MBSE HSSLC Syllabus 2026: Download All Subjects PDFs
The MBSE HSSLC Syllabus 2026 is crucial for exam prep, offering an overview of subjects, study plans, exam patterns, and marking schemes. It's provided by the Mizoram Board of School Education (MBSE). Students must complete their curriculum on time for revision. Download the syllabus at mbse.edu.in.
Table of Contents
MBSE HSSLC syllabus 2026 is significant for student exam preparation. It helps them get an overview of the subjects taught. The stream-wise syllabus will help candidates plan their study schedules, exam patterns, and marking schemes.
The Mizoram Board of School Education (MBSE) is a state-level education board in India that conducts the MBSE HSSLC board exams according to the set syllabus. Students are instructed to complete their curriculum on time to dedicate maximum time to their revision. Candidates will be able to access the MBSE HSSLC 2026 Syllabus at the official website, mbse.edu.in.
Also Read: MBSE HSSLC Routine
MBSE HSSLC Syllabus 2026 Download PDF
The MBSE Board has released the syllabus for the 12th standard. Candidates can download the syllabus from the official website in PDF format. Students can refer to the table below to download the MBSE 2026 HSSLC syllabus.
| Particulars | PDF Link |
| MBSE HSSLC syllabus 2026 | Download Now |
MBSE HSSLC Syllabus 2026 Stream-Wise
MBSE HSSLC exams will be conducted in March 2025 (tentative). The MBSE HSSLC 2026 syllabus for all the core subjects is given below, and candidates can check the syllabus and prepare for examinations accordingly. The MBSE HSSLC syllabus 2026 is divided into three main streams as follows:
| Stream | Major Subjects |
| Science | Physics, Chemistry, Mathematics, Biology, English, and Computer Science. |
| Commerce | Accountancy, Business Studies, Economics, Mathematics, and English. |
| Arts | History, Geography, Political Science, English, Psychology, and Sociology. |
MBSE HSSLC Syllabus 2026 English
The students will be examined on their reading and skills for the English exams. The MBSE HSSLC syllabus 2026 for the English subject is mentioned below.
| Unit Name | Marks |
| Section – A: Reading Skills (Same as before) | 15 |
| Section – B: Writing Skills, Short Compilation (Notice, Advertisements), Letter Writing (Letters of Complaints), (Application for a job 3) Letters to Editors, and Report Writing. | 25 |
| Section – C: Literature, Textbook - Flamingo: (Poetry Section): My Mother at sixty-six, An Elementary School Classroom in a Slum, Keeping Quiet, A Thing of Beauty, (Prose Section): Flamingo: The Last Lesson, Lost Spring Deep Water, The Rattrap, Indigo, Vistas: The Third Level, The Enemy, Should Wizard Hit Mommy? On the Face of it, and Memories of Childhood. | 40 |
MBSE HSSLC Syllabus 2026 for Science
The MBSE HSSLC syllabus for Science incorporates vital subjects such as Physics, Chemistry, Science and Biology. Students can refer to the details below to learn more about the MBSE HSSLC syllabus 2026 for various subjects, which students must refer to.
MBSE HSSLC Syllabus Mathematics
The unit name and marks bifurcation for the MBSE HSSLC Syllabus 2026 for Maths are detailed below. Find below the MBSE HSSLC syllabus for mathematics for the academic year 2026.
| Unit | Unit Name | Marks |
| I | Relation and Functions | 8 |
| II | Algebra | 10 |
| III | Calculus | 34 |
| IV | Vector and Three Dimensional Geometry | 14 |
| V | Linear Programming | 6 |
| VI | Probability | 8 |
MBSE HSSLC Syllabus Physics
Students can strategize their preparation for physics by referring to the information below. Find below the MBSE HSSLC syllabus 2026 for physics for the academic year 2026.
| Unit | Unit Name | Marks |
| I | Electrostatics | 10 |
| II | Current Electricity | 9 |
| III | Magnetic Effect of Current & Magnetism | 7 |
| IV | Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current | 10 |
| V | Electromagnetic Waves | 4 |
| VI | Optics | 16 |
| VII | Dual Nature of Matter | 5 |
| VIII | Atoms and Nuclei | 5 |
| IX | Electronic Devices | 4 |
MBSE HSSLC Syllabus for Chemistry
The vital topics for the MBSE HSSLC Syllabus 2026 for Chemistry are essential to study and prepare for the exams effectively. Find below the syllabus for chemistry.
| Unit | Unit Name | Marks |
| I | Solid State Classification of solids based on different binding forces: molecular, ionic covalent and metallic solids, amorphous and crystalline solids(elementary idea), unit cell in two-dimensional and three-dimensional lattices, calculation of the density of unit cell, packing in solids, packing efficiency, voids, number of atoms per unit cell in a cubic unit cell, point defects. |
5 |
| II | Solutions Types of solutions, expression of concentration of solutions of solids in liquids, the solubility of gases in liquids, solid solutions, colligative properties — relative lowering of vapor pressure, Raoult’s law, the elevation of B.P., depression of freezing point osmotic pressure, determination of molecular masses using colligative properties. |
5 |
| III | Electrochemistry Redox reactions, conductance in electrolytic solutions, specific and molar conductivity variations of conductivity with concentration, Kohlrausch’s Law, electrolysis, EMF of a cell, standard electrode potential, Nernst equation and its application to chemical cells. Relation between Gibbs energy change and EMF of a cell. |
6 |
| IV | Chemical Kinetics Rate of a reaction (average and instantaneous), factors affecting rates of reaction: concentration, temperature, catalyst; order and molecularity of a reaction; rate law and specific rate constant, integrated rate equations, and half life (only for-zero and first-order reactions). |
5 |
| V | Surface Chemistry Adsorption — physisorption, and chemisorption; factors affecting adsorption of gases on solids; colloidal state; distinction between true solutions, colloids and suspensions; lyophilic, lyophobic multi molecular, and macromolecular colloids; properties of colloids; Tyndall effect, Brownian movement, electrophoresis, coagulation. |
4 |
| VII | p-Block Elements Group 15 element: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, oxidation states, and trends. in physical and chemical properties; nitrogen — preparation, properties, and uses; compounds of nitrogen: preparation and properties of ammonia and nitric acid. Group 16 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, oxidation states, occurrence, and trends in physical and chemical properties; dioxygen, properties and uses; classification of oxides; ozone. Sulphur — allotropic forms; compounds of sulfur: preparation, properties, and uses of sulfur dioxide, properties, and uses, oxoacids of sulfur (structures only). Group 17 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, oxidation states, occurrence, and trends in physical and chemical properties; compounds of halogens: preparation, properties, and uses of chlorine and hydrochloric acid, interhalogen compounds, oxoacids of halogens (structure only). Group 18 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, trends in physical and chemical properties, and uses. |
8 |
| VIII | d -and f- Block Elements General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence and characteristics of transition metals, general trends in properties of the first row transition metals – metallic character, ionization enthalpy, oxidation states, ionic radii, color, catalytic property, magnetic properties, interstitial compounds, alloy formation. Lanthanoids - electronic configuration, oxidation states, contraction and its consequences. |
5 |
| IX | Coordination Compounds Coordination compounds: Introduction, ligands, coordination number, color, magnetic properties, and shapes, IUPAC nomenclature of mononuclear coordination compounds, bonding, Werner’s theory VBT, CFT. |
6 |
| X | Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Haloalkanes: Nomenclature, nature of C-X bond, physical and chemical properties, mechanism of substitution reactions. Optical rotation. Haloarenes: Nature of C-X bond, substitution reactions (directive influence of halogen for monosubstituted compounds only) |
4 |
| XI | Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Alcohols: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties (of primary alcohols only); identification of primary, and secondary and tertiary alcohols, mechanism of dehydration. Phenols: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, acidic nature of phenol, electrophilic substitution reactions, uses of phenols. Ethers: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, uses. |
6 |
| XII | Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Aldehydes and Ketones: Nomenclature, nature of carbonyl group, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, and mechanism of nucleophilic addition, reactivity of alpha hydrogen in aldehydes; uses. Carboxylic Acids: Nomenclature, acidic nature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties; uses. |
8 |
| XIII | Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Amines: Nomenclature, classification, structure, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, uses, identification of primary secondary and tertiary amines. Cyanides and Isocyanides – will be mentioned at relevant places in context |
4 |
| XIV | Biomolecules Carbohydrates - Classification (aldoses and ketoses), monosaccharide (glucose and fructose), DL configuration Proteins - Elementary idea of a-amino acids, peptide bond, polypeptides, proteins, primary structure, secondary structure, tertiary structure and quaternary structure (qualitative idea only), denaturation of proteins. Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA |
4 |
Also Read: MBSE HSSLC Exam Pattern
MBSE HSSLC Syllabus 2026 for Arts
MBSE HSSLC arts syllabus consists of History, Geography, Political Science, Psychology, Sociology, and English. Candidates can check the MBSE HSSLC syllabus 2026 for core subjects in the Arts stream.
MBSE HSSLC Syllabus for Political Science
The Political Science MBSE HSSLC Syllabus 2026 is bifurcated into two sections. Find below the MBSE HSSLC political science syllabus for the 2026 academic year.
| Unit | Unit Name | Marks |
| Part A - Contemporary World Politics | ||
| I | Cold War Era in World Politics 2. Disintegration of Second World and the collapse of Bipolary | 16 |
| II | US dominance in World Politics 2. Alternative centres of Economic and Political Power | 16 |
| III | International Organisations in a Unipolar World | 8 |
| Part B - Politics in India since Independence | ||
| V | Nation Building and its Problems Era of One-Party Dominance |
18 |
| VI | India’s External Relations | 10 |
| VII | Crisis of the Constitutional Order 2. Regional Aspirations and Conflicts | 12 |
MBSE HSSLC Syllabus for History
Find below the MBSE HSSLC history syllabus for the academic year 2026.
| Unit | Unit Name | Marks |
| I | BRICKS, BREADS AND BONES, The Harappan Civilisation, KINGS, FARMERS AND TOWNS Early States and Economies, KINSHIP, CASTE AND CLASS, Early Societies (c. 600BCE - 600CE) |
25 |
| II | BHAKTI — SUFI TRADITIONS, Changes in Religious Beliefs and Devotional Texts (c. eighth to eighteenth centuries), IMPERIAL CAPITAL: VIJAYANAGARA (c. fourteenth to sixteenth centuries), PEASANTS, ZAMINDARS AND THE STATE, and Agrarian Society and the Mughal Empire. |
25 |
| III | COLONIALISM AND COUNTRYSIDE, Exploring the Official Archives, REBELS AND RAJ, 1857 Revolt and its Representations, MAHATMA GANDHI AND THE NATIONALIST MOVEMENT, and Civil Disobedience and Beyond. | 25 |
| IV | Map Work | 5 |
MBSE HSSLC Syllabus for Sociology
The MBSE HSSLC Syllabus 2026 for Sociology has two sections. Candidates can refer to the given topics and marks allocation for Sociology to score better grades. Find below the syllabus for sociology for the academic year 2026.
| Unit | Unit Name | Marks |
| Part A - Indian Society | ||
| 1 | The Demographic Structure of Indian Society | 8 |
| 2 | Social Institutions ― Continuity and Change | 10 |
| 3 | The Market as a Social Institution | 10 |
| 4 | Patterns of Social Inequality and Exclusion | 12 |
| Part B - Social Change and Development in Indian Society | ||
| 5 | Structural Change | 7 |
| 6 | Cultural Change | 7 |
| 7 | Change and Development in Rural Society | 7 |
| 8 | Change and Development in Industrial Society | 4 |
| 9 | Globalisation and Social Change | 7 |
| 10 | Social Movements | 8 |
MBSE HSSLC Syllabus for Education
Find below the MBSE HSSLC syllabus 2026 for education for the academic year 2026:
| Unit | Unit Name | Marks |
| 1 | Psychology as a behavioural Science | 10 |
| 2 | Growth and Development | 10 |
| 3 | Heredity and Environment | 8 |
| 4 | Learning | 10 |
| 5 | Attention and Interests | 6 |
| 6 | Memory and Forgetting | 8 |
| 7 | Personality and Intelligence | 10 |
| 8 | Mental Health and Adjustment | 10 |
| 9 | Guidance and Counselling | 8 |
MBSE HSSLC Syllabus for Psychology
Find below the MBSE HSSLC syllabus 2026 for psychology for the academic year 2026:
| Unit | Unit Name | Marks |
| I | Intelligence and Aptitude/Variations in Psychological Attributes | 12 |
| II | Self and Personality | 12 |
| III | Human Strengths and Meeting Life Challenges | 10 |
| IV | Psychological Disorders | 13 |
| V | Therapeutic Approaches | 9 |
| VI | Social Influence and Group Processes | 8 |
| VII | Professional Skills for Psychologists/Developing Psychological Skills | 6 |
MBSE HSSLC Syllabus for Home Science
The vital topics and marks allocation will aid the candidates in scoring better grades. A detailed MBSE HSSLC syllabus 2026 for Home Science is mentioned in the table below:
| Units | Unit Name | Marks |
| I - Know Little Children | Protection from Preventable Childhood Diseases Special needs of Disadvantaged children Substitute Child Care | 15 |
| II - Nutrition for Self and Family | Meal planning for an individual Planning meals for family and their modification for Special Conditions Water for Good health | 15 |
| III - Management and Consumer Education | Family income and Expenditure Consumer education Consumer Protection | 15 |
| IV - My Apparel | Clothing in Relation to Personality Factors Influencing Selection of Clothing Selection and Purchase of Fabrics | 15 |
MBSE HSSLC Syllabus for Geography
Students must follow the MBSE HSSLC Syllabus 2026 for Geography and strategize their preparation for board exams accordingly. Find below the MBSE HSSLC syllabus and marks distribution method for Geography.
| Units | Unit Name | Marks |
| Part A - Fundamentals of Human Geography | ||
| I | Chapter 1. Human Geography – Nature and Scope a) Introduction and definition (p-3) b) Nature of Human Geography c) Scope of Human Geography d) Approaches: Traditional Approaches to Human Geography (p-6) |
3 |
| II | Population Chapter 2. Population of the world – Number, Growth and Density a) Growth of the world population b) Factors of increase in world population c) Distribution of world population d) Factors affecting population distribution and density – an overall viewpoint Chapter 3. Population change a) Introduction b) determinants of population change c) Fertility & its measures d) Mortality & its measures e) Migration f) Factors determining migration Chapter 4: Human development a) Introduction b) HD: Selected indicators |
5 |
| III | Human Activities Chapter 5 : Human Activities a) Primary activities – gathering, pastoralism, mining, minerals, subsistence agriculture, Modern agriculture, Major crops – Rice, Wheat, Beverages – tea, coffee. Fiber crops - Cotton |
10 |
| IV | Transport, Communication and Trade Chapter 6 : transport and communication a) Modes of transport – Roadways, Railways, pipelines, Water transport, Air transport b) Mass communication, Computer Networking and Uses Chapter 7 : International trade a) Basis of International trade, recent trends in International trade and ports. |
10 |
| V | Human Settlements Chapter 8: Human Settlements Types of settlements, rural settlement patterns, classification of towns, or on the basis of size, urban land use structure, functional classification of towns and problems of human settlements in developing countries |
5 |
| VI | Map work (related to Unit 1-5) | 2 |
| Part B - People and Economy | ||
| I | People Chapter 9 : Population composition: Ethnic and Socio-Cultural Attributes a) Tribal population, State-wise distribution. b) Spatial distribution of scheduled caste, state-wise distribution of SC c) Language and dialect groups, classification of Indian languages d) Unity in diversity Chapter 10: Population of India: Aspects of spatial distribution and Growth a) General demographic scene in India b) Census of population c) Distribution of population in India – State level d) Variations in the density of the population e) Trends in population growth in India f) Variations in population growth g) Migration trends in India Chapter 11: Population Composition: Demographic Attributes -Whole Chapter Chapter 13: Population, Environment and Development a) Population growth and environments b) Agricultural development and environmental degradation c) Urbanization and environmental degradation |
5 |
| II | Human Settlements Chapter 14: Human Settlements and House Types - Settlements, table indicating differences between urban and rural settlements, the morphology of an Indian town, House type |
4 |
| III |
Resources and Sustainable Development Chapter 18: Planning in India and the Need for Sustainable Development |
12 |
| IV | Transport, Communication and International Trade Chapter 19: Transport Systems - Rail transport, progress of Indian Railways, factors, distribution of Indian railways, Railway zones - Road transport and classification of roads - Inland waterways, problems, air transport, and pipelines - Power grid Chapter 20: International trade, Seaports and Airports - Nature of Indian foreign trade; present picture, Scope of Export - Seaports - Airports |
11 |
| V | Geographical perspective on Selected issues and problems Chapter 21: Geographical perspective on Selected issues and problems - Environmental pollution – air, and water pollution - Hunger and poverty – causes - Urbanization, Urban waste disposal |
4 |
| VII | Map work (related to Part B Unit 1-5) | 3 |
MBSE HSSLC Syllabus 2026 for Commerce
The Commerce stream consists of core subjects like Accountancy, Business Studies, Economics, Mathematics, and English. Kindly go through the given syllabus and study accordingly.
MBSE HSSLC Syllabus for Economics
Find below the MBSE HSSLC syllabus 2026 for economics for the academic year 2026.
| Unit | Unit Name | Marks |
| Part A - Macroeconomics | ||
| 1 | Introduction: Macroeconomics: Its meaning and scope viz Central Problems: - Growth, Inflation, Employment. Some basic concepts of macroeconomics are business Cycle, Aggregate Demand, Aggregate Supply, Consumption Goods, Capital Goods, Final Goods, Intermediate Goods; Stocks and Flows: Gross Investment and Depreciation. |
6 |
| 2 | National Income and Related Aggregate: Basic concept and measurement ― circular flow of income, method of calculating N.I ― concepts of aggregates related to NI. GNP, NNP, Gross, and Net Domestic Product (GDP & NDP)- at market price, at factor cost, and National Disposable Income (gross and net). | 12 |
| 3 | Theory of Income and employment ― Aggregate demand and its composites, consumption function and Investment functions, propensity to consume and propensity to save, equilibrium output. | 10 |
| 4 | Money and Banking: Money — Meaning, Functions and Types. The supply of money — Currency held by the public and net demand deposits held by commercial banks definition and Functions, Money and Credit Creation by Commercial banks. Central Bank - Meanings and Functions. | 6 |
| 5 | Monetary policy, Fiscal policy, and Govt. budget ― Fiscal Policy – meaning, types, and tools ― Government Budget – meaning, objectives, components, and types. classification of expenditures – revenue expenditure and capital expenditures. Various measures of govt. deficit – revenue deficit, fiscal deficit, primary deficit: their meaning and implications. |
6 |
| Part B - Indian Economic Development | ||
| 6 | Introduction: Parameter of development – per capita income, HDI in India ― Main features, problems, and policies of agriculture and foreign trade. | 10 |
| 7 | Planning and Economic Development in India: Objectives, Targets, Achievements, and drawbacks of different Five Year Plans in India (A brief account). | 6 |
| 8 | Structural Change in the Indian Economy after Liberalization: Meaning, Need, Significance, and Features of Liberalization, Globalization, Disinvestment and Privatization. Current Features of the Indian Economy. | 6 |
| 9 | Current challenges facing Indian Economy ― Poverty – absolute and relative: main programs for poverty allocation; A critical assessment; Rural development; Key issues credit and marketing – the role of co-operative: agricultural diversification: alternative farming – organic farming ― Human capital formation: How people become resources; the role of human capital in economics development ― Sustainable Economic growth; meaning, the effect of economic development on resources and environment. | 16 |
| 10 | Economic Growth and Development: Economic Growth and Development-Meaning and Difference, Comparative Study of India and China on the Following Indicators: i) unemployment ii)GDP growth, iii) GDP per capita, iv) GDP purchasing power parity, v) amount in direct foreign investment, vi) inflation, vii) poverty |
2 |
How to Download MBSE HSSLC Syllabus 2026?
The MBSE HSSLC Syllabus 2026 can be accessed online at the official website of the board. Below are the steps students must follow to download the MBSE HSSLC 2026 syllabus.
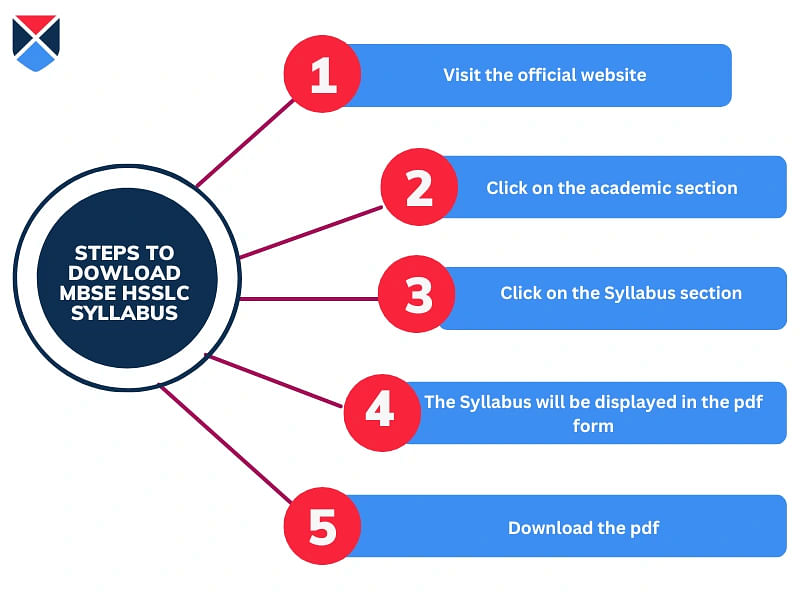
The steps to download the syllabus are given below:
- Step 1: Visit the official website of the Mizoram board - mbse-govt.in
- Step 2: Head to the "academic" menu and click the "Syllabus" option.
- Step 3: The MBSE HSSLC syllabus 2026 will be displayed on the screen.
- Step 4: Download and save the syllabus. One may also take a printout of the syllabus for future reference.
MBSE HSSLC Scheme of Subjects
As per the board, students must choose English and Hindi and one additional subject for the MBSE HSSLC exams. The scheme of subjects for the MBSE HSSLC exam is as follows.
- Each MBSE class 12 student is required to select five subjects.
- The candidate should select at least two languages - English, Mizo, Hindi, Assamese, Bengali, Manipuri, Nepali, Khasi, Garo, and Tenyidie.
- One of the two languages must be English or Hindi, and the other language might be any of the above-mentioned.
- A candidate must select at least three additional optional subjects.
- Internal assessments of General Studies, Work Experience, and Physical and Health Education will be conducted.
- A candidate can choose an extra subject from the list of optional subjects below:
Apply for Change of Subject in MBSE HSSLC
Candidates can seek subject change through school administrators. However, if they have cleared their class 11, they will not be eligible for a subject change. Candidates must follow these points to apply for subject change:
- Students in class 11 might approach their school administrator to change their subject(s) before the specified time.
- Upon passing class 11, no student is permitted to change subjects.
- In class 12, a student cannot choose a subject that they did not study in class 11.
FAQs on MBSE HSSLC Syllabus
Q: Can students download the MBSE HSSLC syllabus 2025-26 in PDF file format?
Q: What is the mode of MBSE HSSLC exam 2026?
Q: Is Mizoram board easier than CBSE board?
Q: Is there any reduction in the MBSE HSSLC 2025-26 syllabus?














