BSEB Class 12 Chemistry Latest Syllabus 2025-26: Download Latest and Revised BSEB Class 12th Chemistry Syllabus PDF
The BSEB Class 12 Chemistry syllabus 2025-26 covers physical, organic & inorganic topics, emphasizing fundamental principles. It's crucial for exam prep, helping students strategize for better scores. The 70-mark theory paper includes 16 units. Download the PDF from biharboardonline.bihar.gov.in for detailed concepts and marking schemes.
Table of Contents
The class 12 Chemistry syllabus Bihar Board 2026 includes physical, organic and inorganic chemistry topics. The class 12 Bihar Board Chemistry syllabus 2026 emphasizes fundamental principles, reactions, and practical applications.
To prepare for the Bihar Board 12th exam 2026 in the science stream and score better marks, students must be familiar with the Bihar Board 12th Chemistry syllabus. Chemistry is a field of study that examines the properties and reactions of the substances that make up matter. It also deals with chemical transformations that result in new compounds.
P-block, D-block, and f-block elements are among the advanced themes in inorganic chemistry, while advanced topics in physical chemistry include electrochemistry and chemical kinetics. Students study different groups of organic substances in organic chemistry, including phenols, ethers, aldehydes, and amines. The curriculum is given a contemporary twist through chapters like Polymers and Chemistry in Everyday Life.
Bihar Board 12th Chemistry Syllabus 2025-26: PDF Download
The Bihar Board of Secondary Education curates and releases the Bihar Board 12th Chemistry Syllabus 2025-26 on the official portal. Students can refer to the detailed concepts and marking schemes to strategise their exam strategy. The PDF link to download the syllabus is given below.
| Particulars | PDF Link |
| Bihar Board 12th Chemistry Syllabus 2025-26 | Download Now |
Bihar Board 12th Chemistry Syllabus 2025-26
Bihar board 12th Chemistry paper is conducted for three hours and 15 minutes and carries 70 marks. The detailed unit-wise topics under the Bihar Board class 12 syllabus 2026 Science are mentioned below.
Unit 1: Solid State
- Classification of solids based on different binding forces: molecular, ionic, covalent and metallic solids, amorphous and crystalline solids (elementary idea).
- Unit cell in two-dimensional and three-dimensional lattices, calculation of the density of unit cell, packing in solids, packing efficiency, voids.
- Number of atoms per unit cell in a cubic unit cell, point defects, electrical and magnetic properties.
Unit 2: Solutions
- Types of solutions, expression of concentration of solutions of solids in liquids, solubility of gases in liquids, solid solutions.
- Colligative properties - relative lowering of vapour pressure, elevation of boiling point, depression of freezing point, osmotic pressure, determination of molecular masses using colligative properties, abnormal molecular mass.
Unit 3: Electrochemistry
- Redox reactions, conductance in electrolytic solutions, specific and molar conductivity, variations of conductivity with concentration.
- Kohlrausch’s Law, electrolysis and law of electrolysis (elementary idea), dry cell -electrolytic cells and Galvanic cells, lead accumulator.
- EMF of a cell, standard electrode potential, Nernst equation and its application to chemical cells, fuel cells, corrosion.
Unit 4: Chemical Kinetics
- Rate of a reaction (Average and instantaneous), factors affecting the rate of reaction, concentration, temperature, catalyst.
- Order and molecularity of a reaction, rate law and specific rate constant, integrated rate equations and half-life (only for zero and first-order reactions).
- Concept of collision theory (elementary idea, no mathematical treatment).
Unit 5: Surface Chemistry
- Adsorption – physisorption and chemisorption, factors affecting adsorption of gases on solids, catalysis, homogenous and heterogenous activity and selectivity.
- Enzyme catalysis colloidal state distinction between true solutions, colloids and suspensions.
- Lyophilic, lyophobic multimolecular and macromolecular colloids; properties of colloids.
- Tyndall effect, Brownian movement, electrophoresis, coagulation, emulsion-types of emulsions.
Unit 6: General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Principles and methods of extraction – concentration, oxidation, reduction – electrolytic method and refining.
- Occurrence and principles of extraction of aluminium, copper, zinc and iron.
Unit 7: p-block Elements
- Group 15 Elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, oxidation states, trends in physical and chemical properties; nitrogen preparation properties & uses; compounds of nitrogen, preparation and properties of ammonia and nitric acid, oxides of nitrogen (Structure only); Phosphorus – allotropic forms, compounds of phosphorus: preparation and properties of phosphine, halides PCl3, PCl5 and oxoacids (elementary idea only).
- Group 16 Elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, oxidation states, occurrence, trends in physical and chemical properties, dioxygen: Preparation, Properties and uses, classification of oxides, Ozone, Sulphur-allotropic forms; compounds of sulphur: Preparation properties and uses of sulphur-dioxide, sulphuric acid: industrial process of manufacture, properties and uses; oxoacids of sulphur (Structures only).
- Group 17 Elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, oxidation states, occurrence, trends in physical and chemical properties; compounds of halogens, Preparation properties and uses of chlorine and hydrochloric acid, interhalogen compounds, oxoacids of halogens (structures only).
- Group 18 Elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, trends in physical and chemical properties.
Unit 8: d and f-block elements
- General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence and characteristics of transition metals, general trends in properties of the first-row transition metals – metallic character, ionization enthalpy, oxidation states, ionic radii, colour, catalytic property, magnetic properties, interstitial compounds, alloy formation, preparation and properties of K2Cr2O7 and KMnO4.
- Lanthanoids – Electronic configuration, oxidation states, chemical reactivity and lanthanoid contraction.
- Actinoids – Electronic configuration, oxidation states.
Unit 9: Coordination Compounds
- Coordination compounds – Introduction, ligands, coordination number, colour, magnetic properties and shapes, IUPAC nomenclature of mononuclear coordination compounds.
- Bonding, Werner’s theory, VBT, and CFT.
- Structure and stereoisomerism, the importance of coordination compounds (in qualitative inclusion, extraction of metals and biological system).
Unit 10: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
- Haloalkanes: Nomenclature, nature of C-X bond, physical and chemical properties, mechanism of substitution reactions.
- Haloarenes: Nature of C -X bond, substitution reactions (Directive influence of halogen in monosubstituted compounds only).Uses and environmental effects of – dichloromethane, trichloromethane, tetrachloromethane, iodoform freons, DDT.
Unit 11: Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers
- Alcohols: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties( of primary alcohols only), identification of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols, mechanism of dehydration, and uses with special reference to methanol and ethanol.
- Phenols: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, acidic nature of phenol, electrophilic substitution reactions, uses of phenols.
- Ethers: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, uses.
Unit 12: Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids
- Aldehydes and Ketones: Nomenclature, nature of carbonyl group, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, mechanism of nucleophilic addition, reactivity of alpha hydrogen in aldehydes; uses.
- Carboxylic Acids: Nomenclature, acidic nature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties; uses.
Unit 13: Organic Compounds and containing Nitrogen
- Amines: Nomenclature, classification, structure, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, uses, and identification of primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
- Cyanides and Isocyanides: will be mentioned at relevant places in context.
- Diazonium salts: Preparation, chemical reactions and importance in synthetic organic chemistry.
Unit 14: Biomolecules
- Carbohydrates: Classification (aldoses and ketoses), monosaccharides (glucose and fructose), D-L configuration oligosaccharides (sucrose, lactose, maltose), polysaccharides (starch, cellulose, glycogen) importance.
- Proteins: Elementary idea of α – amino acids, peptide bond, polypeptides, proteins, structure of proteins – primary, secondary, tertiary structure and quaternary structures (qualitative idea only), denaturation of proteins; enzymes.
- Vitamins: Classification and functions.
- Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA.
Unit 15: Polymers
- Classification – natural and synthetic, methods of polymerization (addition and condensation), copolymerization, some important polymers: natural and synthetic like polythene, nylon, polyesters, bakelite, rubber.
- Biodegradable and non-biodegradable polymers.
Unit 16: Chemistry in Everyday Life
- Chemicals in medicines: analgesics, tranquilizers antiseptics, disinfectants, antimicrobials, antifertility drugs, antibiotics, antacids, and antihistamines.
- Chemicals in food: Preservatives, artificial sweetening agents.
- Cleansing agents: Soaps and detergents, cleansing action.
How to Download Bihar Board 12th Chemistry Syllabus 2025-26?
The PDF link to download the Bihar Board syllabus class 12 2026 is available at the official website, biharboardonline.bihar.gov.in. Students can refer to the process given below to download the class 12th Chemistry syllabus Bihar Board 2026.
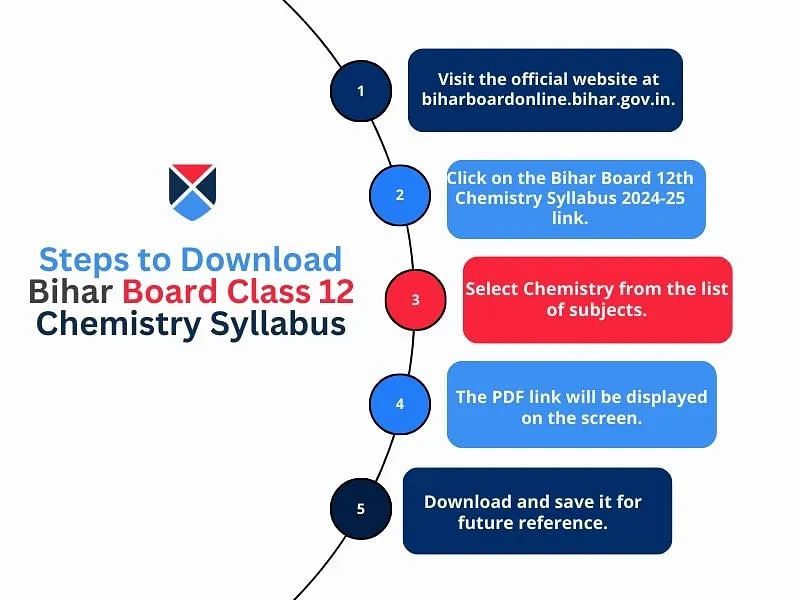
- Visit the official web portal, biharboardonline.bihar.gov.in.
- Navigate to the Bihar Board 12th Chemistry Syllabus 2025-26 link.
- The students will get redirected to a new web page.
- Select Chemistry from the subject options provided.
- Download the PDF of Bihar Board Chemistry Syllabus 2026 for future reference.
Bihar Board 12th Chemistry Marks Distribution
The Bihar Board 12th Chemistry exams are conducted for 100 marks. The theory paper is for 70, and the practicals are for 30 marks. The marks distribution of the BSEB 12th Chemistry paper is mentioned in the table below:
| Unit | Marks |
| Unit 1: Solid State | 04 |
| Unit 2: Solutions | 05 |
| Unit 3: Electrochemistry | 05 |
| Unit 4: Chemical Kinetics | 05 |
| Unit 5: Surface Chemistry | 04 |
| Unit 6: General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements | 03 |
| Unit 7: p-block Elements | 08 |
| Unit 8: d and f-block elements | 05 |
| Unit 9: Coordination Compounds | 03 |
| Unit 10: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes | 04 |
| Unit 11: Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers | 04 |
| Unit 12: Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids | 06 |
| Unit 13: Organic Compounds and containing Nitrogen | 04 |
| Unit 14: Biomolecules | 04 |
| Unit 15: Polymers | 03 |
| Unit 16: Chemistry in Everyday Life | 03 |
Read more: Bihar Board 12th Exam Pattern 2026
Importance of Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus Bihar Board 2026
The Bihar Board 12th Chemistry Syllabus 2025-26 covers topics that will be covered in the board exams. The curriculum assists students in preparing for the exams by helping them understand the concepts in detail. A few essential pointers for the syllabus are given below.
- The Bihar Board 12th Chemistry 2025-26 Syllabus enables students to retain essential topics.
- They can be thorough with the marking scheme followed by BSEB through the syllabus.
- Candidates must refer to the syllabus while preparing and aim to finish the maximum portions in advance to allow time for revision.
- Understanding the varied concepts and solving the unsolved exercises along with Bihar Board 12th Previous Year Question Papers helps in scoring better marks.
Read more: Bihar Board 12th Exam Preparation 2026
FAQs on BSEB 12th Chemistry
Q: What topics does the Bihar Board 12th Chemistry syllabus 2025-26 cover?
Q: What is the duration and total marks for the Bihar Board 12th Chemistry exam?
Q: Where can I download the Bihar Board 12th Chemistry Syllabus 2025-26 PDF?
Q: Which units carry the highest marks in the BSEB Class 12 Chemistry syllabus?
Q: Why is it important to refer to the Bihar Board 12th Chemistry syllabus?