: Vector Equation of plane - normal form, 5.6: Angle between two planes, 5.7: Vector Product (cross product) of two vectors and properties, 5.8: Vector product in (i, j, k) system, 5.9: Vector Areas, 5.10: Scalar Triple product | |
| VI. Trigonometric Ratios upto Transformations |
Compete Chapter |
| IX. Hyperbolic Functions | Definition of Hyperbolic, Functions and Graphs, Addition formulas of Hyperbolic functions |
| X. Properties of Triangles | Complete Chapter |
TS Intermediate 1st Year Botany Syllabus
The botany syllabus consists of chapters like Plant Physiology, Microbiology, Genetics, Molecular Biology, Biotechnology, etc. Find below the TS Inter 1st year Botany syllabus:
| Unit | Unit Name |
| UNIT I: Plant Physiology | Transport in Plants, Mineral Nutrition Methods, Enzymes Chemical Reactions, Photosynthesis in Higher Plants, Respiration of Plants, Plant Growth and Development |
| UNIT II: Microbiology | Bacteria, Viruses |
| UNIT III: Genetics | Principles of Inheritance and Variation |
| UNIT IV: Molecular Biology | Molecular Basis of Inheritance |
| UNIT V: Biotechnology | Principles and Processes of Biotechnology, Biotechnology and its Applications |
| UNIT VI: Plants, Microbes, and Human Welfare | Strategies for enhancement in food production, Microbes in Human Welfare |
TS Intermediate Syllabus for 1st Year Humanities
TS Inter syllabus for 1st year humanities consists of economics, history, political science, etc. Candidates can go through the TS Intermediate 2026 syllabus from the given below sections and prepare accordingly.
TS Intermediate Syllabus for 1st Year Economics
The TS Inter syllabus for Economics 1st year has different units in it. Some of the units include topics like Introduction to Economics, Theories of Consumer Behavior, Product Analysis, Market Analysis, etc. Find below the TS Intermediate 2026 syllabus for Economics:
| Unit | Unit Name |
| I. Introduction to Economics | 1.1 Definitions of Economics, 1.2 Fundamental Problems of an Economy, 1.3 Nature and Scope of Economics, 1.4 Micro Economics and Macro Economics, 1.6 Basic Concepts of Economics |
| II. Theories of Consumer Behavior | 2.1 Utility, 2.2 Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility, 2.4 Shortcomings of Utility Analysis, 2.5 Indifference Curve Analysis |
| III. Product Analysis | 4.1 Concept of Production and Factors of Production, 4.2 Production Function, 4.3 Law of Variable Proportions, 4.4 Law of Returns to Scale, 4.5 Economies of Scale, 4.7 Cost Analysis, 4.8 Revenue Analysis |
| IV. Market Analysis | 5.1 Markets: Meaning and Classification, 5.2 Perfect Competition: Meaning, Characteristics, and, Price Determination, 5.3 Imperfect Competition: Monopoly, Comparison between Perfect Competition and Monopoly, Monopolistic Competition, Oligopoly, and Duopoly (except 5.3.2, 5.3.3 & 5.3.4) |
| V. Theories of Distribution | 6.4 Rent: Concepts and The Ricardian Theory of Rent, 6.5 Wages: Concepts and Types, 6.6 Interest: Concepts, 6.7 Profits: Concepts |
| VI. National Income Analysis | 7.1 Definitions of National Income, 7.2 Determining Factors of National Income, 7.3 Concepts of National Income, 7.4 Components of National Income, 7.5 Measurement of National Income: Methods, Difficulties and Importance, 7.6 Estimation of National Income in India |
| VII. Theories of Employment and Public Finance | 8.2 Keynesian Theory of Income and Employment, 8.3 Public Finance, 8.4 Centre-State Financial Relations (except 8.4.2), 8.5 Budget |
TS Intermediate Syllabus for 1st-Year Geography
The geography syllabus is divided into two sections that include theory and practical work. Find below the TS Intermediate 2026 syllabus for Geography:
| Unit | Unit Name |
| Part A - Fundamentals of Physical Geography | |
| I . Geography as a Discipline | Geography as an integrating discipline, Branches of Geography: Physical, Geography and Human Geography |
| II. The Earth | Interior of the earth; Wegener's continental drift theory and plate tectonics, Earthquakes and volcanoes: causes, types, and effects |
| III. Landforms | Rocks: major types of rocks and their characteristics, Geomorphic processes: weathering; mass wasting; erosion, and deposition |
| IV. Climate | Elements of weather and climate, Atmosphere - composition, and structure; Insolation: heating and cooling of the atmosphere (conduction, convection, terrestrial radiation, and advection) |
| Temperature- factors controlling the temperature, distribution of temperature- horizontal and vertical, Inversion of temperature, Pressure-factors & distribution, pressure belts, winds-planetary, seasonal and local, Rainfall-types and world distribution | |
| V. Oceans: Basics of Oceanography | Ocean: distribution of temperature and salinity, Movement of ocean water waves, tides, and currents; submarine reliefs, Ocean pollution |
| VI. Life on Earth | Biosphere-importance of plants and other organisms, Ecosystem and ecological balance, Biodiversity and Conservation |
| VII. Hazards and Disasters | Causes, Consequences, and Management Floods, Cloudbursts; Droughts: Tsunami, Cyclones: features and impact |
| Part B - Practical Work | |
| I. Fundamentals of Maps | Geospatial data, Concept of Geographical data matrix, Point, line, area data, Maps- types; scales-types; construction of simple linear scale, measuring distance, finding direction and use of symbols |
| II. Topographic and Weather Maps | Study of topographic maps (1:50,000 or 1:25,000 Survey of India maps), contour cross-section and identification of landforms - slopes, hills, valleys, waterfall, cliffs, and distribution of settlements, Use of weather instruments: thermometer, wet and dry-bulb thermometer, barometer, wind vane, and rain gauge |
TS Intermediate Syllabus 2026: 2nd Year
TS Inter syllabus 2026 for 2nd year consists of three streams, i.e., Language, Science, and Humanities. English subject is mandatory for all the candidates. Candidates can go through different streams, study the TS Inter syllabus thoroughly, and prepare accordingly.
The TS Intermediate 2026 syllabus for 2nd year is given below for all subjects.
TS Intermediate Syllabus 2026 for 2nd Year Language
TS Intermediate second language consists of different optional languages such as French, Urdu, Arab, Hindi, Sanskrit, Tamil, Orio, etc. Candidates can go through the TS Inter syllabus for the language that they choose.
TS Intermediate Syllabus 2026 for 2nd Year French
The Inter syllabus for French consists of 5 main units. The units include Prose, Poetry, Lexique, Culture, and Grammaire. Find below the TS Inter syllabus for 2nd year for French.
| Unit | Unit Name |
| I. Prose | Préparatifs d’un voyage, À Lausanne, Un dimanche à la montage, Il était un fois |
| II. Poetry | Pour toi mon amour, Expressions Québécoises, Une chanson pomme, Mon pays |
| III. Lexique | Donner des informations personnelles, Exprimer des faits futures, Le voyage, Vocabulaire de la gare et du train, Exprimer l’ignorance, Exprimer la certitude, Indiquer les éléments du passé, Raconter un événement, Ecrire une lettre personnelle, Types de logement, Raconter une journée, S’informer sur des prix, sur la taille |
| L’échange, Vêtements, équipements de ski, Techniques de sk, Parler d’autrefois, Décrire des habitudes présentes et passées, Inviter quelqu’un, Accepter, refuser les invitations, Parler de l’avenir proche ou lointain, Donner un conseil, La Famille | |
| IV. Culture/Civilisation | Billets de train, La Suisse, Plurilinguisme et multi culturalité de la Suisse, Passer la frontière, Les petites annonces, Les Chiffres Suisses, Le Chalet, Le Lac Léman, Les sports d’hiver, Le Gruyère, Les montagnes, Quelques organisations internationales à Genève, Le château de Chillon |
| V. Grammaire | Le Passé Récent, Le Futur, Les adjectifs possessifs, Les adjectifs démonstratifs, Quelques verbes, La Comparaison, Il faut, Le Passé Composé, Les nombres ordinaux, Les compléments de temps, Les formes de négation, Quelques verbes, Le superlatif |
| Le pronom interrogatif, Le Passé Composé avec la négation, l’interrogation, Les connecteurs de temps, Quelques verbes, L’imparfait |
TS Intermediate Syllabus for 2nd Year Science
Candidates can go through the TS Inter syllabus for Science consists of Chemistry, Zoology, Botany, Physics, and Mathematics. The TS Intermediate 2026 syllabus for the Science stream is provided in the following sections.
TS Intermediate Syllabus for 2nd year Chemistry
Candidates should go through all thirteen units of the TS Inter syllabus for Chemistry with each topic clearly and prepare for exams. Some of the topics include Solid State, Solutions, Electrochemistry and Chemical Kinetics, Surface Chemistry, p-block Elements, Group 15- Elements, d and f-block Elements and Coordination Compounds, etc.
The topics covered in the Chemistry subjects according to the TS Intermediate 2026 syllabus are given below:
| Unit | Unit Name |
| I. Solid State | General characteristics of solids, Amorphous and crystalline solids, Classification of crystalline solids, Probing the structure of solids: X-ray Crystallography |
| Crystal lattices, and unit cells, Number of atoms in a Unit cell, Close packed structures, Packing efficiency, Calculations involving unit cell dimensions, Imperfections in solids | |
| II. Solutions | Types of Solutions, Expressing concentration of solutions, Solubility, Vapour pressure of liquid solutions |
| Ideal and non-ideal solutions, Colligative properties, and determination of molar mass | |
| III. Electrochemistry and Chemical Kinetics | Nernst equation, Conductance of electrolytic solutions, Applications of Kohlrausch’s Law, Chemical kinetics, Electrolysis, Rate of a chemical reaction, Factors influencing the rate of a reaction |
| Integrated rate equations, Pseudo first-order reaction, Temperature dependence of the rate of a reaction | |
| IV. Surface Chemistry | Adsorption and Absorption, Colloids, Classification of Colloids, Colloids Around Us- application of colloids. |
| VI. p-Block Elemennts, Group 15- Elements | Introduction-Occurance, Dinitrogen, Compounds of Nitrogen-preparation and properties of ammonia, Oxides of Nitrogen, Preparation, and properties of Nitric acid, Phosphorous-allotropic forms |
| GROUP-16 Elements, Occurance-Introduction, Dioxygen-preparation, Simple oxides, Ozone-preparation, properties, Sulphur-allotropic forms, Sulphur dioxide-preparation, Oxoacids of sulfur, Sulphuric acid properties and uses | |
| GROUP-17 Elements, Occurance-Introduction, Chlorine-preparation, properties and uses, Hydrogen chloride: preparation, properties, use, Oxoacids of halogens, Interhalogen compounds | |
| GROUP-18 Elements, Introduction-Occurrence, electronic configuration, ionization enthalpy, atomic radii, electron gain enthalpy, physical and chemical properties | |
| VII. d and f-Block Elements and Coordination Compounds | Position in the periodic table, Electronic configuration of the d-block elements, General properties of the transition elements |
| Werner’s theory of coordination compounds, Definitions of some terms used in coordination compounds, Nomenclature of coordination compounds, Isomerism in coordination compounds | |
| Bonding in coordination compounds, Bonding in metal carbonyls, Stability of coordination compounds, Importance and applications of coordination compounds | |
| IX. Biomolecules | Carbohydrates: Classification of carbohydrates, monosaccharides, Amino acids, and Proteins, Nucleic acids |
| XI. Halo Alkanes and Halo Arenes | Classification and nomenclature, Nature of C-X bond |
| Methods of preparation: alkyl and aryl halides, Physical properties of alkyl and aryl halides, Chemical reactions of alkyl and aryl halides. | |
| XII. OrganicCompoundsContaining C, HAND O | Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers - classification, Nomenclature of alcohols, phenols and ethers, Structures of hydroxyl, ether functional groups |
| Methods of preparation of alcohol, Physical properties of alcohols and phenols, Chemical reactions of alcohols and phenol | |
| Ethers–Methods of preparation, Physical properties, and Chemical reactions Aldehydes and Ketones | |
| Nomenclature and structure of carbonyl group, Preparation of aldehydes and ketones, Physical properties of aldehydes and ketones, Chemical reactions of aldehydes and ketones, Uses of aldehydes and ketones | |
| Carboxylic Acids, Nomenclature and structure of carboxyl group, Methods of preparation of carboxylic acids, Physical properties of carboxylic acids, Chemical reactions of carboxylic acids, Uses of carboxylic acids | |
| XIII. Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen | Amines, Structure of amines, Classification, Nomenclature, Preparation of amines, Physical properties of amines, Chemical reactions of amines |
TS Intermediate Syllabus for 2nd Year Mathematics
Mathematics is a scoring subject if the concept is well understood. Find below the TS Inter syllabus for 2nd year Mathematics:
| Unit | Unit Name |
| I. Complex Numbers | Introduction |
| Complex number as an Ordered pair of real numbers Fundamental operations | |
| Representation of Complex numbers in the form a+ib | |
| II. De Moivre's Theorem | Up to exercise 2(b) section-I and related examples |
| III. Quadratic Expressions | Introduction |
| Quadratic expressions, equations in one variable | |
| Sign of quadratic expressions, change of signs, and maximum, and minimum values | |
| IV. Theory of Equations | Complete Chapter |
| V. Permutations and Combinations | Introduction |
| Fundamental Principles of Counting - Linear and Circular permutations | |
| Permutation of dissimilar things at a time Combinations | |
| Exercise 5(e) Section I and II Related Problems | |
| VI. Binomial Theorem | Introduction |
| Exercise 6(a) Section I and Section II up to 4th problem and related examples | |
| Exercise 6(b) Section I and related examples Exercise 6(c) Deleted | |
| VII. Partial Fractions | Up to 7(c) exercise |
| VIII. Measures of Dispersion | Introduction |
| Range | |
| Mean Deviation for ungrouped data | |
| Exercise 8(a) Section I (problems 1 and 2) | |
| IX. Probability | Introduction |
| Random experiments and events | |
| The classical definition of probability, axiomatic approach, and addition theorem on probability | |
| Independent and dependent events, conditional probability, multiplication theorem and problems and related examples | |
| X. Random Variables andProbability Distribution | Introduction |
| Random Variables | |
| Theoretical Discrete Distributions - Binomial and Poisson Distributions |
TS Intermediate Syllabus for 2nd year Humanities
TS Inter syllabus 2026 for 2nd year Humanities stream consists of subjects like Economics, Geography, Accountancy, Statistics, Political Science, etc. Candidates can go through the following sections containing some TS Intermediate 2026 syllabus of the core subjects under the Humanities stream.
TS Intermediate Syllabus for 2nd year Economics
TS Inter syllabus for Economics 2nd year includes topics like Economic Growth and Economic Development, Population and Human Resource Development, National Income, Poverty and Unemployment, Planning and Environment, Agricultural Sector, Industrial Sector, etc.
Find below the TS Intermediate 2nd year Economics syllabus for the academic year 2024.
|
Unit |
Unit Name |
|
I. Economic Growth and Economic Development |
Introduction |
|
Concepts of Economic Growth and Economic Development |
|
|
Objectives of Economic Development |
|
|
Indicators of Economic Development (Except 1.3.4, 1.3.6, 1.3.7 ) |
|
|
Factors Hindering Economic Development |
|
|
Factors Promoting Economic Development |
|
|
Characteristics of Developing Economies with Special Reference to India |
|
|
II. Population and Human Resource Development |
Introduction |
|
Theory of Demographic Transition |
|
|
Demographic Features of the Indian Population |
|
|
Concept of Population Explosion: Causes for the rapid growth of population in India |
|
|
Occupational Distribution of Population in India |
|
|
Human Resource Development: Concept and Importance |
|
|
Role of Education in Economic Development and Education in India |
|
|
Role of Health in Economic Development and Health in India |
|
|
Human Development Index (Except 2.9.1 & 2.9.2) |
|
|
III. National Income, Poverty, and Unemployment |
Introduction |
|
A Backdrop to National Income Studies |
|
|
trends in National Income and Per Capita Income in India |
|
|
Sectoral Contribution to National Income |
|
|
Inequalities in the distribution of income and wealth Causes Remedial Measures |
|
|
Poverty in India: Concept, Incidence, Causes and Consequences |
|
|
Unemployment in India: Concepts, Types, Concepts, Causes and Consequences and Redial Measures |
|
|
Poverty elevation and employment generation programs in India |
|
|
IV. Planning and Environment |
Introduction |
|
Part-A: Planning |
|
|
Concept, Importance of Planning (except 4.1.2) |
|
|
Major Objectives of Five-Year Plans in India |
|
|
Review of Five-Year Plans |
|
|
NITI Aayog |
|
|
Part –B: Environment |
|
|
Concept of environment-Importance of the Environment in Economic Development (Except:4.7.2) |
|
|
Concepts of Eco-System, Pollution, and Environmental Degradation, Except 4.8.3(II) |
|
|
Need for environmental protection |
|
|
Sustainable Development |
|
|
V. Agricultural Sector |
Introduction |
|
Importance and Growth of Agriculture in the Indian Economy |
|
|
Causes for Low Productivity in Agriculture and Measures to Improve Agricultural Productivity in India |
|
|
Land Reforms in India |
|
|
Green Revolution in India and its Impact on Indian Economy 137 5.5 Agricultural Credit and Rural Indebtedness (Except 5.5.2) |
|
|
VI. Industrial Sector |
Industrial Sector - Introduction |
|
Structure of Indian Industry |
|
|
Growth and Pattern of Industrial Development in India (Except 6.2.5) |
|
|
Industrial Backwardness |
|
|
Industrial Policy Resolutions (Except 6.4.3, 6.4.4 ) |
|
|
Special Economic Zones (SEZ) |
|
|
Small Scale Industries' role, problems, and issues of sickness |
|
|
Industrial Finance (Except 6.11.1 (G) |
|
|
VII. Tertiary Sector |
Introduction |
|
Tertiary Sector in India: Components and importance 7.2 Infrastructure development in India |
|
|
Transport Sector in India |
|
|
Energy Sector |
|
|
Communications |
|
|
Information Technology |
|
|
Science and Technology |
|
|
Insurance |
|
|
VIII. New Economic Reforms and Foreign Sector |
Introduction |
|
New Economic reforms |
|
|
Liberalization |
|
|
Privatization and Disinvestment |
|
|
Globalization |
|
|
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) |
|
|
Impact of Economic Reforms on the Indian Economy |
|
|
Balance of Payments and Balance of Trade with special reference to India |
|
|
Role of International Trade in the Indian Economy |
|
|
IX. Economic Features of Telangana |
Introduction |
|
Structure of Telangana State |
|
|
Economic features of Telangana: Sectors SGDP and PCI 9.3 Demographic Features of Telangana |
|
|
Poverty and Unemployment in Telangana |
|
|
Welfare Programmes in Telangana |
|
|
X. Structural Transformation of Telangana Economy |
Introduction |
|
Sectoral Growth in Telangana Economy |
|
|
Infrastructural Development in Telangana: Energy, Irrigation and Transport |
|
|
Communication and Information Technology |
|
|
Banking and Insurance |
|
|
Tourism Sector |
|
|
Environment |
|
|
Regional imbalances in Telangana in comparison to AP |
|
|
Rural and Urban Disparities |
TS Intermediate Syllabus for 2nd year Geography
The TS Inter syllabus for 2nd year Geography consists of three major parts and several units under them. Find below the TS Intermediate 2nd year Geography syllabus for the academic year 2024.
|
Unit |
Unit Name |
|
Part A - Fundamentals of Human and Economic Geography |
|
|
I. Human Geography |
Meaning, Nature, scope, and relevance of human Geography |
|
Man–Environment relationships |
|
|
II. World Population |
Distribution, density of population, Growth of population in the world |
|
Factors affecting/influencing the distribution of the population |
|
|
III. Economic Geography |
Economic Geography: Definition, Scope, and Significance |
|
Sectors of economic activity: Concepts, changing trends |
|
|
Primary Activities: Concepts, changing trends. Food gathering, pastoral, mining, and subsistence agriculture |
|
|
Secondary Activities: conceptsManufacturing industries: Locational factors, types, distribution, and production; Agro-based: Textile (cotton), Mineral-based (Iron and steel): Petrochemical |
|
|
Mineral resources: Iron ore, Bauxite |
|
|
Power resources: Coal, Petroleum, and Non-conventional sources of energy |
|
|
Tertiary Economic activities: Concepts, people engaged in tertiary activities with some examples |
|
|
Quaternary Economic activities: Concepts, people engaged in the quaternary activities with some examples |
|
|
IV. World Transportation and Trade |
Relative significance of different means of transport- Land transport, Railways – Transcontinental Railways, Airways, and Waterways. |
|
World oceanic routes, Important inland waterways, and important canals |
|
|
International trade |
|
|
V. Environment and Resources |
Resources: Definition, Classification - Resource depletion |
|
Environment: Meaning, Definition, and Components |
|
|
Environmental Conservation and Management |
|
|
Sustainable Development |
|
|
VI. Human Settlements |
Settlement types - Rural and Urban. |
|
Part B - Geography of India |
|
|
VII. Physiography |
Locational characteristics, Physical setting, Physiographic divisions |
|
Drainage system: The Himalayan and Peninsular System |
|
|
VIII. Climate |
Origin of monsoon, Climatic regions in India, Distribution of Temperature and Rainfall |
|
Soils: types and distribution |
|
|
Vegetation: Types and Distribution |
|
|
IX. Population |
Population: Size, Growth, Distribution, and Density from 1901-2011 |
|
Trends of Urbanization, Population problems |
|
|
Migration: International, National, Causes and Consequences |
|
|
Human Development: Introduction and Regional Pattern |
|
|
X. Resources |
Mineral and Energy Resource Base: Distribution and Production |
|
Minerals –Iron ore, Manganese |
|
|
Power resources- Coal, Petroleum, and Non-conventional sources of Energy (Solar, Wind and Biogas) |
|
|
Conservation of Resources |
|
|
XI. Land Resources |
Agriculture: General Land Use, Land Use Classification |
|
Distribution and Production of Major Crops- Wheat, Rice, Sugarcane, Cotton, Castor, Groundnut, Coffee, and Tea |
|
|
XII. Water Resources |
Irrigation and Power: Types of Irrigation, Wells, canals, and tanks |
|
Major multipurpose projects: Bhakra Nangal, Nagarjuna Sagar, Rain Water Harvesting and Watershed Management. |
|
|
XIII. Industries |
Location factors, Growth, Distribution, and Trade |
|
Pharmaceuticals, and Knowledge-based Industries (IT) |
|
|
Globalization and Economic Development |
|
|
XIV. Transport and Trade |
Means of transport: Roadways, Railways, Airways, Waterways, Major Ports of India |
|
Part C - Telangana |
|
|
XV. Telangana |
Administrative regions; physiography and Drainage |
|
XVI. Climate |
Distribution of Climate, Temperature, and Rainfall |
|
Soils: Types, Distribution, Characteristics |
|
|
Vegetation: Types and Distribution |
|
|
XVII. Population |
Size, Growth, Distribution, and Density from 1961-2011 |
|
Demographic characteristics: Literacy, Sex Ratio; Rural and Urban populations |
|
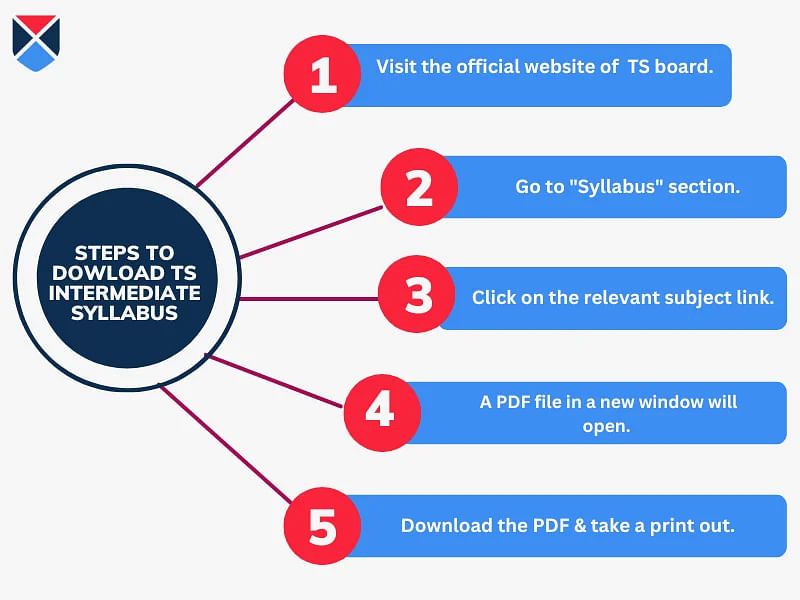
How to Download TS Intermediate Syllabus 2026?
The syllabus for TS Intermediate exams can be downloaded as PDF files. Follow the steps mentioned below to download the TS Inter syllabus.
- Step 1: Visit the official website of the TS board.
- Step 2: Select the "Syllabus" option from the left menu on the home page.
- Step 3: Choose the relevant subject and click on it.
- Step 4: This will open the PDF file on a new tab.
- Step 5: Save it for further reference.
Previous Year's TS Intermediate Syllabus 1st and 2nd Year PDFs
Candidates can download the TS Intermediate syllabus for the 1st and 2nd years for different streams from the following table.
| Stream | Link |
| TS Intermediate 1st Year Syllabus | |
| Humanities | Download Now |
| Science | Download Now |
| Language | Download Now |
| TS Intermediate 2nd Year Syllabus | |
| Humanities | Download Now |
| Science | Download Now |
| Language | Download Now |
TS Intermediate Exam Pattern 2026
Along with the TS Intermediate syllabus 2026, students must know the exam pattern which will help plan daily exam preparation schedules. The TS Inter Exam Pattern 2026 is given in the table below:
| Parameters | TS Inter 1st Year | TS Inter 2nd Year |
|---|---|---|
| Sections Covered | English, Second language, Non-language subjects. | English, Second language, Non-language subjects. |
| Maximum Marks | 100 | 100 |
| Time Duration | 3 Hours | 3 Hours |
| Qualifying Marks | 35 marks in each subject | 35 marks in each subject |
| Negative Marking | NO | NO |
FAQs on TS Intermediate Syllabus
Q: What are the important points students must remember for the TS Intermediate syllabus 2024-2025?
Q: Are all the subjects mandatory as per the TS Intermediate syllabus 2024-2025?
Q: How many streams are there for 2nd year based on the TS Intermediate 2024-2025 syllabus?
Q: From where can the students download the TS Intermediate syllabus 2024-2025?
Q: What are the passing marks as per the TS Intermediate syllabus 2024-2025?