Maharashtra HSC Syllabus 2025-26 Released : Download Latest and Revised Maharashtra HSC Syllabus PDF with Subject-wise
Table of Contents
- Maharashtra HSC Syllabus 2025-26: Subject-wise Download Link
- How to Download Maharashtra HSC Syllabus 2025-26 PDF Files?
- Maharashtra HSC 2025-26 Syllabus: Details
- Maharashtra HSC Syllabus 2025-26: Stream-wise Details
- Maharashtra HSC 2025-26 Syllabus: Subjects under the Science Stream
- Maharashtra HSC Syllabus 2025-26: Subjects under the Arts Stream
- Maharashtra HSC 2025-26 Syllabus: Subjects under the Commerce Stream
The Maharashtra HSC syllabus 2025-26 is available for all the subjects on the official website. The board conducts the Maharashtra HSC exam based on the completed HSC syllabus. Moreover, all the essential topics are included in the Maharashtra class 12 syllabus, along with the marking scheme for all the subjects.
The Maharashtra HSC exams are conducted using pen and paper. Furthermore, students can take the help of the Maharashtra HSC 2025-26 syllabus and make a better strategy for the upcoming board exams.
| Maharashtra HSC Result 2026 | Maharashtra HSC Supplementary Exam 2026 |
| Maharashtra HSC Exam Pattern 2026 | Maharashtra HSC Previous Year Question Papers |
Maharashtra HSC Syllabus 2025-26: Subject-wise Download Link
Below are the direct links to download the HSC syllabus PDF files. In addition, candidates can download the Maharashtra HSC syllabus 2025-26 PDFs for reference and practice purposes.
| Subjects | Links |
| English | Download |
| Marathi | Download |
| Gujarati | Download |
| Hindi | Download |
| Urdu | Download |
| Kannada | Download |
| Sindhi | Download |
| Malayalam | Download |
| Tamil | Download |
| History | Download |
| Geography | Download |
| Maths and Statistics | Download |
How to Download Maharashtra HSC Syllabus 2025-26 PDF Files?
Students can acquire the syllabus of Class 12 Maharashtra Board 2025-26 online from the official website and practice a month before the board exams. Here are the steps to download the Maharashtra HSC syllabus 2025-26 from the board's official website:
- Step 1: Visit the official website of Maharashtra HSC board - mahahsscboard.in.
- Step 2: Click on the section "Subjects & Syllabus" from the primary menu tab on the Home page.
- Step 3: Select "HSC General Subject Codes and Syllabus" from the dropdown menu.
- Step 4: Selecting the HSC General syllabus option will redirect you to the HSC syllabus page.
- Step 5: Select the subject to download and save it for future reference.
Maharashtra HSC 2025-26 Syllabus: Details
The reduced syllabus of class 12 Maharashtra board includes some of the compulsory subjects such as english, environmental education, health and physical education. Mentioned below are some of the details provided about the new Maharashtra HSC syllabus 2025-26 that the student needs to follow.
| Chapters | Page Numbers |
|---|---|
| (A) Compulsory Subjects | |
| 1. English | 01 |
| 2. Environmental Education | 07 |
| 3. Health and Physical Education | 10 |
| Modern Indian Languages | |
| 1. Marathi | 16 |
| 2. Hindi | 17 |
| 3. Gujarati | 19 |
| 4. Urdu | 22 |
| 5. Kannada | 25 |
| 6. Tamil | 27 |
| 7. Telugu | 29 |
| 8. Malayalam | 31 |
| 9. Sindhi | 33 |
| 10. Bengali | 35 |
| 11. Punjabi | 38 |
| Modern Foreign Languages | |
| 12. German | 44 |
| 13. French | 46 |
| 14. Russian | 48 |
| 15. Japanese | 50 |
| Classical Languages | |
| 16. Sanskrit | 56 |
| 17. Pali | 58 |
| 18. Ardhamagadhi | 60 |
| 19. Persian | 63 |
| 20. Arabic | 64 |
| 21. Avesta Pahlavi | 66 |
| (B) Elective Subjects | |
| 1. A Modern Indian Language | |
| 2. A Modern Foreign Language | |
| 3. A Classical Language | |
| 4. Marathi Literature | 68 |
| 5. Hindi Applied | 70 |
| 6. English Literature | 71 |
| 7. History | 74 |
| 8. Geography | 76 |
| 9. Mathematics and Statistics (For Arts and Science) | 79 |
| 10. Mathematics and Statistics (For Commerce) | 88 |
| 11. Geology | 92 |
| 12. Political Science | 98 |
| 13. Home Management | 100 |
| 14. Food Science | 102 |
| 15. Child Development | 106 |
| 16. Textiles | 109 |
| 17. Sociology | 111 |
| 18. Logic | 115 |
| 19. Philosophy | 118 |
| 20. Psychology | 120 |
| 21. Economics | 124 |
| 22. Book Keeping and Accountancy | 127 |
| 23. Organization of Commerce & Accountancy | 135 |
| 24. Secretarial Practice | 140 |
| 25. Co-operation | 145 |
| 26. Physics | 149 |
| 27. Chemistry | 156 |
| 28. Biology | 166 |
| 29. Drawing | 175 |
| 30. Design and Color | 177 |
| 31. Pictorial Composition | 181 |
| 32. History of Art and Appreciation | 183 |
| 33. History and Development of Indian Music | 186 |
| 34. Vocal Light Music | 190 |
| 35. Vocal Classical Music | 195 |
| 36. Instrumental Music | 200 |
| 37. Percussion Instruments | 205 |
| 38. Agricultural Science | 209 |
| 39. Animal Science | 213 |
| 40. Defense Studies | 219 |
| 41. Education | 226 |
| 42. Occupational Orientation | 229 |
| 43. Information Technology (Science) | 237 |
| 46. Information Technology (Arts) | 242 |
| 47. Information Technology (Commerce) | 246 |
| 48. General Knowledge | 250 |
Maharashtra HSC Syllabus 2025-26: Stream-wise Details
Students appearing for Maharashtra board 12th exams 2025 must go through the syllabus to know the topics and chapters to be covered. Maharashtra HSC syllabus 2025-26 consists of different subjects under three main streams - Science, Commerce, and Arts which is tabulated below.
Maharashtra HSC Science Subjects List
The list of subjects under the Maharashtra HSC Science stream are tabulated below for the student's reference.
| Compulsory Subjects | Elective Subjects |
| Modern Indian Language or Modern Foreign Language or Classical Language | Mathematics and Statistics, Geology, Child Development, Textile, Psychology, Economics, Geography, Defence-Studies, Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Agriculture Science and Technology, Animal Science and Technology, Sociology, Sanskrit, Education, Information Technology, English literature. |
| Health and Physical Education Elective Subjects | |
| Environment Education | |
| English |
Maharashtra HSC Commerce Subjects List
The list of subjects under the Maharashtra HSC Commerce stream are tabulated below:
| Compulsory Subjects | Elective Subjects |
| Modern Indian Language or Modern Foreign Language or Classical Language | Mathematics and statistics, Economics, Geography, Book-keeping and Accountancy, Organization of Commerce and Management, Mathematics and Statistics, Secretarial Practice, Co-operation, Occupational Orientation, Defense Studies, English Literature, Information Technology |
| Environment Education | |
| Health and Physical Education Elective Subjects | |
| English |
Maharashtra HSC Arts Subjects List
The list of subjects under the Maharashtra HSC Arts stream is given below:
| Compulsory Subjects | Elective Subjects |
| Modern Indian Language or Modern Foreign Language or Classical Language | A Modern Indian Language, A Modern Foreign Language, Sanskrit, Ardhamagadhi, Pali, Arabic, Persian, Avesta-Pahlavi, History, Geography, Mathematics and Statistics, Political Science, Child Development, Textile, Sociology, Philosophy, Logic, Psychology, Economics,Defense Studies, Drawing, Design and Colour, Composition, History of Art & Appreciation, History and Development of Indian Music, Vocal Light Music (Practical I), Vocal Classical Music (Practical II), Instrumental Music (Practical III) or, Percussion, European Music, Historical Development of Indian Classical Dance, Book-Keeping & Accountancy, Co-operation, Information Technology, English Literature |
| Environment Education | |
| Health and Physical Education Elective Subjects | |
| English |
Maharashtra HSC 2025-26 Syllabus: Subjects under the Science Stream
The Maharashtra HSC science stream consists of Mathematics, Physics, Chemistry and Biology. Mentioned below are some of the details and chapters for each stream which students can refer.
Maharashtra HSC Syllabus 2025-26 for Mathematics
The Mathematics HSC syllabus 2025-26 PDF consists of two parts. Topics in the first part include Mathematics logic, Matrics, Circles, Conics, Vectors, etc. Topics in the second part include Differentiation, Application of Definite Integral, Probability Distribution, Statistics, etc. The detailed Maharashtra HSC syllabus for Mathematics is mentioned in the table below:
| S.No | Topic Name |
| Part I | |
| 1 | Mathematics Logic |
| 2 | Matrics |
| 3 | Trigonometric Function |
| 4 | Pair of a straight line |
| 5 | Circle |
| 6 | Conics |
| 7 | Vectors |
| 8 | Three-dimensional geometry |
| 9 | Line |
| 10 | Plane |
| 11 | Linear Programming Problems |
| Part-II | |
| 1 | Continuity |
| 2 | Differentiation |
| 3 | Application of Derivatives |
| 4 | Integration |
| 5 | Application of Definite Integral |
| 6 | Differential Equation |
| 7 | Statistics |
| 8 | Probability Distribution |
| 9 | Bernoulli trials and Binomial distribution |
2. Maharashtra HSC Syllabus 2025-26 for Physics
Topics in the physics reduced syllabus class 12 HSC include Circular Motion, Gravitation, Rotational Motion, Oscillations, Elasticity, etc. Maharashtra HSC syllabus for Physics consists of 20 units as mentioned below:
| S.No | Topic Name | Subtopic |
| 1 | Circular motion | Angular displacement, Angular velocity and angular acceleration, Relation between linear velocity and angular velocity, Uniform circular motion, Radial acceleration, Centripetal and centrifugal forces, Banking of roads, Vertical circular motion due to earth’s gravitation, Equation for velocity and energy at different positions of vertical circular motion. Kinematical equations for circular motion in analogy with linear motion. |
| 2 | Gravitation | Newton’s law of gravitation, Projection of a satellite, Periodic time, Statement of Kepler’s laws of motion, Binding energy and escape velocity of a satellite, Weightlessness condition in orbit, Variation of ‘g’ due to altitude, latitude, depth and motion, Communication satellite and its uses. |
| 3 | Rotational Motion | Definition of M.I., K.E. of the rotating body, Rolling motion, Physical significance of M.I., Radius of gyration, Torque, Principle of parallel and perpendicular axes, M.I. of some regular shaped bodies about specific axes, Angular momentum and its conservation. |
| 4 | Oscillations | Explanation of periodic motion, S.H.M., Differential equation of linear S.H.M. Projection of U.C.M. on any diameter, Phase of S.H.M., K.E. and P.E. in S.H.M., Composition of two S.H.M.’s having same period and along same line, Simple pendulum, Damped S.H.M. |
| 5 | Elasticity | General explanation of elastic property, Plasticity, Deformation, Definition of stress and strain, Hooke’s law, Poisson’s ratio, Elastic energy, Elastic constants and their relation, Determination of ‘Y’, Behaviour of metal wire under increasing load, Applications of elastic behaviour of materials. |
| 6 | Surface Tension | Surface tension on the basis of molecular theory, Surface energy, Surface tension, Angle of contact, Capillarity and capillary action, Effect of impurity and temperature on surface tension. |
| 7 | Wave Motion | Simple harmonic progressive waves, Reflection of transverse and longitudinal waves, Change of phase, Superposition of waves, Formation of beats, Doppler effect in sound. |
| 8 | Stationary waves | Study of vibrations in a finite medium, Formation of stationary waves on string, Study of vibrations of air columns, Free and Forced vibrations, Resonance. |
| 9 | Kinetic theory | Concept of an ideal gas, Assumptions of kinetic theory, Mean free path, Derivation for pressure of a gas, Degrees of freedom, Derivation of Boyle’s law, Thermodynamics- Thermal equilibrium and definition of temperature, 1st law of thermodynamics, 2nd law of thermodynamics, Heat engines and refrigerators, Qualitative idea of black body radiation,Wein’s displacement law, Green house effect, Stefan’s law, Maxwell distribution, Law of equipartition of energy and application to Specific heat capacities of gases. |
| 10 | Wave theory | Wave theory of light, Huygens’ Principle, Construction of plane and spherical wave front, Wave front and wave normal, Reflection at plane surface, Refraction at plane surface, Polarisation, Polaroids, Plane polarised light, Brewster’s law, Doppler effect in light. |
| 11 | Interference and diffraction | Interference of light, Conditions for producing steady interference pattern, Young’s experiment, Analytical treatment of interference bands, Measurement of wavelength by biprism experiment, Diffraction due to single slit, Rayleigh’s criterion, Resolving power of a microscope and telescope, Difference between interference and diffraction. |
| 12 | Electrostatics | Gauss’ theorem proof and applications, Mechanical force on unit area of a charged conductor, Energy density of a medium, Dielectrics and electric polarisation, Concept of condenser, Capacity of parallel plate condenser, Effect of dielectric on capacity, Energy of charged condenser, Condensers in series and parallel, van-deGraaff generator. |
| 13 | Current electricity | Kirchhoff’s law, Wheatstone’s bridge, Meter bridge, Potentiometer. |
| 14 | Magnetic effects of electric current | Ampere’s law and its applications, Moving coil galvanometer, Ammeter, Voltmeter, Sensitivity of moving coil galvanometer, Cyclotron. |
| 15 | Magnetism | Circular current loop as a magnetic dipole, Magnetic dipole moment of revolving electron, Magnetisation and magnetic intensity, Diamagnetism, Paramagnetism, Ferromagnetism on the basis of domain theory, Curie temperature. |
| 16 | Electromagnetic inductions | Laws of electromagnetic induction, proof of, e = – dØ/dt Eddy currents, Self induction and mutual induction, Need for displacement current, Transformer, Coil rotating in uniform magnetic induction, Alternating currents, Reactance and impedance, LC oscillations (qualitative treatment only) Power in a.c circuit with resistance, inductance and capacitance, Resonant circuit, Wattless current, AC generator. |
| 17 | Electromagnetic inductions | Photoelectric effect, Hertz and Lenard’s observations, Einstein’s equation, Particle nature of light. |
| 18 | Atoms, Molecules, and Nuclei | Alpha particle scattering experiment, Rutherford’s model of atom. Bohr’s model, Hydrogen spectrum, Composition and size of nucleus, Radioactivity, Decay law, massenergy relation, mass defect, B.E. per nucleon and its variation with mass number, Nuclear fission and fusion, de Broglie hypothesis, Matter waves – wave nature of particles, Wavelength of an electron, Davisson and Germer experiment, Continuous and characteristics X-rays. |
| 19 | Semiconductors | Energy bands in solids, Intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors, P-type and Ntype semiconductor, P-N junction diode, I-V characteristics in forward and reverse bias, Rectifiers, Zener diode as a voltage regulator, Photodiode, Solar cell, I-V characteristics of LED, Transistor action and its characteristics, Transistor as an amplifier (CE mode), Transistor as a switch, Oscillators and Logic gates (OR, AND, NOT, NAND, NOR). |
| 20 | Communication systems | Elements of communication system, the bandwidth of signals, the bandwidth of transmission medium, Need for modulation, Production and detection of amplitude modulated wave, space communication, Propagation of electromagnetic waves in the atmosphere. |
3. Maharashtra HSC 2025-26 Syllabus for Chemistry
The Maharashtra HSC syllabus 2025-26 for Chemistry consists of 16 units, as mentioned below. Topics under those units include Solid State, Solutions and colligative properties, Chemical Thermodynamics and energetic, Electrochemistry, p-Block Elements, d and f Block Elements, Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers, etc. Find the detailed syllabus in the table below.
| Topic Name | Subtopic |
| Solid State | Classification of solids, unit cell in 2 & 3-dimensional lattices, calculation of density, voids, point defects, electrical and magnetic properties, Band theory of metals, conductors, semiconductors, insulators and n-p type semiconductors. |
| Solutions and colligative properties | Types of solutions, concentration of solids in liquids, Raoult’s law elevation of boiling point, solubility of gases in liquids, solid solutions, colligative properties, depression of freezing point, osmotic pressure, determination of molecular masses using colligative properties, Van’t Hoff factor, etc |
| Chemical Thermodynamics and energetic | Work, heat, energy, First law of thermodynamics, Hess’ law of constant heat summation, extensive and intensive properties, enthalpy of bond dissociation, Second and third law of thermodynamics, etc |
| Electrochemistry | Kohlrausch’s Law, lead accumulator, dry cell –electrolytic and galvanic cells, EMF, fuel cells, Nernst equation |
| Chemical Kinetics | Activation energy, rate law and specific rate constant, Arrhenius equation, concept of collision theory, etc |
| General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements | Principles and methods of extraction, reduction electrolytic method and refining |
| p-Block Elements | Group 15 elements, Group 16 elements, Classification of oxides, Group 17 elements, Group 18 elements, etc. |
| d and f Block Elements | Lanthanoids, Actinoids, first row transition metals, interstitial compounds, alloy formation |
| Coordination Compounds | IUPAC nomenclature, Werner’s theory, coordination number, magnetic properties, VBT, CFT. isomerism, |
| Halogen derivatives of alkanes (and arenas) | Haloalkanes, Haloarenes, stability of carbocations, d-l and R-S configurations. |
| Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers | Nomenclature, physical and chemical properties, and methods of preparation. |
| Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids | Nomenclature, physical and chemical properties, and methods of preparation. |
| Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen | Amines, Diazonium salts, Cyanides and isocyanides |
| Biomolecules | Carbohydrates, Proteins, Vitamins, and Nucleic acids |
| Polymers | Classification, methods of polymerization, copolymerization, polythene, bakelite, nylon, polyesters, and rubber, Biodegradable, and non-biodegradable polymers. |
| Chemistry in Everyday life | Chemicals in medicines, Chemicals in food, and Cleansing agents |
4. Maharashtra HSC 2025-26 Syllabus for Biology
Maharashtra HSC syllabus 2025-26 for Biology consists of two sections - Botany and Zoology. There are 6 units in both sections. The units and the sub-topics under them are mentioned in the table below:
| S.No | Topic Name |
| SECTION I - BOTANY | |
| Unit 1- Genetics and Evolution | |
| 1 | Genetic Basis of Inheritance |
| 2 | Gene: its nature, expression, and regulation |
| Unit 2 - Biotechnology and its application | |
| 3 | Biotechnology: Process and Application |
| Unit 3 - Biology and Human Welfare | |
| 4 | Enhancement in Food Production |
| 5 | Microbes in Human Welfare |
| Unit 4 - Plant Physiology | |
| 6 | Photosynthesis |
| 7 | Respiration |
| Unit 5 - Reproduction in Organisms | |
| 8 | Reproduction in Plants |
| Unit 6 - Ecology and Environment | |
| 9 | Organisms and Environment -I |
| SECTION II - Zoology | |
| Unit 1 - Genetics and Evolution | |
| 10 | Origin and the Evolution of Life |
| 11 | Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance |
| Unit 2 - Biotechnology and its application | |
| 12 | Genetic Engineering and Genomics |
| Unit 3 - Biology and Human Welfare | |
| 13 | Human Health and Diseases |
| 14 | Animal Husbandry |
| Unit 4 - Human Physiology | |
| 15 | Circulation |
| 16 | Excretion and osmoregulation |
| 17 | Control and Co-ordination |
| Unit 5 - Reproduction in Organisms | |
| 18 | Human Reproduction |
| Unit 6 - Ecology and Environment | |
| 19 | Organisms and Environment-II |
Maharashtra HSC 2025-26 Syllabus for English
Maharashtra HSC syllabus 2025-26 includes English and it is considered as a compulsory subject. The evaluation is done on student's reading, writing, and English grammar skills. The Grammar section comprises of given topics.
- Tenses
- Types of sentences
- Clauses
- Reported speech
- Prepositions
- Word formation
- Infinitives
- Gerunds and Participles
- Linking words/discourse markers
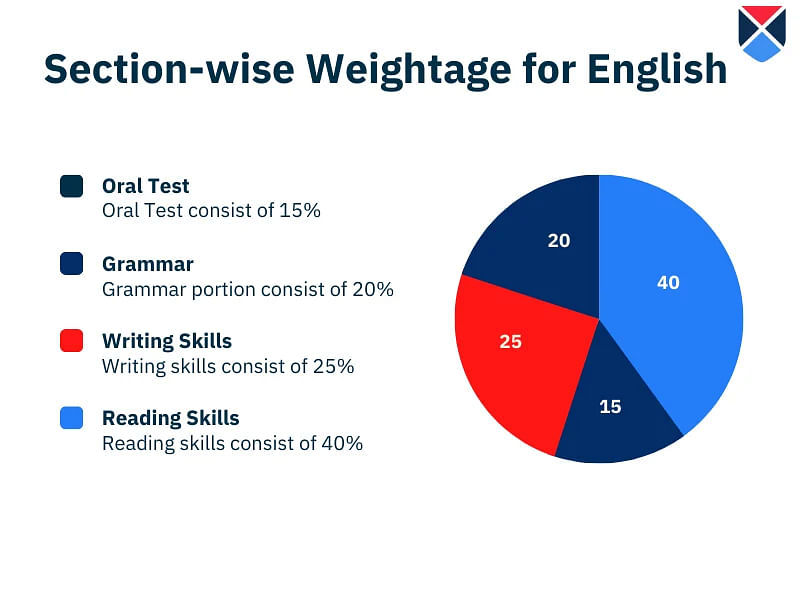
Maharashtra HSC Subject-wise Weightage for English
The weightage of chapters in the 12th board HSC for English is mentioned below which comprises reading skills, grammar, writing skills, and oral tests. Students can refer to the given chart to know the weightage each section carries.
| Sections | Weightage |
| Reading Skills (Textual and non-textual) | 40% |
| Grammar | 15% |
| Writing Skills | 25% |
| Orla test | 20% |
Maharashtra HSC Syllabus 2025-26: Subjects under the Arts Stream
The Maharashtra HSC syllabus consists of arts stream and mentioned below are some of the important details that the student needs to consider while preparing for the board exams.
Maharashtra HSC 2025-26 Syllabus for Political Science
Some of the important Maharashtra HSC syllabus 2025-26 for Political Science are mentioned below for the student's reference.
| Sub-Topics | Chapters Name |
| Part 1-Indian Constitution: Characteristics |
|
| Part 2- Politics in India | Patterns of Party Competition
|
Maharashtra HSC Syllabus 2025-26 for Sociology
Some of the important chapters of sociology are given below.
- Formation of Indian Society
- Segments of Indian Society
- Social Institutions in India
- Major Social Problems in India
- National Integration
- Social Change in India
- Social reformers in India
- Globalization and Mass Media
Maharashtra HSC 2025-26 Syllabus: Subjects under the Commerce Stream
The Maharashtra HSC syllabus 2025-26 details are mentioned below for the Commerce stream. It will assist the students in developing a more effective strategy for the upcoming board exams.
Maharashtra HSC 2025-26 Syllabus for Accountancy
Students must check the details of course curriculum provided in these latest syllabus. The Maharashtra HSC syllabus 2025-26 for Accountancy is mentioned below for the student's reference.
- Introduction to Partnership
- Partnership Final Accounts
- Reconstitution of Partnership
- Dissolution of Partnership Firm
- Accounts of “Not for Profit” concerns
- Single entry system
- Bill of Exchange (Only Trade Bill)
- Company Accounts
- Analysis of financial statements
- Accounting for shares
Maharashtra HSC 2025-26 Syllabus for Economics
The Economics details for the Maharashtra HSC syllabus 2025-26 is displayed below for the students reference.
- Introduction to Microeconomics
- Consumers behaviour
- Analysis of Supply
- Types of Market & Price determination
- Factors of Production
- Introduction to Macroeconomics
- National Income
- Determinants of Aggregates
- Money
- Commercial Bank
- Central Bank
- Public Economics
FAQs on Maharashtra HSC Syllabus
Q: What are the compulsory subjects for the HSC exam as per the Maharashtra HSC syllabus 2025-26?
Q: What are the major streams for the HSC exam as per the Maharashtra HSC syllabus 2025-26?
Q: From where can the students download the Maharashtra HSC 2025-26 syllabus?
Q: Do the student needs to take a printout of the Maharashtra HSC syllabus 2025-26?
Q: What is the exam pattern as per the Maharashtra class 12 syllabus 2025-26?

![Mahatma Phule Agriculture Vidyapeeth, [MPAV] Ahmednagar](https://media.getmyuni.com/azure/college-image/small/mahatma-phule-agriculture-vidyapeeth-mpav-ahmednagar.jpg)






![Shri Sai Baba Institute of Engineering Research and Allied Sciences, [SSBIERAS] Ahmednagar](https://media.getmyuni.com/azure/college-image/small/shri-sai-baba-institute-of-engineering-research-and-allied-sciences-ssbieras-ahmednagar.jpg)




























