UP Class 12 Physics Latest Syllabus 2025-26: Download Latest and Revised UP Class 12th Physics Syllabus PDF
Table of Contents
A total of 9 chapters are included in the UP Board Class 12 Physics syllabus 2025-26. The vital chapters such as Optics, Electronic Devices, Atoms & nuclei, Magnetic Effect of Current and Magnetism, Electromagnetic Induction, and Alternating Currents carry the highest weightage in the UP Board Class 12 Exam for Physics.
All chapters in the class 12 Physics syllabus 2025-26 UP Board are important for students to cover before appearing in the board exam. Students can review the UP Board Class 12 exam pattern to check question patterns and marking-wise topic allocation from the syllabus.
UP Board Class 12 Physics Syllabus 2025-26
Students should refer to the UP Board Class 12 syllabus for Physics as it helps with the UP Class 12 preparation. A total mark of 70 is allocated for the UP Board Class 12 Exam for Physics. All the questions in the exam are curated based on the syllabus
Refer to the table below to download the Class 12 Physics syllabus UP Board 2025-26 in PDF format.
| Particulars | PDF Link |
| Class 12 Physics syllabus 2025-26 UP Board | Download Now |
UP Board Class 12 Physics Syllabus 2025-26: Marking Scheme
The two sections under the Physics class 12 UP Board syllabus contain 35 marks each. Out of 70 marks, A total score of 33 divided into 23 marks for theory and 10 marks for practical is required to meet the passing requirement of the board exam.
Each chapter under the syllabus contains marks ranging from 4 to 13, illustrated in the table below.
| Chapters | Marks |
| Optics | 13 |
| Static electricity | 08 |
| Magnetic effect of Current and Magnetism | 08 |
| Electromagnetic induction and alternating currents | 08 |
| Atoms and nuclei | 08 |
| Electronic Devices | 08 |
| Electric current | 07 |
| Matter and dual nature | 06 |
| Electromagnetic waves | 04 |
UP Board Class 12 Marking Scheme For Practical Exam
The UP 12th Physics exam contains 30 marks of practical assessment. According to the UP Board class 12 Physics practical syllabus the evaluation criteria for practical exams depend on the performance in several assessments, experiments, and project work.
The table below shows the marking allocation for each assessment.
| Types of Assessment | Task Details | Marks |
| External Assessment | Any two experiments | 10 |
| Viva based on experiments | 5 | |
| Internal Assessment | Practical Record | 4 |
| Project work and viva | 8 | |
| Assignment | 3 |
UP Board Class 12 Physics 2025-26: Question Pattern
The UP Board Class 12 Physics exam has different questions such as MCQ, short answer, and long answer questions from the syllabus. Check the table below for a detailed summary of the question patterns and types of questions in the exam.
| Question No. | Marks For Each Question | Question Types |
| 5 | 1 | MCQ |
| 8 | 1 | Very Short Answer Questions |
| 8 | 2 | Short Answer Questions |
| 2 | 3 | Long Answer Questions |
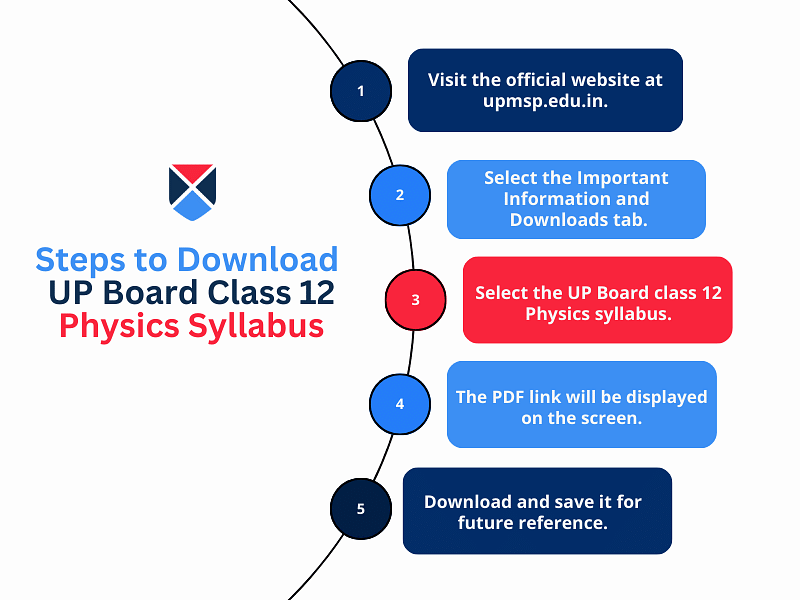
Steps to Download the UP Board Class 12 Physics Syllabus 2025-26
Students can refer to the UP Class 12 syllabus 2026, available for all subjects on the UPMSP board’s website. The following instructions explain the procedure to download the class 12 UP Board Physics syllabus.
- Step 1: Visit the official website of UPMSP.
- Step 2: Select the link mentioning ‘Course 2025-26’ from the menu bar, which is located on the left side of the home page.
- Step 3: Go to the ‘Syllabus Class 12th’ table and select the link for the subject name - Physics.
- Step 4: Syllabus of Physics class 12 UP Board will open on a new page.
- Step 5: Students can download the syllabus in PDF format for future reference.