The ICSE Class 10 Biology syllabus 2025-26 includes details about the chapter-wise topics, practicals, and evaluation scheme. Students must get the detailed Biology syllabus to help them plan their studies and finish it on time. Moreover, students will get enough time for revision, and after the completion, they can also practice the ICSE class 10 previous year question papers.
The Biology syllabus class 10 ICSE 2025-26 consists of 6 chapters: Plant Physiology, Human Anatomy and Physiology, Population, Human Evolution, etc. The total mark for the theory paper is 80, while the internal assessment will be 20 marks. Students are required to score at least 33% marks to pass the ICSE class 10 exam.
The Biology syllabus class 10 ICSE 2025-26 is available on the official website. Students must download it in the PDF format and should start their preparation for the upcoming board exams. Following the class 10 Biology syllabus will also help them to understand the exam pattern.
Moreover, students can also refer to the link provided below to download the updated Biology syllabus.
ICSE Class 10th Biology Syllabus 2025-26
| Particulars |
PDF Link |
| ICSE Class 10 Biology Syllabus |
Download PDF |
Read more: ICSE Class 10 Biology Reduced Syllabus
The board has updated the ICSE class 10 Biology syllabus by reducing certain topics and sub-topics. This will help in making the concepts more simple and clear. Therefore the detailed updated syllabus for Biology is given below for the student's reference.
Biology Syllabus Class 10 ICSE 2025-26 Chapter 1: Basic Biology
Tabulated below is the detailed ICSE class 10 Biology chapter one for the student's reference.
ICSE Class 10 Chapter 1 Basic Biology
| Topics |
Sub-Topics |
| Cell Cycle and Cell Division |
Cell cycle – Interphase (G1, S, G2) and Mitotic phase. Cell Division:
- Mitosis and its stages.
- A basic understanding of Meiosis as a reduction division (stages not required).
- A brief idea of homologous chromosomes and crossing over leading to variations.
- Significance and major differences between mitotic and meiotic division.
|
| Structure of chromosome |
- Basic structure of chromosome with elementary understanding of terms such as chromatin, chromatid, gene structure of DNA and centromere
|
| Genetics: Mendel’s laws of inheritance and sex-linked inheritance of diseases |
- The three laws of Mendel. Monohybrid cross – phenotype and genotype.
- Dihybrid cross – Only phenotype.
- The following terms to be covered: gene, allele, heterozygous, homozygous, dominant, recessive, mutation, variation, phenotype, genotype.
- Sex determination in human beings. Sex linked inheritance of diseases to include only X-linked like haemophilia and colour blindness
|
ICSE Class 10 2025-26 Biology Syllabus Chapter 2: Plant Physiology
The topic-wise detailed ICSE class 10 Biology syllabus is mentioned below.
ICSE Class 10 Chapter 2 Plant Physiology
| Topics |
Sub-Topics |
| Absorption by Roots |
- Understanding of the processes related to absorption of water by the roots. Characteristics of roots, which make them suitable for absorbing water.
- Structure of a single full-grown root hair.
- A general idea of Cohesive, Adhesive forces and transpirational pull.
- Experiments to show the conduction of water through the xylem.
|
| Transpiration |
- Concept of transpiration and its importance to plants
- Experiments related to transpiration: (a)Loss in weight of a potted plant or a leafy shoot in a test tube as a result of transpiration. (b)Use of cobalt chloride paper to demonstrate unequal rate of transpiration in a dorsiventral leaf.
- Mechanism of stomatal transpiration on the basis of potassium ion exchange theory.
- Adaptations in plants to reduce transpiration.
- A brief idea of guttation and bleeding.
|
| Photosynthesis |
- The process and significance of Photosynthesis.
- The internal structure of chloroplast to be explained to give an idea of the site of light and dark reactions.
- Opening and closing of stomata based on potassium ion exchange theory.
- Overall balanced chemical equation to represent photosynthesis. Introduction of the terms "photochemical" for light phase and "biosynthetic" for dark phases.
- Light reaction - activation of chlorophyll followed by photolysis of water, release of O2, formation of ATP (photophosphorylation) and NADPH. Dark reaction - only combination of hydrogen released by NADP with CO2 to form glucose. (detailed equations are not required).
- Adaptations in plants for photosynthesis. Experiments with regard to the factors essential for photosynthesis; emphasis on destarching and the steps involved in starch test.
- A diagrammatic representation of “carbon cycle”.
|
| Chemical coordination in Plants |
- A brief idea of the physiological effects of Auxins, Gibberellins, Cytokinins, Abscisic acid and Ethylene in regulating the growth of plants.
- A basic understanding of the tropic movements in plants with reference to – Phototropism, Geotropism, Hydrotropism, Thigmotropism and Chemotropism (supported with suitable examples).
|
Biology Syllabus Class 10 ICSE 2025-26 Chapter 3: Human Anatomy and Physiology
The topic-wise list of topics included in ICSE class 10 Biology Syllabus 2025-26 is provided in the table below:
ICSE Class 10 Chapter 2 Human Anatomy and Physiology
| Topics |
Sub-Topics |
| Circulatory System |
- Composition of blood (structure and functions of RBC, WBC and platelets).
- Brief idea of tissue fluid and lymph. Increase in efficiency of mammalian red blood cells due to absence of certain organelles; reasons for the same.
- A brief idea of blood coagulation.
- Structure and working of the heart along with names of the main blood vessels entering and leaving the heart, the liver and the kidney.
- Concept of systole and diastole; concept of double circulation.
- Brief idea of pulse and blood pressure.
- Blood vessels: artery, vein and capillary to be explained with the help of diagrams to bring out the relationship between their structure and function.
- Brief idea of the lymphatic organs: spleen and tonsils.
- ABO blood group system, Rh factor.
- Significance of the hepatic portal system.
|
| Excretory System |
- A brief idea of different excretory organs in the human body.
- External and internal structure of the kidney;
- Parts of the urinary system along with the blood vessels entering and leaving the kidney; functions of various parts of the urinary system (emphasis on diagramwith correct labelling). A general idea of the structure of a kidney tubule/ nephron. 124
- A brief idea of ultra-filtration (emphasis on the diagram of malpighian capsule); selective reabsorption and tubular secretion in relation to the composition of blood plasma and urine formed.
|
| Nervous System |
- Parts of a neuron.
- Various parts of the external structure of the brain and its primary parts: Medulla Oblongata, Cerebrum, Cerebellum, Thalamus, Hypothalamus and Pons; their functions.
- Reference to the distribution of white and gray matter in Brain and Spinal cord.
- Voluntary and involuntary actions – meaning with examples.
- Diagrammatic explanation of the reflex arc, showing the pathway from receptor to effector.
- A brief idea of the peripheral and autonomic nervous system in regulating body activities.
- Differences between natural and acquired reflex.
- External and Internal structure and functions of the Eye and Ear and their various parts.
- A brief idea of stereoscopic vision, adaptation and accommodation of eye.
- Defects of the eye (myopia, hyperopia hypermetropia, presbyopia, astigmatism and cataract) and corrective measures (diagrams included for myopia and hyperopia only)
- The course of perception of sound in human ear.
- Role of ear in maintaining balance of the body.
|
| Endocrine System |
- Differences between Endocrine and Exocrine glands.
- Exact location and shape of the endocrine glands in the human body.
- Hormones secreted by the following glands: Pancreas: insulin and glucagon; Thyroid: only thyroxin; Adrenal gland: Cortical hormones and adrenaline; Pituitary: growth hormone, tropic hormones, ADH and oxytocin.
- Effects of hypo secretion and hyper secretion of hormones.
- A brief idea of Feedback mechanism withreference to TSH.
|
| The Reproductive System |
- Functions of Male and Female reproductive organs and male accessory glands. An idea of secondary sexual characters.
- Structure and functions of the various parts of the sperm and egg.
- Explanation of the terms: Fertilization, implantation, placenta, gestation and parturition.
- A brief idea of the role of placenta in nutrition, respiration and excretion of the embryo; its endocrinal function.
- Functions of Foetal membranes and amniotic fluid.
- Menstrual cycle outline of menstrual cycle.
- Role of Sex hormones: Testosterone, Oestrogen and Progesterone in reproduction.
- Identical and fraternal twins: meaning and differences only.
|
ICSE Class 10 Biology Syllabus Chapter 4: Population
The Biology syllabus class 10 ICSE 2025-26 chapter 4 is mentioned below in a detailed format for the student's reference.
ICSE Class 10 Chapter 4 Population
| Topics |
Sub-Topics |
| Population explosion in India |
- Main reasons for the sharp rise in human population in India and in the world.
- A brief explanation of the terms: demography, population density, birth rate, death rate and growth rate of population.
- Problems faced due to population explosion: unemployment, over exploitation of natural resources, low per capita income, price rise, pollution, unequal distribution of wealth.
- Methods of population control: Surgical methods – Tubectomy and vasectomy
|
ICSE Class 10 2025-26 Biology Syllabus Chapter 5: Human Evolution
Refer to the table mentioned below to understand the ICSE class 10 Biology syllabus chapter 5.
ICSE Class 10 Chapter 5 Human Evolution
| Topics |
Sub-Topics |
| Basic introduction to Human evolution and Theories of evolution |
- A brief idea of human ancestors – Australopithecus, Homo habilis, Homo erectus, Neanderthals, Cro-Magnon and Homo sapiens sapiens (Modern Man) with reference to the following characteristics: Bipedalism, Increasing Cranial capacity, Reduction of size of canine teeth, Forehead and brow ridges, Development of chin, Reduction in body hair, Height and Posture
- Lamarck’s theory of inheritance of acquired characteristics – with reference to use of organs (e.g.: neck and forelimbs of giraffe) and disuse of organs (e.g.: vestigial organs in humans like wisdom teeth, vermiform appendix, pinnae).
- Darwin’s theory of Natural selection: Survival of the fittest - e.g. adaptation of peppered moth.
|
ICSE Class 10 Biology Syllabus Chapter 6: Pollution
The ICSE class 10 Biology syllabus for chapter 6 is mentioned below for the student's reference.
ICSE Class 10 Chapter 6 Pollution
| Topics |
Sub-Topics |
| Types and Sources of Pollution; Major Pollutants |
- Air: Vehicular, industrial, burning garbage, brick kilns.
- Water: Household detergents, sewage, industrial waste, oil spills.
- Thermal pollution.
- Soil: Industrial waste, urban commercial and domestic waste, chemical fertilizers.
- Biomedical waste – used and discarded needles, syringes, soiled dressings etc.
- Radiation: X-rays; radioactive fallout from nuclear plants.
- Noise: Motor Vehicles, Industrial establishments, Construction Sites, Loudspeakers etc.
|
| Biodegradable and Non-biodegradable wastes |
- Biodegradable wastes: meaning and example; paper, vegetable peels, etc. Non biodegradable wastes: meaning and example; plastics, glass, Styrofoam etc. Pesticides like DDT etc.
|
| Effects of Pollution on Climate |
- Brief explanation of: Greenhouse effect and Global warming, Acid rain, Ozone layer depletion.
- Measures to control pollution: Use of unleaded petrol / CNG in automobiles, Switching of engines at traffic signal lights, Social forestry, Setting of sewage treatment plants, Ban on polythene and plastics, Organic farming, Euro Bharat vehicular standard. (A brief idea of the above measures)
- A brief mention of “Swachh Bharat Abhiyan”- A national campaign for Clean India.
|
The exam pattern for the ICSE class 10 Biology will help the students to schedule their preparation accordingly. The Biology theory paper is divided into two section carrying 40 mark each. Tabulated below is the detailed marking scheme for the class 10 Biology syllabus.
ICSE Class 10 Biology Syllabus Marking Scheme
| Marks |
Details |
Number of Questions |
| 80 marks |
Section 1: Short questions |
Multiple (All questions are compulsory) |
| Section 2: Long answer questions |
6 questions (Answer any 4 out of 6) |
| 20 Marks |
Practical Assessment |
- |
Read More: ICSE Class 10 Passing Marks
The practical exams for the ICSE class 10 Biology syllabus carry 20 marks. It is conducted by the school authorities to allow students to observe accurately from plant and animal specimens. Some of the other points are mentioned below:
- In the Plant life section, candidates will perform experiments on diffusion and osmosis using potassium permanganate and thistle funnel, and they will also demonstrate transpiration using various methods such as Bell Jar, cobalt chloride paper, and Ganong's photometer.
- The experiment also includes highlighting the essential elements for photosynthesis and the release of oxygen during the process.
- In the Animal life section, students will examine different types of blood cells under a microscope.
- The experiment will also include identifying the internal structures of the Ear and Eye through models and charts.
Refer to the image mentioned below to understand the detailed internal assessment for ICSE class 10 Biology.
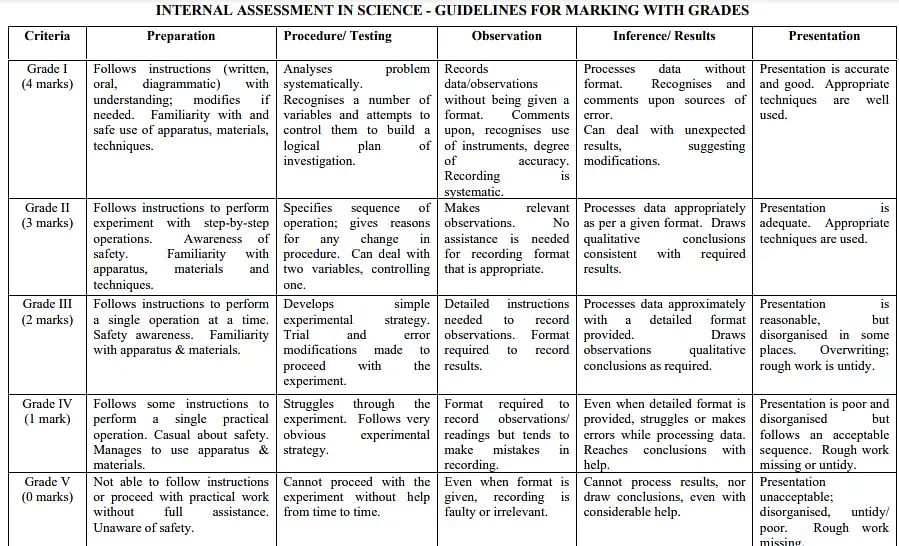
The subject teacher (internal examiner) and an external examiner are responsible for evaluating the practical work and project work in Biology for ICSE class 10. The Head of the School will nominate the external examiner. The detailed marks distribution is tabulated below.
Marks Evaluation for ICSE Class 10 Biology Syllabus
| Evaluation |
Marks Awarded |
| Subject Teacher (Internal Examiner) |
10 marks |
| External Examiner |
10 marks |
| Total Marks (Combined) |
20 marks |
Read more: ICSE Class 10 Sample Papers








![Motilal Nehru National Institute of Technology, [MNNIT] Allahabad](https://media.getmyuni.com/azure/college-image/small/motilal-nehru-national-institute-of-technology-mnnit-allahabad.webp)